Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Murakami, Takahiko; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
New experiments simulating fuel debris in the new criticality assembly, STACY, are designed to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations for criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. In the new STACY experiment, a two-region core consisting of a driver region and a test region was investigated in order to configure a debris-simulated core with under-moderation condition (lattice pitch 1.27-cm) having the constraint of available fuel rod number. The test region with a 1.27-cm lattice pitch is surrounded by the driver region, in which fuel rods are arranged in a checkerboard pattern on a 1.27-cm lattice plate, with a 1.80-cm lattice pitch. Neutron spectra and sensitivity were calculated by using MCNP6 and ENDF/B-VII. The core which has a 17 17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17
17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17 17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13
17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13 13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of
13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of  Si and
Si and  Ca (n,
Ca (n, ) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Kida, Takashi; Sono, Hiroki; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
In the criticality experiment in the new STACY, pseudo fuel debris samples are used to acquire data for validation of the system used for 1F debris criticality safety assessment. The pseudo fuel debris is a pellet with a diameter of 8 mm and a height of 10 mm containing uranium oxide and structural materials (iron, silicon, zirconium, etc.). The pellets are made by mixing, pressing and sintering uranium dioxide powder and structural materials powder. The UO powder uses the same composition of uranium as the STACY driver fuel rods, in order to reduce the errors in fuel composition. The pseudo fuel debris fabrication devices and analysis equipment are installed at the BECKY in order to evaluate the critical properties of fuel debris with high accuracy in dimension and analysis. This equipment is located in the same laboratory and can quickly respond to experimental needs such as preparation of the pseudo fuel debris and analysis before and after irradiation.
powder uses the same composition of uranium as the STACY driver fuel rods, in order to reduce the errors in fuel composition. The pseudo fuel debris fabrication devices and analysis equipment are installed at the BECKY in order to evaluate the critical properties of fuel debris with high accuracy in dimension and analysis. This equipment is located in the same laboratory and can quickly respond to experimental needs such as preparation of the pseudo fuel debris and analysis before and after irradiation.
 pellet in molten Zr cladding
pellet in molten Zr claddingIto, Ayumi*; Yamashita, Susumu; Tasaki, Yudai; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.450 - 459, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nomura, Mitsuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nakayama, Takuya; Yaita, Yumi*; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Murata, Eiichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104396_1 - 104396_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)When dismantling centrifuges in uranium-enrichment facilities, decontamination techniques must be developed to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces of dismantled parts selectively. Dismantled uranium-contaminated parts can be disposed of as nonradioactive wastes or recycled after decontamination appropriate for clearance. previously, we developed a liquid decontamination technique using acidic electrolyzed water to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces. However, further developments are still needed for its actual application. Dismantled parts have various uranium-contaminated surface features due to varied operational conditions, inhomogeneous decontamination using iodine heptafluoride gas, and changes in long-term storage conditions after dismantling. Here, we performed liquid decontamination on specimens with varying uranium-contaminated surfaces cut from a centrifuge made of low-carbon steel. From the results, the liquid decontamination can effectively remove the uranium-contaminated surfaces, and radioactive concentrations fell below the target value within twenty minutes. Although the required time should also depend on dismantled parts' sizes and shapes in their actual application, we demonstrated that it could be an effective decontamination technique for uranium-contaminated steels of dismantled centrifuges.
