Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Aine*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Ishii, Koji*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Takeuchi, Yasunao*; Sato, Yoichi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.19 - 23, 2023/01
In the J-PARC main ring, density modulation due to longitudinal beam instability occurs during the debunching process of coasting beams. This leads to the generation of an electron cloud, which in turn causes transverse beam instabilities. The transverse beam instability causes beam loss and the electron cloud is assumed to cause vacuum degradation, both of which hinder the beam intensity enhancement, so it is essential to clarify the causes and countermeasures. In particular, the longitudinal impedance of several hundred MHz has been investigated as relevant, and measures to reduce the impedance of individual devices are underway. The Eddy-current type septum magnet, newly installed this year, was found to have a large impedance by simulation. Therefore, we are investigating a method to reduce the impedance by a flange loaded with SiC radio wave absorber, which can be applied to locations where there is no spatial margin to install a taper. In this report, we will discuss the characterization of SiC to be used in actual devices, impedance simulation reflecting the results of SiC evaluation, and evaluation of the effect of impedance countermeasures by impedance measurement using the wire method, and progress in evaluating the effect on the beam by beam simulation and beam study.
Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Sato, Kiminori*; Yamawaki, Masato*; Michishio, Koji*; Oka, Toshitaka; Washio, Masakazu*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 202, p.110590_1 - 110590_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Chemistry, Physical)Because of their different charge states, positrons and positronium (Ps) behave quite differently in macromolecules. The behavior of positively charged positrons is strongly influenced by electrostatic interactions. In nonpolar macromolecules such as polyethylene, energetic positrons, if not incorporated into Ps, fall into a delocalized state. These positrons are sensitively trapped by polar groups, if any. On the other hand, charge-neutral Ps is localized in a free volume regardless of the macromolecule's chemical structure. In this study, we discuss the behavior and annihilation characteristics of positrons and Ps in various macromolecules, emphasizing their differences.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
Watanabe, Jin*; Araki, Yasufumi; Kobayashi, Koji*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(8), p.083702_1 - 083702_5, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:58.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate magnetic orderings on kagome lattice numerically from the tight-binding Hamiltonian of electrons, governed by the filling factor and spin-orbit coupling (SOC) of electrons. We find that even a simple kagome lattice model can host both ferromagnetic and noncollinear antiferromagnetic orderings depending on the electron filling, reflecting gap structures in the Dirac and flat bands characteristic to the kagome lattice. Kane-Mele- or Rashba-type SOC tends to stabilize noncollinear orderings, such a magnetic spirals and 120-degree antiferromagnetic orderings, due to the effective Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction from SOC. The obtained phase structure helps qualitative understanding of magnetic orderings in various kagome-layered materials with Weyl or Dirac electrons.
 molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ion
molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ionYamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Kobayashi, Keita; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Shimojo, Kojiro; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
iScience (Internet), 25(8), p.104763_1 - 104763_12, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:68.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Sato, Kiminori*; Yamawaki, Masato*; Michishio, Koji*; Oka, Toshitaka; Washio, Masakazu*
Applied Physics Express, 15(7), p.076001_1 - 076001_4, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.67(Physics, Applied)We discuss the energy dissipation of short-lived 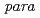 -positronium (
-positronium (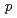 -Ps) in polymers and silica glass. The
-Ps) in polymers and silica glass. The  parameter characterizing the Doppler broadening of
parameter characterizing the Doppler broadening of 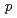 -Ps annihilation is determined from the previously reported systematic data of positron annihilation age momentum correlation for various polymers and silica glass. A comparison of the
-Ps annihilation is determined from the previously reported systematic data of positron annihilation age momentum correlation for various polymers and silica glass. A comparison of the  parameter with that expected for thermalized
parameter with that expected for thermalized 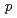 -Ps trapped in a free volume reveals that
-Ps trapped in a free volume reveals that 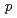 -Ps is not thermalized and possesses excess energy in fluorinated polymers and silica glass, indicating that it is difficult for Ps to lose energy in substances containing heavy elements such as fluorine and silicon.
-Ps is not thermalized and possesses excess energy in fluorinated polymers and silica glass, indicating that it is difficult for Ps to lose energy in substances containing heavy elements such as fluorine and silicon.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Michishio, Koji*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Oshima, Nagayasu*
Chemical Physics Letters, 795, p.139507_1 - 139507_4, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We obtained the temperature dependence up to 150 C of the triplet positronium (
C of the triplet positronium (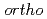 -Ps) lifetime in N,N,N-Trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by the vertical slow positron beamline installed at AIST. Positrons penetrate into the liquid surface of TMPA-TFSI with the positron energies of 2 keV and 12 keV to investigate at the near-surface and the balk. The surface structure was visible at 150
-Ps) lifetime in N,N,N-Trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by the vertical slow positron beamline installed at AIST. Positrons penetrate into the liquid surface of TMPA-TFSI with the positron energies of 2 keV and 12 keV to investigate at the near-surface and the balk. The surface structure was visible at 150 C, 120
C, 120 C above the melting temperature. The
C above the melting temperature. The 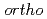 -Ps lifetime became shorter at higher temperatures for both positron energies. Similar temperature dependence had appeared just in water as the result of the reaction of
-Ps lifetime became shorter at higher temperatures for both positron energies. Similar temperature dependence had appeared just in water as the result of the reaction of 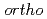 -Ps and radiolysis products such as the OH radicals. The temperature dependence observed for TMPA-TFSI suggested that the chemical reaction of
-Ps and radiolysis products such as the OH radicals. The temperature dependence observed for TMPA-TFSI suggested that the chemical reaction of 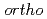 -Ps occurred.
