Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 = 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of
= 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of  Ar
ArCort s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men
s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men ndez, J.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Schwenk, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
ndez, J.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Schwenk, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064320_1 - 064320_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:73.66(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying excited states in the  = 32 isotope
= 32 isotope  Ar were investigated by in-beam
Ar were investigated by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy following proton- and neutron-knockout, multinucleon removal, and proton inelastic scattering at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. The energies of the two previously reported transitions have been confirmed, and five additional states are presented for the first time, including a candidate for a 3
-ray spectroscopy following proton- and neutron-knockout, multinucleon removal, and proton inelastic scattering at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. The energies of the two previously reported transitions have been confirmed, and five additional states are presented for the first time, including a candidate for a 3 state. The level scheme built using
state. The level scheme built using 
 coincidences was compared to shell-model calculations in the
coincidences was compared to shell-model calculations in the 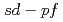 model space and to
model space and to  predictions based on chiral two- and three-nucleon interactions. Theoretical proton- and neutron-knockout cross sections suggest that two of the new transitions correspond to 2
predictions based on chiral two- and three-nucleon interactions. Theoretical proton- and neutron-knockout cross sections suggest that two of the new transitions correspond to 2 states, while the previously proposed 4
states, while the previously proposed 4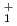 state could also correspond to a 2
state could also correspond to a 2 state.
state.
Murata, Kazutoshi*; Noda, Shinei*; Oike, Takahiro*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Takahashi, Takeo*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(4), p.658 - 664, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:55.86(Biology)The effect of carbon ion irradiation on cell motility through the Rho signaling pathway in the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 was studied. At 48 h after irradiation, the cell motility of A549 cells became significantly greater, and the formation of protrusions significantly increased in cells irradiated with carbon ion. The observed increase in cell motility due to carbon ion irradiation was similar to that observed due to X-ray irradiation. Western-blot analysis showed that carbon ion irradiation increased P-MLC2-S19 expression compared with in unirradiated controls, while total MLC2 expression was unchanged. Exposure to a non-toxic concentration of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of ROCK, reduced the expression of P-MLC2-S19 after C-ion irradiation, resulting in a significant reduction in migration. These data suggest that carbon irradiation increases cell motility in A549 cells via the Rho signaling pathway and that ROCK inhibition reduces that effect.
Musha, Atsushi*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Takahashi, Takeo*; Ando, Koichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Negishi, Akihide*; Yokoo, Satoshi*; Nakano, Takashi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(4), p.545 - 550, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:45.05(Biology) 1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation
1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiationKiyohara, Hiroki*; Ishizaki, Yasuki*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Kato, Hiroyuki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Takahashi, Takeo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Nakano, Takashi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 52(3), p.287 - 292, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.48(Biology)Kaminuma, Takuya*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Shirai, Katsuyuki*; Mizui, Toshiyuki*; Noda, Shinei*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Funayama, Tomoo; Takahashi, Takeo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Shirao, Tomoaki*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(6), p.627 - 631, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.86(Biology)Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Imaoka, Tatsuhiko*; Masunaga, Shinichiro*; Ogata, Toshiyuki*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kato, Takamitsu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Onishi, Takeo*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(4), p.365 - 383, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:115 Percentile:91.16(Biology)Matsumoto, Hideki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Onishi, Takeo*
