Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Fushimi, Tomokazu*; Mizukoshi, Hirofumi*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 38(48), p.14656 - 14665, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 and Eu
and Eu ions onto sedimentary rock in the presence of gamma-irradiated humic acid
ions onto sedimentary rock in the presence of gamma-irradiated humic acidZhao, Q.*; Saito, Takeshi*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, p.128211_1 - 128211_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:62.11(Engineering, Environmental)The influence of humic acid and its radiological degradation on the sorption of Cs and Eu
and Eu by sedimentary rock was investigated to understand the sorption process of metal ions and humic substances. Aldrich humic acid (HA) solution was irradiated with different doses of gamma irradiation using a Co-60 gamma-ray source prior to the contact between the metal ions and the solid sorbent. The HA molecule decomposed to smaller molecules with a lower complexation affinity. Batch sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effect of gamma-irradiated HA on the sorption of Cs
by sedimentary rock was investigated to understand the sorption process of metal ions and humic substances. Aldrich humic acid (HA) solution was irradiated with different doses of gamma irradiation using a Co-60 gamma-ray source prior to the contact between the metal ions and the solid sorbent. The HA molecule decomposed to smaller molecules with a lower complexation affinity. Batch sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effect of gamma-irradiated HA on the sorption of Cs and Eu
and Eu ions. The addition of non-irradiated HA weakened the sorption of Eu because of the lower sorption of the neutral or negatively charged Eu-HA complexes compared with free Eu ions. The sorption of monovalent Cs ions was barely affected by the presence of HA and its gamma irradiation. The concentration ratio of HA complexed species and non-complexed species in the solid and liquid phases was evaluated by sequential filtration and chemical equilibrium calculations. The ratios supported the minimal contribution of HA to Cs sorption. However, the concentration ratio for Eu
ions. The addition of non-irradiated HA weakened the sorption of Eu because of the lower sorption of the neutral or negatively charged Eu-HA complexes compared with free Eu ions. The sorption of monovalent Cs ions was barely affected by the presence of HA and its gamma irradiation. The concentration ratio of HA complexed species and non-complexed species in the solid and liquid phases was evaluated by sequential filtration and chemical equilibrium calculations. The ratios supported the minimal contribution of HA to Cs sorption. However, the concentration ratio for Eu in the liquid phase was high, indicating that the complexing ability of HA to Eu
in the liquid phase was high, indicating that the complexing ability of HA to Eu was higher than that of HA to Cs
was higher than that of HA to Cs ions. Therefore, the sorption of free Eu
ions. Therefore, the sorption of free Eu would predominate with the gamma irradiation dose applied to the HA solution under a radiation field near the HLW package.
would predominate with the gamma irradiation dose applied to the HA solution under a radiation field near the HLW package.
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takeda, Shino*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*
The Chemistry of Thorium, Plutonium and MA, 254 Pages, 2022/03
The chemistry of nuclear materials such as Thorium (Part 1) and Plutonium (Part 2) was described in relation from the fundamentals on solid chemistry and solution chemistry to the practicals on the experiment and evaluation method in detail. Minor actinides such as Neptunium, Americium, Curium and Protoactinium, was introduced the basics on the solid and solution chemistry.
Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Oba, Yojiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Heller, W. T.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 578, p.121352_1 - 121352_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.84(Materials Science, Ceramics) Sr and
Sr and  Cs in soils near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Cs in soils near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationSasaki, Takayuki*; Matoba, Daisuke*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Iijima, Kazuki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 326(1), p.303 - 314, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.51(Chemistry, Analytical) -isosaccharinic acid
-isosaccharinic acidKobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 138, p.151 - 158, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.74(Thermodynamics)The effect of  -isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH
-isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) range of 6
) range of 6 13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]
13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]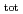 ) = 10
) = 10
 10
10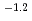 mol/dm
mol/dm . The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH
. The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH and [ISA]
and [ISA]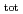 suggested the existence of U(OH)
suggested the existence of U(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 as a dominant species within the investigated pH
as a dominant species within the investigated pH range of 6
range of 6 12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO
12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO (OH)
(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 was suggested as a dominant species at pH
was suggested as a dominant species at pH 7
7 13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Nakajima, Shogo*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 35(24), p.7995 - 8006, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.5(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) (am) solubility at 25
(am) solubility at 25 C in the Ca
C in the Ca -Na
-Na -H
-H -Cl
-Cl -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; A Critical review
O system; A Critical reviewRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Altmaier, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 47(5), p.855 - 891, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:8.45(Chemistry, Physical)We have critically reviewed experimental data for Zr hydrolysis constant values for formation of several mononuclear and polynuclear species and a solubility product value for ZrO (am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
(am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH) (aq), Zr(OH)
(aq), Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH)
 and Ca
and Ca Zr(OH)
Zr(OH)
 , and the solubility product for ZrO
, and the solubility product for ZrO (am) after the critical review.
(am) after the critical review.
Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kokami, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kirishima, Akira*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Mizuno, Takashi; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Miyakawa, Kazuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(3), p.373 - 381, 2017/03
Trace amounts of natural thorium and uranium in deep groundwater were investigated at two underground research laboratories situated at Horonobe and Mizunami, Japan. The groundwater was sampled from underground boreholes, and the colloid contribution was checked by in situ two size-fractionated ultrafiltration systems. A decrease in the concentration after in situ filtration suggested the presence of natural colloids and suspended matter that were carriers of a portion of the elements. The result of the Th and U concentrations in groundwater after 10 kDa filtration was analyzed thermodynamically using existing hydrogeological and geochemical data such as the mineral components in the groundwater at a given pH, ionic strength, concentration of co-existing ions, redox potential, and solid phase assumed. A crystalline solid phase made the solubility very low compared with that of the amorphous phase, and the solubility agreed well with the concentrations measured.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Teshima, Takeshi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(2), p.233 - 241, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zr solubility in the presence of gluconic acid (GLU) and isosaccharinic acid (ISA) was investigated as a function of hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH
) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH)
and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH) (GLU)
(GLU)
 in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH)
in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH) (GLU)(GLU
(GLU)(GLU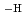 )
) in the alkaline pH region above pH
in the alkaline pH region above pH 10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10
10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10 - 10
- 10 mol/dm
mol/dm (M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH)
(M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 and Zr(OH)
and Zr(OH) (ISA)(ISA
(ISA)(ISA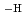 )
) were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH)
were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH) (am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
(am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
 (cr)
(cr)Rai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Radiochimica Acta, 104(8), p.583 - 592, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.41(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility studies were conducted with HfO (cr) solid as a function of acid concentrations. These studies involved (1) using two different amounts of the solid phase, (2) acid washing the bulk solid phase, (3) preheating the solid phase to 1400
(cr) solid as a function of acid concentrations. These studies involved (1) using two different amounts of the solid phase, (2) acid washing the bulk solid phase, (3) preheating the solid phase to 1400  C, and (4) heating amorphous HfO
C, and (4) heating amorphous HfO (am) suspensions to 90
(am) suspensions to 90  C to ascertain whether the HfO
C to ascertain whether the HfO (am) converts to HfO
(am) converts to HfO (cr) and to determine the solubility from the oversaturation direction. Based on the results of these treatments it is concluded that the HfO
(cr) and to determine the solubility from the oversaturation direction. Based on the results of these treatments it is concluded that the HfO (cr) contains a small fraction of less crystalline, but not amorphous, material [HfO
(cr) contains a small fraction of less crystalline, but not amorphous, material [HfO (lcr)] and this, rather than the HfO
(lcr)] and this, rather than the HfO (cr), is the solubility-controlling phase in the range of experimental variables investigated in this study. The solubility data are interpreted using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The log
(cr), is the solubility-controlling phase in the range of experimental variables investigated in this study. The solubility data are interpreted using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The log of the solubility product of HfO
of the solubility product of HfO (cr) is estimated. The observation of a small fraction of less crystalline higher solubility material is consistent with the general picture that mineral surfaces are often structurally and/or imperfect leading to a higher solubility than the bulk crystalline solid. This study stresses the urgent need, during interpretation of solubility data, of taking precautions to make certain that the observed solubility behavior for sparingly-soluble solids is assigned to the proper solid phase.
