Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takamatsu, Misao; Kawahara, Hirotaka; Ito, Hiromichi; Ushiki, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Nobuhiro; Sasaki, Jun; Ota, Katsu; Okuda, Eiji; Kobayashi, Tetsuhiko; Nagai, Akinori; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(1), p.32 - 42, 2016/03
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, it was confirmed that the top of the irradiation test sub-assembly of "MARICO-2" (material testing rig with temperature control) had been broken and bent onto the in-vessel storage rack as an obstacle and had damaged the upper core structure (UCS). This paper describes the results of the in-vessel repair techniques for UCS replacement, which are developed in Joyo. UCS replacement was successfully completed in 2014. In-vessel repair techniques for sodium cooled fast reactors (SFRs) are important in confirming its safety and integrity. In order to secure the reliability of these techniques, it was necessary to demonstrate the performance under the actual reactor environment with high temperature, high radiation dose and remained sodium. The experience and knowledge gained in UCS replacement provides valuable insights into further improvements for In-vessel repair techniques in SFRs.
Ito, Hiromichi; Suzuki, Nobuhiro; Kobayashi, Tetsuhiko; Kawahara, Hirotaka; Nagai, Akinori; Sakao, Ryuta*; Murata, Chotaro*; Tanaka, Junya*; Matsusaka, Yasunori*; Tatsuno, Takahiro*
Proceedings of 2015 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2015) (CD-ROM), p.1058 - 1067, 2015/05
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo (Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR)), it was confirmed that the top of the irradiation test sub-assembly had bent onto the in-vessel storage rack as an obstacle and had damaged the upper core structure (UCS). There is a risk of deformation of the UCS and guide sleeve (GS) caused by interference between them unless inclination is controlled precisely. To mitigate the risk, special jack-up equipment for applying three-point suspension was developed. The existing damaged UCS (ed-UCS) jack-up test using the jack-up equipment was conducted on May 7, 2014. As a result of this test, it was confirmed that the ed-UCS could be successfully jacked-up to 1000 mm without consequent overload. The experience and knowledge gained in the ed-UCS jack-up test provides valuable insights and prospects not only for UCS replacement but also for further improving and verifying repair techniques in SFRs.
 C discharge at RI facilities; A Comparison of collection and oxidation methods
C discharge at RI facilities; A Comparison of collection and oxidation methodsUeno, Yumi; Koarashi, Jun; Iwai, Yasunori; Sato, Junya; Takahashi, Teruhiko; Sawahata, Katsunori; Sekita, Tsutomu; Kobayashi, Makoto; Tsunoda, Masahiko; Kikuchi, Masamitsu
Hoken Butsuri, 49(1), p.39 - 44, 2014/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has conducted a monthly monitoring of airborne  C discharge at the forth research building (RI facility) of the Tokai Research and Development Center. In the current monitoring,
C discharge at the forth research building (RI facility) of the Tokai Research and Development Center. In the current monitoring,  C, which exists in various chemical forms in airborne effluent, is converted into
C, which exists in various chemical forms in airborne effluent, is converted into  CO
CO with CuO catalyst and then collected using monoethanolamine (MEA) as CO
with CuO catalyst and then collected using monoethanolamine (MEA) as CO absorbent. However, this collection method has some issues on safety management because the CuO catalyst requires a high heating temperature (600
absorbent. However, this collection method has some issues on safety management because the CuO catalyst requires a high heating temperature (600 C) to ensure a high oxidation efficiency and the MEA is specified as a poisonous and deleterious substance. To establish a safer, manageable and reliable method for monitoring airborne
C) to ensure a high oxidation efficiency and the MEA is specified as a poisonous and deleterious substance. To establish a safer, manageable and reliable method for monitoring airborne  C discharge, we examined collection methods that use different CO
C discharge, we examined collection methods that use different CO absorbents (MEA and Carbo-Sorb E) and oxidation catalysts (CuO, Pt/Alumina and Pd/ZrO
absorbents (MEA and Carbo-Sorb E) and oxidation catalysts (CuO, Pt/Alumina and Pd/ZrO ). The results showed 100% CO
). The results showed 100% CO collection efficiency of MEA during a 30-day sampling period under the condition tested. In contrast, Carbo-Sorb E was found to be unsuitable for the monthly-long CO
collection efficiency of MEA during a 30-day sampling period under the condition tested. In contrast, Carbo-Sorb E was found to be unsuitable for the monthly-long CO collection because of its high volatile nature. Among the oxidation catalysts, the Pd/ZrO
collection because of its high volatile nature. Among the oxidation catalysts, the Pd/ZrO showed the highest oxidation efficiency for CH
showed the highest oxidation efficiency for CH at a lower temperature.