Journal of Radiation Research, 48(2), p.97 - 106, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:122 Percentile:90.34(Biology)The risks of low dose ionizing irradiation ( 100 mSv) have been estimated using a linear no-threshold model by extrapolating from data obtained after high dose irradiation. The validity of this dose-response model is, however, controversial because evidence accumulated for over the past decade has shown that response of living organisms including humans to low dose/low dose-rate radiation is different from that to high dose/high dose-rate radiation. In another words, findings that cannot be explained by the classical "target theory" of radiobiology have accumulated. The radiation-induced adaptive response, bystander effects, low-dose radio-hypersensitivity, and genomic instability are specifically observed in response to low dose/low dose-rate radiation, and underpinnings of these responses often involve biochemical/molecular signals responding to targeted and non-targeted events. Recently, interrelations between the radioadaptive and bystander responses have been increasingly reported. We review observations supporting the existence of the latter two phenomena, and discuss the possible link between them from the aspect of production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
100 mSv) have been estimated using a linear no-threshold model by extrapolating from data obtained after high dose irradiation. The validity of this dose-response model is, however, controversial because evidence accumulated for over the past decade has shown that response of living organisms including humans to low dose/low dose-rate radiation is different from that to high dose/high dose-rate radiation. In another words, findings that cannot be explained by the classical "target theory" of radiobiology have accumulated. The radiation-induced adaptive response, bystander effects, low-dose radio-hypersensitivity, and genomic instability are specifically observed in response to low dose/low dose-rate radiation, and underpinnings of these responses often involve biochemical/molecular signals responding to targeted and non-targeted events. Recently, interrelations between the radioadaptive and bystander responses have been increasingly reported. We review observations supporting the existence of the latter two phenomena, and discuss the possible link between them from the aspect of production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
Komaki, Yoshihide; ; ; ; Sakurai, Tsutomu; ; Kobayashi, Yoshii; Adachi, Takeo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 33(5), p.489 - 497, 1991/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Adachi, Takeo; ; *; ; *; Takeishi, Hideyo; Gunji, Katsubumi; Kimura, Takaumi; ; Nakahara, Yoshinori; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 174, p.60 - 71, 1990/00
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:94.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ashikawa, Naoko*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Takao; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Kurata, Rie*; Kobayashi, Makoto*; Muroga, Takeo*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*
no journal, ,
Dust control is an important issue related to tritium retentions in thermonuclear fusion devices with magnetic confinements. In particular, remained hydrogen isotope in dust particles at shadow areas are serious problem related the limitation t capacity in ITER. In previous work of dust collection in LHD and JT-60U, typical diameters of dust particles were shown to be 0.001-10 micron in LHD, and 0.1-100 micron in JT-60U. Some tokamak device groups in TFTR, TEXTOR, JT-60 and JET tried to measure the hydrogen isotopes retentions in dust particles. However, they measured the retention only in the dust flakes with sizes exceeding about 10 microns. In this study, we tried to measure hydrogen isotope retentions in the dusts with small amount including those with small diameters. The estimation of the amount of remained hydrogen isotopes in the dust particles will be useful to estimate tritium inventory and optimize cleaning methods specific dusts in ITER and future fusion devices.
Kobayashi, Kensei*; Kawamoto, Yukinori*; Sarker, P. K.*; Ono, Keisuke*; Kuwahara, Hideharu*; Obayashi, Yumiko*; Kaneko, Takeo*; Mita, Hajime*; Yabuta, Hikaru*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Kobayashi, Kensei*; Kawamoto, Yukinori*; Okabe, Takuto*; Sarker, P. K.*; Obayashi, Yumiko*; Kaneko, Takeo*; Mita, Hajime*; Kanda, Kazuhiro*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Kensei*; Kawamoto, Yukinori*; Sarker, P. K.*; Kuwahara, Hideharu*; Obayashi, Yumiko*; Kaneko, Takeo*; Mita, Hajime*; Yabuta, Hikaru*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Narumi, Issei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murata, Kazutoshi*; Noda, Shinei*; Oike, Takahiro*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Takahashi, Takeo*; et al.
no journal, ,
This study aimed to investigate the effect of carbon ion (C-ion) irradiation on cell motility through the ras homolog gene family member (Rho) signaling pathway in the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549. Cell motility was assessed by a wound-healing assay, and the formation of cell protrusions was evaluated by F-actin staining. Cell viability was examined by the WST-1 assay. The expression of myosin light chain 2 (MLC2) and the phosphorylation of MLC2 at Ser19 (P MLC2-S19) were analyzed by Western blot. The data suggest that C-ion irradiation increases cell motility in A549 cells via the Rho signaling pathway and that ROCK inhibition reduces that effect.