Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,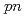 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 subnanoclusters and Pt single atoms over porous carbon supports and their structural analyses with X-ray absorption spectroscopy
subnanoclusters and Pt single atoms over porous carbon supports and their structural analyses with X-ray absorption spectroscopyItoi, Hiroyuki*; Nishihara, Hirotomo*; Kobayashi, Shunsuke*; Ittisanronnachai, S.*; Ishii, Takafumi*; Berenguer, R.*; Ito, Masashi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Kyotani, Takashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 121(14), p.7892 - 7902, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:71.76(Chemistry, Physical)Adachi, Taihei*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Strasser, P.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kojima, Kenji*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036017_1 - 036017_4, 2015/09
Hada, Kazuyoshi*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Masuda, Kai*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Isayama, Akihiko; Kajiwara, Ken
Fusion Science and Technology, 67(4), p.693 - 704, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Maiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Nakata, Motoki; Miyato, Naoaki; Kamada, Yutaka
Nuclear Fusion, 53(8), p.083022_1 - 083022_10, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.26(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Time and special responses of electron channels and ion channels with central electron cyclotron heating (ECH) have been investigated in JT-60U positive shear H-mode and internal transport barrier (ITB) plasmas. The ion temperature reduces with ECH after the increase in the electron temperature where an increase in the ion heat transport with ECH accompanies an increase in the electron thermal transport. The core electron density decreases with ECH when the density profile is peaked before ECH injection. The counter intrinsic rotation with ECH is identified using H-mode plasmas with small torque input (BAL-NBI). The counter intrinsic rotation is generated after the increase in the electron temperature and correlates with the change in the electron temperature with ECH around the EC deposition. Time scale of the change in the toroidal rotation velocity is about 90-200 ms around the ECH deposition and the time scale is longer compared to those in 
 and
and 
 .
.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 225, p.012036_1 - 012036_7, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:92.71(Physics, Applied)Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Kato, Mineo*; Takeshita, Soshi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 225, p.012050_1 - 012050_8, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:95.21(Physics, Applied)Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Yoshida, Maiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Physical Review Letters, 103(6), p.065003_1 - 065003_4, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:81.98(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The role of electron cyclotron range of frequency (ECRF) wave on the toroidal rotation velocity profile has been investigated in JT-60U plasmas by separating the effects of the momentum transport, the intrinsic rotation by pressure gradient and the intrinsic rotation by ECRF. It is found that ECRF increases the toroidal momentum diffusivity and the convection velocity. ECRF drives the CO-intrinsic rotation inside the EC deposition and drives the CTR-intrinsic rotation outside the EC deposition. This CTR-rotation starts from the EC deposition radius and propagates to the edge region.
Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kai, Tetsuya; Sakai, Kenji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.179 - 181, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)At the J-PARC MLF muon science facility (MUSE), muon experimental instruments are operated by means of a Muon Control System. The following are subject to the Muon Control System: (1) Muon production target and the beam scrapers, (2) M1/M2 line air-conditioning system, (3) Cryogenic system for the superconducting solenoid magnet, (4) Muon secondary line vacuum system, (5) Muon secondary line magnets, and (6) Muon beam blockers and related safety instruments. Details of the muon control system are described.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Suzuki, Yoshio; Totsuka, Toshiyuki; Iba, Katsuyuki*; Sakata, Shinya; Miyato, Naoaki; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Urso, L.*; Behler, K.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Yoshida, Maiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Nakata, Motoki; Miyato, Naoaki; Kamada, Yutaka
no journal, ,
Temporal and spatial responses of electron channels (the electron density, ne and the electron temperature) and ion channels (the ion temperature, Ti and the toroidal rotation velocity) to central electron cyclotron heating (ECH) have been investigated in positive shear H-mode plasmas with relatively peaked Ti profile and internal transport barrier (ITB) plasmas on JT-60U.
Yoshida, Maiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Nakata, Motoki; Miyato, Naoaki; Kamada, Yutaka
no journal, ,
In this study, the temporal and spatial responses of electron channels and ion channels to central electron cyclotron heating (ECH) have been investigated in positive shear H-mode plasmas and weak shear plasmas with internal transport barriers (ITBs) on JT-60U. The flattening of ne profile is observed after the increase in Te in the core region. Linear gyrokinetic stability analyses predict that the growth rate of the trapped electron modes, which increase outward particle flux, becomes more pronounced during ECH. Ion temperature around the ITB foot rapidly reduces and the increase in Te precedes the reduction in Ti. From the observations and theoretical analyses, the reduced Ti can be interpreted as the decrease in the critical temperature gradient for the ion temperature gradient mode with ECH. The counter intrinsic rotation with ECH is identified on H-mode plasmas with small torque input where co-current NBs and counter-current NBs are simultaneously injected with the same power.
 -phase based titanium alloys
-phase based titanium alloysWakai, Eiichi; Ishida, Taku*; Kano, Sho*; Shibayama, Tamaki*; Sato, Koichi*; Noto, Hiroyuki*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; et al.
no journal, ,
Titanium materials have been applied to beam window materials and beam dumps in large accelerator systems because of their low specific gravity, high corrosion resistance, strength, and other advantages. As the beam power becomes higher, further improvement of irradiation resistance is required. We have investigated further the properties of titanium alloys based on the  -phase, and it was found that Ti-15-3-3-3 alloys have excellent irradiation resistance when subjected to ion irradiation. In order to investigate the cause of this, microstructures and point defects in this and related materials were evaluated by TEM, positron lifetime measurement, electrical resistivity, and stress-induced changes, among others. In addition, we have recently begun to develop a prototype of a titanium-based high-entropy alloy based on
-phase, and it was found that Ti-15-3-3-3 alloys have excellent irradiation resistance when subjected to ion irradiation. In order to investigate the cause of this, microstructures and point defects in this and related materials were evaluated by TEM, positron lifetime measurement, electrical resistivity, and stress-induced changes, among others. In addition, we have recently begun to develop a prototype of a titanium-based high-entropy alloy based on  -titanium, which is attracting worldwide attention and is being developed, and have also begun to evaluate the emotional properties of this alloy. We have examined the various properties of this material and found that it has considerably higher strength than conventional iron- and titanium-based materials.
-titanium, which is attracting worldwide attention and is being developed, and have also begun to evaluate the emotional properties of this alloy. We have examined the various properties of this material and found that it has considerably higher strength than conventional iron- and titanium-based materials.
 La
LaGoto, Yu*; Ito, Yuki*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Endo, Shunsuke; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya*; Okuizumi, Mao*; Kameda, Kento*; Kawamura, Shiori*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakabe, Rintaro*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Noto, Hiroyuki*; Shibayama, Tamaki*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishida, Taku*; Sato, Koichi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Takahashi, Toshiharu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, it has been reported that high-entropy alloys (HEA) have high strength but good ductility, and they are being researched and developed by cutting-edge research institutions around the world with the aim of finding various applications in progress. In this study, we considered several Fe-based, W-based, and Ti-based HEAs, excluding Co and Ni elements, in order to aim for use in high radiation fields and considering low-activation properties. These materials mainly have a bcc crystal structure and were fabricated using a melting method and their material properties were evaluated. As a result, it was found that Fe-based HEA has properties that exceed the hardness of pure W and has excellent irradiation resistance. In addition, a Ti-based HEA that can be subjected to high-temperature forging and high-temperature rolling has been found, and evaluation of the optimal heat treatment temperature is progressing. The hardness of W-based HEA increased through Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) treatment, and it was found to have the world's highest hardness among HEA materials.
Snow, W. M.*; Auton, C.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Goto, Yu*; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English