at a lower temperature.
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Ochiai, Kentaro; Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro*; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Nakamichi, Masaru; Konno, Chikara; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(7-8), p.1253 - 1257, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium generation and recovery study on lithium ceramic packed bed was started by use of FNS in JAEA. Lithium titanate was selected as tritium breeding material. In this work, the effect of sweep gas species on tritium release behavior was investigated. In case of sweep by helium with 1% of hydrogen, tritium in water form was released sensitively corresponding to the irradiation. This is due to existence of the water vapor in the sweep gas. On the other hand, in case of sweep by dry helium, tritium in gaseous form was released first, and release of tritium in water form was delayed and was gradually increased.
Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(3), p.1025 - 1028, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have tested a number of polymeric materials used as gasket, insulator, glove and casing panel in the solid-polymer-electrolyte (SPE) tritiated water electrolyzer to evaluate the contamination by tritiated water and the change in contamination by irradiation. HTO contamination on polymeric materials both being exposed to 740-1110 Bq/cm of HTO vapor with a 1kPa of H
of HTO vapor with a 1kPa of H O pressure and being immersed in 70000 Bq/cm
O pressure and being immersed in 70000 Bq/cm of HTO water was considered in the test. The exposed time affected negligibly the total amount of leached HTO from the rubber samples exposed to HTO vapor. The immersed time in contrast affected strongly the total amount of leached HTO from the rubber samples. The total amount of leached HTO from radiation-crosslinkable butyl rubber and radiation-degradable perfluoro Karlez rubber immersed in HTO was considerably increased as the integrated dose was increased. However, we found that the total amount of leached HTO from the irradiated rubber can maintain the similar amount from unirradiated by setting the hydrogen/fluoride ratio of the polymeric component to the suitable number.
of HTO water was considered in the test. The exposed time affected negligibly the total amount of leached HTO from the rubber samples exposed to HTO vapor. The immersed time in contrast affected strongly the total amount of leached HTO from the rubber samples. The total amount of leached HTO from radiation-crosslinkable butyl rubber and radiation-degradable perfluoro Karlez rubber immersed in HTO was considerably increased as the integrated dose was increased. However, we found that the total amount of leached HTO from the irradiated rubber can maintain the similar amount from unirradiated by setting the hydrogen/fluoride ratio of the polymeric component to the suitable number.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Inomiya, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Takumi
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(3), p.1083 - 1087, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium Process Laboratory (TPL) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been established as the only test facilities to handle over 1 gram of in Japan. From March 1988, TPL has been operated with tritium, and no tritium release accident has been observed. The average tritium concentration in a stream from a stack of the TPL to environment was 71 Bq/m , and was 1/70 of the Japanese regulation value for HTO. The failure data have been analyzed for several main components of the safety systems such as pumps, valves, and monitors. The data on the tritium waste and accountancy has also been accumulated. As a study of the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, these data are analysed and are reported.
, and was 1/70 of the Japanese regulation value for HTO. The failure data have been analyzed for several main components of the safety systems such as pumps, valves, and monitors. The data on the tritium waste and accountancy has also been accumulated. As a study of the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, these data are analysed and are reported.
Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.1187 - 1190, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The concept of tritium containment and confinement is the root of fusion safety. Hence, HTO contamination on concretes and epoxy paint should be reduced as low as possible. Several kinds of hydrophobic coatings, a commercial silicic paint, a commercial acrylic paint, a commercial fluoric paint, methoxytrimethylsilane paint or metallic stick-sheets, were tested on concrete and epoxy samples. These samples were exposed to 740-1110Bq/cm of HTO vapor at room temperature for a given period from 1 to 60 weeks. Static leaching tests were carried out for every HTO absorbed sample in distilled water, and the amount of leached HTO was evaluated. The hydrophobic barriers were effective to reduce HTO penetration into concrete. After exposure to HTO for 1 week, the HTO amount penetrated into concrete was reduced to 54.2% of non-paint sample for methoxytrimethylsilane paint, 56.0% for a commercial fluoric paint, 66.8% for a commercial silicic paint, respectively. Effectiveness of these hydrophobic barriers became less as the samples were exposed to HTO for a longer period.
of HTO vapor at room temperature for a given period from 1 to 60 weeks. Static leaching tests were carried out for every HTO absorbed sample in distilled water, and the amount of leached HTO was evaluated. The hydrophobic barriers were effective to reduce HTO penetration into concrete. After exposure to HTO for 1 week, the HTO amount penetrated into concrete was reduced to 54.2% of non-paint sample for methoxytrimethylsilane paint, 56.0% for a commercial fluoric paint, 66.8% for a commercial silicic paint, respectively. Effectiveness of these hydrophobic barriers became less as the samples were exposed to HTO for a longer period.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Iwai, Yasunori; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.1183 - 1186, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In a fusion reactor of high safety and acceptability, safe confinement of tritium is one of key issues for the fusion reactor. Tritium should be well-controlled and not excessively released to environment and to prevent workers from excess exposure. Especially, the hot cell and tritium facility of ITER will be used various construction materials such as the concrete, the organic materials. As the results, the concrete materials were almost saturated with HTO vapor within about 1month except for cement paste and it was larger in the order of cement paste  mortar
mortar  concrete. Even if one month passes from the exposure beginning, the amount of sorbed tritium to cement paste did not reach saturation. The chemical form of desorbed tritium from the sample was almost HTO. In addition, the tritium behavior that adsorbs the surface of concrete materials will be discussed by using FT-IR.
concrete. Even if one month passes from the exposure beginning, the amount of sorbed tritium to cement paste did not reach saturation. The chemical form of desorbed tritium from the sample was almost HTO. In addition, the tritium behavior that adsorbs the surface of concrete materials will be discussed by using FT-IR.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Suzuki, Takumi; Yamada, Masayuki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 85(7-9), p.1002 - 1006, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The R&D for tritium technologies to a demonstration reactor (DEMO) is planned to be carried out in the Broader Approach (BA) program in Japan by JAEA with Japanese universities: (1) tritium analysis technology; (2) basic tritium safety research; and (3) tritium durability test. A multi-purpose RI facility is under construction at Rokkasho in Aomori to carry out the above R&D subjects. A preliminary safety study has been carried out for the amount of tritium released to the environment and for the radiation dose of workers. The main subjects of the R&D of tritium analysis are the technologies for real-time analysis for hydrogen isotopes, gas, liquid and solid. The materials of interest include F82H, SiC, ZrCo, solid and liquid advanced breeder and multipliers. In the tritium durability tests, organic materials and metals are studied for the radiation and the corrosion damage. A series of preliminary studies for the above subjects has been started.
Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Perevezentsev, A.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 85(7-9), p.1386 - 1390, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish effective ITER atmosphere detritiation system (DS), JAEA has investigated the performance and the durability at various incident/accident conditions, and supported to finalize the DS conceptual design through the ITER design review. The current DS at the safety important component has been discussed and mainly consists of catalytic reactors, wet scrubber column (SC) and blowers. The functional failure of the DS design with SC was evaluated using database of failure experiences of valves, controllers and components. Even in the tritium release into the biggest confinement sector of Tokamak gallery, it improved more than tow orders of magnitude comparing with that of original DS design using Molecular Sieve (MS) dryer beds in the 2001 design report. This improvement is achieved mainly by the minimization of valve operation like MS dryers and by the standardized module arrangement of DS with SC.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Nuclear Fusion, 49(5), p.055019_1 - 055019_8, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:37.12(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Tritium technologies have reached the level where they allow us to design the main fuel cycle of ITER. On the other hand, for the blanket tritium recovery system, a series of fundamental studies have still been carried out even though the system is essential to realize the fusion reactor from the viewpoint of the fuel production. In the case of a water cooling solid breeder blanket, the blanket tritium recovery system will be composed of three processes: tritium recovery from the helium sweep gas as hydrogen, that as water vapor and tritium recovery from the coolant water. For these processes, the present authors have proposed a set of advanced systems, and have proved that the proposed systems would be feasible for a DEMO reactor.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Arita, Tadaaki; Hoshi, Shuichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(10-12), p.1359 - 1363, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)At TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory) of JAEA, ITER relevant tritium technologies have been studied. The design studies of Air Detritiation System have been carried out in JAEA as a contribution of Japan to ITER. For the tritium processing technologies, our efforts have been focused on the research of the tritium recovery system of ITER test blanket system. A ceramic proton conductor has been studied as an advanced blanket system. A series of fundamental studies on tritium safety technologies not only for ITER but also for fusion DEMO plants has also been carried out at TPL of JAEA. The main research activities in this field are the tritium behavior in a confinement and its barrier materials; monitoring; accountancy; detritiation and decontamination etc. In this paper, the results of above recent activities at TPL of JAEA are summarized from viewpoint of ITER relevant and future fusion DEMO reactors.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(1), p.45 - 50, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The R&D for tritium technologies towards to the DEMO plants are carried out in Broader Approach (BA) program in Japan: (1) tritium accountancy technology; (2) basic tritium safety research; and (3) tritium durability test. A multi-purpose facility is constructed at Rokkasho in Japan to carry out the above R&Ds. Beta  radioisotopes as well as tritium (370 TBq/year) can be handled in the facility. At TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory) of JAEA, a series of R&Ds for the tritium technologies relevant to the above BA program have been started. A series of basic studies for the tritium-materials has also been carried out. The main R&D activities in this field are the tritium behavior in a confinement; monitoring; detritiation; and decontamination. In this paper, the results of above recent activities at TPL of JAEA are also summarized from viewpoint of future fusion DEMO reactors.
radioisotopes as well as tritium (370 TBq/year) can be handled in the facility. At TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory) of JAEA, a series of R&Ds for the tritium technologies relevant to the above BA program have been started. A series of basic studies for the tritium-materials has also been carried out. The main R&D activities in this field are the tritium behavior in a confinement; monitoring; detritiation; and decontamination. In this paper, the results of above recent activities at TPL of JAEA are also summarized from viewpoint of future fusion DEMO reactors.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hoshi, Shuichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(1), p.315 - 318, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The construction of the building and safety systems of the TPL was completed until 1985. The operations of the safety systems with tritium have been started from March 1988. The amount of tritium held at the TPL was 13 PBq at March 2007. The average tritium concentration in a stream from a stack of the TPL to environment was 6.0 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm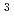 ; and is 1/100 smaller than that of the regulation value for the concentration of HTO in the air in Japan. The safety operation results with tritium have thus been obtained. A set of failure data of several main components of the TPL was also obtained as the valuable data for fusion tritium facilities.
; and is 1/100 smaller than that of the regulation value for the concentration of HTO in the air in Japan. The safety operation results with tritium have thus been obtained. A set of failure data of several main components of the TPL was also obtained as the valuable data for fusion tritium facilities.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Willms, R. S.*; Carlson, R. V.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(1), p.311 - 314, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to obtain the data for actual tritium behavior in the room and/or building, a series of intentional tritium release experiments were planed and carried out within a radiological controlled area at Tritium System Test Assembly (TSTA) in Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) under US-JAPAN collaboration program. In these experiments, influence of a difference of the release point and a difference of the amount of hydrogen isotope were suggested. In this report, the results of intentional tritium release experiments at TSTA in LANL are summarized. The released tritium was reached a uniform value about 30  40 minutes in all the experiments. The influence of the difference of the release point and the difference of the amount of hydrogen isotope were not seen in these experiments drastically. The initial tritium behavior in the room is also discussed by comparing calculated values with experimental results.