Sueoka, Shigeru; Kobayashi, Yumi*; Fukuda, Shoma; Kohn, B. P.*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Sano, Naomi*; Hasebe, Noriko*; Tamura, Akihiro*; Morishita, Tomoaki*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Tectonophysics, 828, p.229231_1 - 229231_17, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.53(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The South Fossa Magna zone, central Japan, has been an active collision zone between the Honshu Arc and the Izu-Bonin Arc since the middle Miocene and provides an excellent setting for reconstructing the earliest stages of continent formation. Multi-system geo-thermochronometry was applied to different domains of the South Fossa Magna zone, together with some previously published data, to reveal mountain formation processes, i.e., vertical crustal movements. Nine granitic samples yielded zircon U-Pb ages of 10.2-5.8 Ma ( = 2), apatite (U-Th)/He (AHe) ages of 42.8-2.6 Ma (
= 2), apatite (U-Th)/He (AHe) ages of 42.8-2.6 Ma ( = 7), and apatite fission-track (AFT) ages of 44.1-3.0 Ma (
= 7), and apatite fission-track (AFT) ages of 44.1-3.0 Ma ( = 9). Thermal history inversion modeling based on the AHe and AFT data suggested rapid cooling events confined within the study region at
= 9). Thermal history inversion modeling based on the AHe and AFT data suggested rapid cooling events confined within the study region at  6-2 Ma. The Kanto Mountains may have undergone a domal uplift in association with their collision with the Tanzawa Block at
6-2 Ma. The Kanto Mountains may have undergone a domal uplift in association with their collision with the Tanzawa Block at  5 Ma. However, this uplift may have slowed down following the migration of the plate boundary and late Pliocene termination of the Tanzawa collision. The Minobu Mountains and possibly adjacent mountains may have been uplifted by the motional change of the Philippine Sea plate at
5 Ma. However, this uplift may have slowed down following the migration of the plate boundary and late Pliocene termination of the Tanzawa collision. The Minobu Mountains and possibly adjacent mountains may have been uplifted by the motional change of the Philippine Sea plate at  3 Ma. Therefore, the mountain formation in the South Fossa Magna zone was mainly controlled by collisions of the Tanzawa and Izu Blocks and motional change of the Philippine Sea plate. Earlier collisions of the Kushigatayama Block at
3 Ma. Therefore, the mountain formation in the South Fossa Magna zone was mainly controlled by collisions of the Tanzawa and Izu Blocks and motional change of the Philippine Sea plate. Earlier collisions of the Kushigatayama Block at  13 Ma and Misaka Block at
13 Ma and Misaka Block at  10 Ma appeared to have had little effect on mountain formation. Together with a
10 Ma appeared to have had little effect on mountain formation. Together with a  90 deg. clockwise rotation of the Kanto Mountains at 12-6 Ma, these observations suggest that horizontal deformation predominated during the earlier stage of arc-arc collision, and vertical movements due to buoyancy resulting from crustal shortening and thickening developed at a later stage.
90 deg. clockwise rotation of the Kanto Mountains at 12-6 Ma, these observations suggest that horizontal deformation predominated during the earlier stage of arc-arc collision, and vertical movements due to buoyancy resulting from crustal shortening and thickening developed at a later stage.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.13(Physics, Nuclear)Kobayashi, Yumi*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Fukuda, Shoma; Hasebe, Noriko*; Tamura, Akihiro*; Morishita, Tomoaki*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Fuisshon, Torakku Nyusureta, (33), p.25 - 27, 2020/10
no abstracts in English
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of European Research Reactor Conference 2020 (RRFM 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/10
Critical experiments of thermal neutron system are still expected to be playing an important role for wide technical issues. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is renovating the Static Experimental Critical Facility (STACY) to maintain the experimental capability. The new STACY is designed as a general-purpose criticality facility. Its core mainly consists of low enriched UO fuel rods, grid plates, and light water moderator. The first experiment campaign in the new STACY aims to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris, which will be used in validation of criticality analysis methods. The designs of the experimental core configurations are in progress.
fuel rods, grid plates, and light water moderator. The first experiment campaign in the new STACY aims to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris, which will be used in validation of criticality analysis methods. The designs of the experimental core configurations are in progress.
Kobayashi, Yumi*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Fukuda, Shoma*; Hasebe, Noriko*; Tamura, Akihiro*; Morishita, Tomoaki*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Fuisshon, Torakku Nyusureta, (32), p.8 - 11, 2019/12
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Kokusen, Junya; Uchida, Shoji; Kaminaga, Jota; Oki, Keiichi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sono, Hiroki
JAEA-Technology 2016-025, 42 Pages, 2016/11
A preliminary test on MOX fuel dissolution for the STACY critical experiments had been conducted in 2000 through 2003 at Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. Accordingly, the uranyl / plutonium nitrate solution should be reconverted into oxide powder to store the fuel for a long period. For this storage, the moisture content in the oxide powder should be controlled from the viewpoint of criticality safety. The stabilization of uranium / plutonium solution was carried out under a precipitation process using ammonia or oxalic acid solution, and a calcination process using a sintering furnace. As a result of the stabilization operation, recovery rate was 95.6% for uranium and 95.0% for plutonium. Further, the recovered oxide powder was calcined again in nitrogen atmosphere and sealed immediately with a plastic bag to keep its moisture content low and to prevent from reabsorbing atmospheric moisture.
