Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Kurita, Keisuke; Sakai, Takuro; Suzui, Nobuo*; Yin, Y.-G.*; Sugita, Ryohei*; Kobayashi, Natsuko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; Kawachi, Naoki*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 60(11), p.116501_1 - 116501_4, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.86(Physics, Applied)Radioisotope tracer imaging is useful for studying plant physiological phenomena. In this study, we developed an autoradiography system with phosphor powder (ZnS:Ag), "Live-autoradiography", for imaging radioisotope dynamics in a living plant. This system visualizes the element migration and accumulation in intact plants continuously under a light environment. An imaging test was performed on point sources of  Cs, with a radioactivity of 10-100 kBq of being observed; this indicates satisfactory system linearity between the image intensity and the radioactivity of
Cs, with a radioactivity of 10-100 kBq of being observed; this indicates satisfactory system linearity between the image intensity and the radioactivity of  Cs. Moreover, dynamics imaging of
Cs. Moreover, dynamics imaging of  Cs was performed on an intact soybean plant for four days. The serial images indicated
Cs was performed on an intact soybean plant for four days. The serial images indicated  Cs accumulation in the node, vein, and growing point of the plant. The developed system can be used for studying plant physiological phenomena and can be employed for quantitative measurement of radionuclides.
Cs accumulation in the node, vein, and growing point of the plant. The developed system can be used for studying plant physiological phenomena and can be employed for quantitative measurement of radionuclides.
Saito, Junichi; Kobayashi, Yohei*; Shibutani, Hideo*
Materials Transactions, 62(10), p.1524 - 1532, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Kobayashi, Yohei*; Shibutani, Hideo*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 85(3), p.110 - 119, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.06(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter
clusters in dilute neutron-rich matterTanaka, Junki*; Yang, Z.*; Typel, S.*; Adachi, Satoshi*; Bai, S.*; van Beek, P.*; Beaumel, D.*; Fujikawa, Yuki*; Han, J.*; Heil, S.*; et al.
Science, 371(6526), p.260 - 264, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:99.12(Multidisciplinary Sciences)By employing quasi-free  -cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of
-cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of  clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between
clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between  -cluster formation and the neutron skin.
-cluster formation and the neutron skin.
 spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo mission
spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo missionKawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Takasu, Masako*; Narumi, Issey*; Sato, Katsuya; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Nakagawa, Kazumichi*; Tanigawa, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Origins of Life and Evolution of Biospheres, 43(4-5), p.411 - 428, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:80.34(Biology)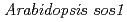 mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance
mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt toleranceAriga, Hirotake*; Katori, Taku*; Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Iuchi, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Masatomo*; Tezuka, Kenji*; Sakata, Yoichi*; et al.
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 8(7), p.e24779_1 - e24779_5, 2013/07
Based on analysis of the salinity tolerance among 354  accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.

 hort (cv. White Aga)
hort (cv. White Aga)Kondo, Masayoshi*; Koike, Yosuke*; Okuhara, Hiroyuki*; Oda, Masayuki*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 67, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Ago, Tomonori*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; Harada, Kentaro*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Honda, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.205 - 207, 2008/06
Future synchrotron light sources based on the energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) are expected to be capable of producing super-brilliant and/or ultra-short pulses of synchrotron radiation. Our Japanese collaboration team is making efforts for realizing an ERL-based hard X-ray source. We report recent progress in our R&D efforts.
 Zn
Zn Cr
Cr Se
Se
Iikubo, Satoshi*; Yasui, Yukio*; Oda, Keisuke*; Ono, Yohei*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 71(11), p.2792 - 2799, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kondo, Masayoshi*; Koike, Yosuke*; Okuhara, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Hoshi, Yosuke*; Nomizu, Toshikazu*; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakui, Ryohei; Higuchi, Hidetoshi; Kitagaki, Toru; Washiya, Tadahiro; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Kobayashi, Tsuguyuki*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Suganuma, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Taji, Teruaki*; Katori, Taku*; Ariga, Hirotake*; Iuchi, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Masatomo*; Shinozaki, Kazuo*; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Nozawa, Shigeki; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Kobayashi, Kensei*; Mita, Hajime*; Yabuta, Hikaru*; Nakagawa, Kazumichi*; Narumi, Issei; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; Tomita, Kaori*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo mission
spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo missionKawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Narumi, Issey*; Sato, Katsuya; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Nakagawa, Kazumichi*; Tanigawa, Yoshiaki*; Momoki, Yohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
 spp. under space
spp. under spaceKawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Murano, Yuka*; Harada, Miyu*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Takasu, Masako*; Narumi, Issey*; Sato, Katsuya; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Kobayashi, Yohei*; Shibutani, Hideo*
no journal, ,
Kobayashi, Yohei*; Saito, Junichi; Shibutani, Hideo*
no journal, ,