40 minutes in all the experiments. The influence of the difference of the release point and the difference of the amount of hydrogen isotope were not seen in these experiments drastically. The initial tritium behavior in the room is also discussed by comparing calculated values with experimental results.
Hayashi, Takumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Shu, Wataru; Suzuki, Takumi; Yamada, Masayuki; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(1), p.319 - 322, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sakanaka, Shogo*; Ago, Tomonori*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; Harada, Kentaro*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Honda, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.205 - 207, 2008/06
Future synchrotron light sources based on the energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) are expected to be capable of producing super-brilliant and/or ultra-short pulses of synchrotron radiation. Our Japanese collaboration team is making efforts for realizing an ERL-based hard X-ray source. We report recent progress in our R&D efforts.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Shu, Wataru; Suzuki, Takumi; Yamada, Masayuki; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Proceedings of 2nd Japan-China Workshop on Blanket and Tritium Technology, p.74 - 78, 2008/05
In order to accumulate the tritium behavior in the future fusion reactor included ITER, intentional tritium release experiments have been carried out using Caisson Assembly for Tritium Safety study (CATS) at Tritium Process Laboratory (TPL) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Main objectives of CATS are (1) to demonstrate the initial tritium behavior in the room and to develop 3D simulation code of tritium behavior in the room. (2) to demonstrate the performance of integrated system for tritium confinement after intentional tritium release accident, (3) to accumulate the data for the detritiation behavior and the interaction between various materials and tritium (tritiated water) in the confinement. The study using CATS has been continued for about 10 yeas in TPL/JAEA.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Iwai, Yasunori; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Miura, Hidenori*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(12), p.1645 - 1651, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:11.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The confinement and removal of tritium are the key subjects for safety of ITER. The ITER buildings are confinement barriers of tritium. In a hot cell building, tritium is often released, as vapor and is in contact with the inner walls. Also those of an ITER tritium plant building will be exposed to tritium in an accident. However, the data are scarce, especially on the penetration of tritium into the concrete of the wall materials. The tritium released in the buildings is removed by the Atmosphere Detritiation Systems (ADS), where the tritium is oxidized by catalysts and is removed as water. Special gas of SF is used in ITER, and is expected to be released in an accident such as fire. Although the SF
is used in ITER, and is expected to be released in an accident such as fire. Although the SF gas has the potential as a catalyst poison, the performance of ADS with the existence of SF
gas has the potential as a catalyst poison, the performance of ADS with the existence of SF has not been confirmed yet. Tritiated water is produced in the regeneration process of ADS, and is subsequently processed by the ITER Water Detritiation System (WDS). One of the key components of WDS is an electrolysis cell. The electrolysis cell is made of organic compounds, and there is no data on the durability of the cell exposed to tritium. To overcome these issues in a global tritium confinement, a series of experimental studies have been carried out as an ITER R&D task: (1) tritium behavior in concrete; (2) effect of SF
has not been confirmed yet. Tritiated water is produced in the regeneration process of ADS, and is subsequently processed by the ITER Water Detritiation System (WDS). One of the key components of WDS is an electrolysis cell. The electrolysis cell is made of organic compounds, and there is no data on the durability of the cell exposed to tritium. To overcome these issues in a global tritium confinement, a series of experimental studies have been carried out as an ITER R&D task: (1) tritium behavior in concrete; (2) effect of SF on performance of ADS; and (3) tritium durability of electrolysis cell of ITER-WDS.
on performance of ADS; and (3) tritium durability of electrolysis cell of ITER-WDS.