Narita, Ayumi; Kaminaga, Kiichi; Yokoya, Akinari; Noguchi, Miho; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; Fujii, Kentaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 166(1-4), p.192 - 196, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.54(Environmental Sciences)For the knowledge about irradiation effects of mammalian cells depending on the cell cycle, most of them had been analyzed by statistical approches. Our purpose is to establish the method for real-time observation of irradiated cells under a microscope. Fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) human cancer (HeLa) cells (red indicates G1; green, S/G2) were exposed to a synchrotron X-ray microbeam. Cells in either G1 or S/G2 were selectively irradiated according to cell color observed in the same microscopic field in a culture dish. Time-lapse micrographs of the irradiated cells were acquired for 24 h after irradiation. The cell cycle was strongly arrested by irradiation at S/G2 and never progressed to G1. In contrast, cells irradiated at G1 progress to S/G2 with a similar time course as non-irradiated control cells. These results show single FUCCI cell exposure and live cell imaging are powerful methods for studying radiation effects on the cell cycle.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
Kakuhan, Kongo Gijutsu To Toraburu Taisaku, p.341 - 344, 2014/10
The silver mediated electrochemical oxidation (Ag/MEO) process with the ultrasound agitation has been developed for the purpose of the mineralization of organic wastes containing transuranium nuclides at the nuclear fuel reprocessing process. In the Ag/MEO process, organic solvents are decomposed by divalent silver cations under the relatively low temperature and the ambient pressure condition. The ultrasound agitation is effective in mixing the electrolytic solutions and the organic solvents, and is expected to promote the oxidation of the organic solvents. Therefore, the Ag/MEO process with the ultrasound agitation could be a candidate for the treatment of organic solvents. Destruction tests of TBP and dodecane by the Ag/MEO process were conducted to optimize some treatment conditions. Under optimized conditions, the destruction tests of kerosene and TODGA were carried out. It was confirmed that the Ag/MEO process is effective for the mineralization of these organic solvents.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationArisaka, Makoto; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sugo, Yumi; Kobayashi, Kumiko*; Kanao, Osamu*; Kimura, Takaumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(4), p.457 - 464, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)Toward the development of a practical separation method for trivalent actinides and lanthanides, we used extraction chromatography with alkyl-pyridinedicarboxyamides as the extractant. The results confirmed that the performance degradation of the adsorbent caused by contact with HNO and/or irradiation with
and/or irradiation with  rays would be very small during the operation of column chromatography. The optimal conditions for the column separation were also determined: eluent, 5M HNO
rays would be very small during the operation of column chromatography. The optimal conditions for the column separation were also determined: eluent, 5M HNO ; flow rate, 0.1 mL/min.
; flow rate, 0.1 mL/min.
 C discharge at RI facilities; A Comparison of collection and oxidation methods
C discharge at RI facilities; A Comparison of collection and oxidation methodsUeno, Yumi; Koarashi, Jun; Iwai, Yasunori; Sato, Junya; Takahashi, Teruhiko; Sawahata, Katsunori; Sekita, Tsutomu; Kobayashi, Makoto; Tsunoda, Masahiko; Kikuchi, Masamitsu
Hoken Butsuri, 49(1), p.39 - 44, 2014/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has conducted a monthly monitoring of airborne  C discharge at the forth research building (RI facility) of the Tokai Research and Development Center. In the current monitoring,
C discharge at the forth research building (RI facility) of the Tokai Research and Development Center. In the current monitoring,  C, which exists in various chemical forms in airborne effluent, is converted into
C, which exists in various chemical forms in airborne effluent, is converted into  CO
CO with CuO catalyst and then collected using monoethanolamine (MEA) as CO
with CuO catalyst and then collected using monoethanolamine (MEA) as CO absorbent. However, this collection method has some issues on safety management because the CuO catalyst requires a high heating temperature (600
absorbent. However, this collection method has some issues on safety management because the CuO catalyst requires a high heating temperature (600 C) to ensure a high oxidation efficiency and the MEA is specified as a poisonous and deleterious substance. To establish a safer, manageable and reliable method for monitoring airborne
C) to ensure a high oxidation efficiency and the MEA is specified as a poisonous and deleterious substance. To establish a safer, manageable and reliable method for monitoring airborne  C discharge, we examined collection methods that use different CO
C discharge, we examined collection methods that use different CO absorbents (MEA and Carbo-Sorb E) and oxidation catalysts (CuO, Pt/Alumina and Pd/ZrO
absorbents (MEA and Carbo-Sorb E) and oxidation catalysts (CuO, Pt/Alumina and Pd/ZrO ). The results showed 100% CO
). The results showed 100% CO collection efficiency of MEA during a 30-day sampling period under the condition tested. In contrast, Carbo-Sorb E was found to be unsuitable for the monthly-long CO
collection efficiency of MEA during a 30-day sampling period under the condition tested. In contrast, Carbo-Sorb E was found to be unsuitable for the monthly-long CO collection because of its high volatile nature. Among the oxidation catalysts, the Pd/ZrO
collection because of its high volatile nature. Among the oxidation catalysts, the Pd/ZrO showed the highest oxidation efficiency for CH
showed the highest oxidation efficiency for CH at a lower temperature.
at a lower temperature.