(cr) is estimated. The observation of a small fraction of less crystalline higher solubility material is consistent with the general picture that mineral surfaces are often structurally and/or imperfect leading to a higher solubility than the bulk crystalline solid. This study stresses the urgent need, during interpretation of solubility data, of taking precautions to make certain that the observed solubility behavior for sparingly-soluble solids is assigned to the proper solid phase.
 on Na-montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modeling
on Na-montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modelingSasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Saito, Takumi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Takagi, Ikuji*; Kimura, Takaumi; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.592 - 601, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influences of pH and the concentrations of Eu and NaNO
and NaNO on the sorption of Eu
on the sorption of Eu to Na-montmorillonite were investigated through batch sorption measurements and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The pH had a little effect on the distribution coefficients (Kd) in 0.01 M NaNO
to Na-montmorillonite were investigated through batch sorption measurements and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The pH had a little effect on the distribution coefficients (Kd) in 0.01 M NaNO , whereas the Kd strongly depended on pH at 1 M NaNO
, whereas the Kd strongly depended on pH at 1 M NaNO . A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was successfully applied to the measured Kd. The TRLFS spectra of Eu
. A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was successfully applied to the measured Kd. The TRLFS spectra of Eu sorbed were processed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), which corresponded to one outer-sphere (factor A) and two inner-sphere (factor B and C) complexes. It turned out that factors A and B correspond to Eu
sorbed were processed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), which corresponded to one outer-sphere (factor A) and two inner-sphere (factor B and C) complexes. It turned out that factors A and B correspond to Eu sorbed by ion exchange sites and inner-sphere complexation with hydroxyl groups of the edge faces, respectively. Factor C became dominant at relatively high pH and ionic strength and likely correspond to the precipitation of Eu(OH)
sorbed by ion exchange sites and inner-sphere complexation with hydroxyl groups of the edge faces, respectively. Factor C became dominant at relatively high pH and ionic strength and likely correspond to the precipitation of Eu(OH) on the surface.
on the surface.
 (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH

Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Kitamura, Akira
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.231 - 236, 2013/10
For the nuclear waste management of TRU waste, it is necessary to assess the impact of nitrate salts contained in the waste. In the present study, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was investigated in the presence of NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 . Under different NH
. Under different NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 concentration, pH and ionic strength conditions, distribution coefficient (
concentration, pH and ionic strength conditions, distribution coefficient ( ) of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was determined by batch experiment. For Ni system, the
) of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was determined by batch experiment. For Ni system, the  values showed no significant dependence on the initial NH
values showed no significant dependence on the initial NH
 concentration in neutral pH region, agrees with the prediction from thermodynamic data. For Pd system, the
concentration in neutral pH region, agrees with the prediction from thermodynamic data. For Pd system, the  values decreased with an increase of [NH
values decreased with an increase of [NH
 ]ini, suggesting the formation of stable ammine complex (Pd(NH
]ini, suggesting the formation of stable ammine complex (Pd(NH )
)
 (
( : 1 - 4)). The obtained
: 1 - 4)). The obtained  values for Ni and Pd were analyzed using the surface complexation model. By taking complexes predicted by thermodynamic data into account, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd in the presence of NH
values for Ni and Pd were analyzed using the surface complexation model. By taking complexes predicted by thermodynamic data into account, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd in the presence of NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 were well explained.
were well explained.
Tachi, Yukio; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 18(2), p.113 - 115, 2011/12
The 13th International Conference on the Chemistry and Migration Behavior of Actinides and Fission Products in the Geosphere (MIGRATION 2011) was held at Peking University, China on 18th-23rd, September, 2011. This report summaries overview of the conference and topics in each technical session, which indicate the state-of-the-art of international research activities on radionuclide migration for geological disposal.
Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kubo, Shintaro*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kirishima, Akira*; Kimura, Takaumi; Kubota, Takumi*; Takagi, Ikuji*; Moriyama, Hirotake*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6(1), p.51 - 54, 2005/07
no abstracts in English
Ichimura, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Sato, Shoichi*; Katano, Makoto*; Ouchi, Toshiaki*; Muro, Taishi*; Sekihara, Yusuke*; Murakami, Tatsuya*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; et al.
no journal, ,
Fluctuations in the ion cyclotron range of frequency are investigated both on GAMMA 10 and JT-60U. Ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) due to deuterium-deuterium fusion-product (FP) ions on JT-60U are described. ICE due to H-ions is newly identified. ICE(T) with lower frequency has larger wave numbers than ICE ( He) in the same discharge. The excitation of slow Alfv
He) in the same discharge. The excitation of slow Alfv n waves is elucidated for the first time as the mechanism for ICE due to T-ions. The anisotropy of T-ions at the outer plasma edge is evaluated by using Escape Particle Orbit analysis Code (EPOC).
n waves is elucidated for the first time as the mechanism for ICE due to T-ions. The anisotropy of T-ions at the outer plasma edge is evaluated by using Escape Particle Orbit analysis Code (EPOC).
 solutions
solutionsKobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
no journal, ,
We focused on the solubility of TcO .
.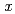 H
H O(s) in the existence of the dilute to concentrated NaNO
O(s) in the existence of the dilute to concentrated NaNO in order to investigate the potential effect of nitrate on the Tc species. It was found that the solublity of TcO
in order to investigate the potential effect of nitrate on the Tc species. It was found that the solublity of TcO .
.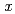 H
H O(s) was promoted under high NaNO
O(s) was promoted under high NaNO and/or electrolyte conditions.
and/or electrolyte conditions.
 solutions
solutionsKobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
no journal, ,
Solubility of amorphous technetium(IV) hydroxide was investigated using redox buffers to control various redox potentials in NaNO media. Aqueous technetium concentration increased with increasing NaNO
media. Aqueous technetium concentration increased with increasing NaNO concentration. It was found that the obtained aqueous technetium concentration was well interpreted by thermodynamic calculations using the obtained redox potentials.
concentration. It was found that the obtained aqueous technetium concentration was well interpreted by thermodynamic calculations using the obtained redox potentials.
 on montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modeling
on montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modelingSasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Saito, Takumi*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Takagi, Ikuji*; Kimura, Takaumi; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The influence of pH, ionic strength, and the concentrations of Eu and nitrate salts on the sorption of Eu
and nitrate salts on the sorption of Eu on Na-montmorillonite was investigated by batch sorption measurements. The distribution coefficient (Kd) indicated that the cation exchange reaction is significant in pH 4-7 at low ionic strength, and the formation of surface complexation is related to the pH dependence of Kd at high ionic strength. The Eu
on Na-montmorillonite was investigated by batch sorption measurements. The distribution coefficient (Kd) indicated that the cation exchange reaction is significant in pH 4-7 at low ionic strength, and the formation of surface complexation is related to the pH dependence of Kd at high ionic strength. The Eu surface species were investigated using time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). The PARAFAC modeling indicated two surface species, the outer-sphere (factor A) and inner-sphere (factor B) Eu
surface species were investigated using time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). The PARAFAC modeling indicated two surface species, the outer-sphere (factor A) and inner-sphere (factor B) Eu complexes. Factor B was dominant at high pH and ionic strength, which was determined to be a Eu colloidal species formed at high Eu
complexes. Factor B was dominant at high pH and ionic strength, which was determined to be a Eu colloidal species formed at high Eu concentrations. A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was applied to the measured Kd data, using the results of the TRLFS-PARAFAC analyses.
concentrations. A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was applied to the measured Kd data, using the results of the TRLFS-PARAFAC analyses.