-Ps occurred.
Kobayashi, Aine*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Ishi, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1031, p.166515_1 - 166515_12, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The beam power of the main ring of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) is currently being increased. For high-power beam realization, it is essential to suppress the beam instability that limits the beam power and to estimate and enact countermeasures against the beam coupling impedance of individual devices. The fast-extraction (FX) septum magnet will be replaced with another magnet that copes with higher numbers of repetition cycles. Despite their different structures, both septa demonstrated a large impedance in estimates performed by the CST studio suite wake-field solver. The widely used taper impedance-reduction method would be effective but receives spatial constraints. By attaching a copper plate and SiC to the flange of the septum magnet, we could effectively reduce the impedance. The copper plate on the flange reduces the impedance below the cut-off frequency. Moreover, when SiC was loaded, the remaining impedance was three times lower than when using the copper plate alone. After applying this method to the new septum magnet, the maximum longitudinal impedance was reduced to 1% of the value without countermeasures, largely improving the beam stability condition. We also estimated the required thickness of SiC and the calorific value. This method saves space and is installed by simple attachment to the flange, regardless of the shape of the beam pipe. Therefore, it is also applicable to other devices.
Matsuda, Shohei; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Kaneta, Yui; Simonnet, M.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimojo, Kojiro; Doi, Reisuke; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 8(20), p.eabn1991_1 - eabn1991_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.16(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Keita; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Tanida, Hajime; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
Hosha Kagaku, (45), p.28 - 30, 2022/03
no abstracts in English
Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Oba, Yojiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Heller, W. T.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 578, p.121352_1 - 121352_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.84(Materials Science, Ceramics)Kobayashi, Aine*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Ishii, Koji*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.287 - 291, 2021/10
no abstracts in English
Simonnet, M.; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(17), p.13409 - 13418, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:87.32(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Hirahara, Toru*; Otrokov, M. M.*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Sumida, Kazuki*; Tomohiro, Yuta*; Kusaka, Shotaro*; Okuyama, Yuma*; Ichinokura, Satoru*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Takeda, Yukiharu; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.4821_1 - 4821_8, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:93.11(Multidisciplinary Sciences) O
O
Yoshioka, Satoru*; Tsuruta, Konosuke*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Sugiyama, Takeharu*; Oba, Yojiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobayashi, Eiichi*; Okudaira, Koji*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 103(8), p.4654 - 4663, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.05(Materials Science, Ceramics)X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) reveal the damaged structures in MgAl O
O spinel induced by swift heavy ions. SAXS indicates the formation of ion tracks with cylindrical shape with a diameter of 5 nm. XANES indicates the cationic disordering between tetrahedral and octahedral sites by the irradiation. Quantitative analysis of XANES also reveals that cations preferably occupy the octahedral sites at high fluence.
spinel induced by swift heavy ions. SAXS indicates the formation of ion tracks with cylindrical shape with a diameter of 5 nm. XANES indicates the cationic disordering between tetrahedral and octahedral sites by the irradiation. Quantitative analysis of XANES also reveals that cations preferably occupy the octahedral sites at high fluence.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Michishio, Koji*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Oshima, Nagayasu*
Acta Physica Polonica A, 137(2), p.109 - 112, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recently, it was reported that the positronium (Ps) bubble in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids (RTILs) showed some phenomena that were very different from them observed in other molecular liquids. Now the reason of these interesting phenomena is being understood. The structure caused by the ionic interaction between anions and cations can exist even at the higher temperatures than the melting temperatures. It was the reason why the oscillation of Ps bubble was observed at the temperatures near the melting temperatures in RTILs. The temperature dependence of the Ps bubble size estimated by the triplet Ps (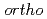 -Ps) pick-off annihilation lifetime indicated that there was a nano-meter structure remained by ionic interactions even at high temperatures. The
-Ps) pick-off annihilation lifetime indicated that there was a nano-meter structure remained by ionic interactions even at high temperatures. The 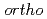 -Ps pick-off annihilation lifetime will be a strong tool to study nano-structure in RTILs.
-Ps pick-off annihilation lifetime will be a strong tool to study nano-structure in RTILs.

Ikeda, Shugo*; Kaneko, Koji; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Mochizuki, Kensei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(1), p.014707_1 - 014707_7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sugita, Yutaka; Kageyama, Takeshi*; Makino, Hitoshi; Shimbo, Hiroshi*; Hane, Koji*; Kobayashi, Yuichi*; Fujisawa, Yasuo*; Makanae, Koji*; Yabuki, Nobuyoshi*
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering (ICCCBE 2018) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/06
This paper presents status of development of the iSRE (integrated system for repository engineering) as a design supporting system that enables rational designing of a geological disposal repository. The complimentary technique of construction information modeling/management (CIM) has been employed for the development of iSRE. CIM uses a shared three dimensional (3D) model of associated data through common data models. In this paper, as a design support system that conforms to the characteristics of information management about engineering technology represented by repetition of design during the disposal project period, we examined and designed the function of the "iSRE", constructed a prototype, and confirmed the function through a trial simulating actual work in the disposal project. As a result, with respect to the functions of DB and IF of the iSRE, we got a prospect that these functions can be the foundation of information management on engineering technology, and development of the prototype of the iSRE and its test run extracted issues for practical use of such system.