Yamada, Katsunori; Fujii, Katsutoshi; Kanda, Hiroshi; Higashi, Daisuke; Kobayashi, Toshiaki; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Fukami, Tomoyo; Yoshida, Keisuke; Ueno, Yumi; Nakajima, Junya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-033, 51 Pages, 2013/12
After the accident at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, various numerical criteria relevant to radiation protection were defined. We surveyed these criteria through internet. As a result of survey, the following 13 items were identified: (1) criteria for taking stable iodine tablets, (2) criteria for the screening of surface contamination, (3) evacuation area, sheltering area, etc., (4) activity concentrations in food, drinking water, etc., (5) dose limit for radiation workers engaged in emergency work, (6) guideline levels of radioactive substances in bathing areas, (7) criteria for use of school buildings and schoolyards, (8) restriction on planting rice, (9) acceptable activity concentrations in feedstuff, (10) acceptable activity concentrations in compost, (11) criteria for export containers and ships, (12) criteria for contaminated waste, (13) standards for radiation workers engaged in decontamination work. In this report, the basis of and issues on these criteria are summarized.
Kokusen, Junya; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Umeda, Miki
JAEA-Technology 2012-041, 32 Pages, 2013/02
Uranyl nitrate solution fuel used in the STACY and the TRACY is adjusted in the Fuel Treatment System, in which such parameters are varied as concentration of uranium, free nitric acid, soluble neutron poison, and so on. Operations for concentration and denitration of the solution fuel were carried out with an evaporator from JFY 2004 to JFY 2008 in order to adjust the fuel to the experimental condition of the STACY and the TRACY. In parallel, the solution fuel in which some kinds of soluble neutron poison were doped was also adjusted in JFY 2005 and JFY 2006 for the purpose of the STACY experiments to determine neutron absorption effects brought by fission products, etc. After these experiments in the STACY, a part of the solution fuel including the soluble neutron poison was purified by the solvent extraction method with mixer-settlers in JFY 2006 and JFY 2007. This report summarizes operation data of the Fuel Treatment System from JFY 2004 to JFY 2008.
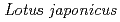 nodules
nodulesHakoyama, Tsuneo*; Oi, Ryo*; Hazuma, Kazuya*; Suga, Eri*; Adachi, Yuka*; Kobayashi, Mayumi*; Akai, Rie*; Sato, Shusei*; Fukai, Eigo*; Tabata, Satoshi*; et al.
Plant Physiology, 160(2), p.897 - 905, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:67.42(Plant Sciences)Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Uchida, Shoji; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-068, 20 Pages, 2010/03
At Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility, the cerium mediated electrolytic oxidation method which is a decontamination technique to decrease the radioactivity of TRU wastes to the clearance-level has been developed for the effective reduction of TRU wastes generated from the decommissioning of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility and so on. This method corrodes the oxide layer and the surface of metallic TRU metal wastes by the strong oxidation power of Ce in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce
in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2
initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2 4
4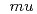 m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3
m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3  m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20
m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20  m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-056, 16 Pages, 2009/11
The silver mediated electrochemical oxidation (Ag/MEO) process with the ultrasound agitation has been developed for the purpose of the mineralization of organic wastes containing transuranium nuclides at the nuclear fuel reprocessing process. In the Ag/MEO process, organic solvents are decomposed by divalent silver cations under the relatively low temperature and the ambient pressure condition. The ultrasound agitation is effective in mixing the electrolytic solutions and the organic solvents, and is expected to promote the oxidation of the organic solvents. Therefore, the Ag/MEO process with the ultrasound agitation could be a candidate for the treatment of organic solvents. Destruction tests of TBP and dodecane by the Ag/MEO process were conducted to optimize some treatment conditions. Under optimized conditions, the destruction tests of kerosene and TODGA were carried out. It was confirmed that the Ag/MEO process is effective for the mineralization of these organic solvents.