Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Be activity concentrations in Dazaifu (western Japan)
Be activity concentrations in Dazaifu (western Japan)Narazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 284, p.107612_1 - 107612_7, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Atmospheric  Be activity concentration was continuously measured in Dazaifu, western Japan, from 1999 to 2020, and its variation was analyzed. Daily
Be activity concentration was continuously measured in Dazaifu, western Japan, from 1999 to 2020, and its variation was analyzed. Daily  Be data analysis, encompassing an analysis for 22 years, revealed a concentration range of not detected - 18 mBq/m
Be data analysis, encompassing an analysis for 22 years, revealed a concentration range of not detected - 18 mBq/m , characterized by substantial monthly variation and smoothed annual variation. An average daily
, characterized by substantial monthly variation and smoothed annual variation. An average daily  Be activity concentration of 5.0
Be activity concentration of 5.0  2.6 mBq/m
2.6 mBq/m was considered to be representative at the ground-surface-level in 30-40
was considered to be representative at the ground-surface-level in 30-40 N. Results from a two-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated statistical significance in monthly and annual
N. Results from a two-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated statistical significance in monthly and annual  Be variabilities. The monthly variability of
Be variabilities. The monthly variability of  Be activity concentration was approximately four times greater than the annual variability. Frequency analysis revealed that the monthly variability comprised major 12-month and minor 6-month periodicities. The substantial decrease in
Be activity concentration was approximately four times greater than the annual variability. Frequency analysis revealed that the monthly variability comprised major 12-month and minor 6-month periodicities. The substantial decrease in  Be activity concentration during summer, a primary driver of monthly variation, was also observed at other locations in Japan, attributed to a stable high-pressure system in the Pacific Ocean that stalled over Japan's southern seas, followed by the inflow of air masses containing low
Be activity concentration during summer, a primary driver of monthly variation, was also observed at other locations in Japan, attributed to a stable high-pressure system in the Pacific Ocean that stalled over Japan's southern seas, followed by the inflow of air masses containing low  Be activity concentrations. The annual variation was primarily influenced by the 11-year solar activity cycle, which affects the intensity of cosmic rays that produce
Be activity concentrations. The annual variation was primarily influenced by the 11-year solar activity cycle, which affects the intensity of cosmic rays that produce  Be.
Be.
 Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network
with a honeycomb networkAdachi, Tadashi*; Ogawa, Taiki*; Komiyama, Yota*; Sumura, Takuya*; Saito-Tsuboi, Yuki*; Takeuchi, Takaaki*; Mano, Kohei*; Manabe, Kaoru*; Kawabata, Koki*; Imazu, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.L100508_1 - L100508_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
 H
H O
OFujihara, Masayoshi; Hagihara, Masato; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014406_1 - 014406_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:82.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) SR studies on copper minerals
SR studies on copper mineralsFujihara, Masayoshi; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Koda, Akihiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.13_1 - 13_6, 2024/12
Quantum states are difficult to observe experimentally. In addition, ideal model materials have not been found for some of the lattice systems in which exotic quantum states are predicted to be realized. Numerous candidates for low-dimensional quantum magnets are hidden in copper minerals, and the number of candidates is increasing every year. We succeeded to synthesize seven copper minerals by imitating the environment where they are discovered and reported their quantum states. The properties of pulsed muons are very suitable for investigating the spin state of artificial copper minerals.
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
Tsutsui, Satoshi; Ito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jin*; Yoshida, Mio*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Koda, Akihiro*; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 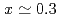
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kanzaki, Norie; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Nihon Onsen Kiko Butsuri Igakukai Zasshi, 16 Pages, 2024/11
Spa therapy in Misasa (Tottori Prefecture, Japan) is renowned worldwide for its radon therapy (particularly high-concentration radon hot-air bath therapy) along with mine therapy in Bad Gastein (Austria) and Montana (USA). Radon therapy is indicated for diseases related to the respiratory system, pain, digestive disorders, chronic degeneration, and aging caused by reactive oxygen species; however, most of these indications are based on empirical prescriptions. To address this, the authors have been conducting basic research to experimentally and mathematically identify significant radon and its progeny exposure pathways and their related behaviors in the body. The aim is to quantitatively evaluate the relationship between the biological reactions caused by radon inhalation and the absorbed doses in tissues and organs, and to elucidate new mechanisms related to these indications. Therefore, the mechanisms are being elucidated in terms of a series of moderate physiological stimuli caused by small amounts of oxidative stress induced by radon inhalation. Specifically, radon inhalation enhances antioxidant, immune regulation, and damage-repair functions; promotes anti-inflammation, hormone secretion, and circulatory metabolism; and induces apoptosis and heat shock proteins. New indications have been suggested, including inflammatory and neuropathic pain, inflammatory edema, gastric mucosal damage, ulcerative colitis, hyperuricemia, type 1 diabetes, liver and kidney damage, transient cerebral ischemia, and depression. Furthermore, combining radon therapy with antioxidants and therapeutic agents has been suggested to synergistically enhance the disease-suppressing effects of the therapy. Further clinical verification of the combined effects of radon therapy and conventional treatments is required to reduce the dosage of drugs that cause severe side effects.
Naoe, Shota*; Tanaka, Ayumi*; Kanzaki, Norie; Takenaka, Reiju*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Miyaji, Takaaki*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*; Kataoka, Takahiro*
Acta Medica Okayama (Internet), 78(5), p.387 - 399, 2024/10
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 59(3), p.109 - 117, 2024/09
International organizations such as WHO and ICRP recommended reference levels with the range of 100 300 Bq/m
300 Bq/m against residential radon exposure. In Japan, indoor radon activity concentration is generally low, and a national plan and reference level have not been set so far. This study aimed to evaluate the risks of indoor radon among Japanese populations and to discuss the effectiveness of an assumed reference level in terms of reduction in the number of lung cancer deaths. The US EPA model was used to calculate lifetime risks and population attributable fractions for ever smokers and never smokers using the recent Japanese-specific information such as demographic data and smoking prevalence. The result indicated that the number of lung cancer deaths was very low (i.e., less than 10 in 2020) among the population exposed to more than 100 Bq/m
against residential radon exposure. In Japan, indoor radon activity concentration is generally low, and a national plan and reference level have not been set so far. This study aimed to evaluate the risks of indoor radon among Japanese populations and to discuss the effectiveness of an assumed reference level in terms of reduction in the number of lung cancer deaths. The US EPA model was used to calculate lifetime risks and population attributable fractions for ever smokers and never smokers using the recent Japanese-specific information such as demographic data and smoking prevalence. The result indicated that the number of lung cancer deaths was very low (i.e., less than 10 in 2020) among the population exposed to more than 100 Bq/m . This means that even if a reference level of 100 Bq/m
. This means that even if a reference level of 100 Bq/m is set, the statistically significant reduction in lung cancer deaths could not be observed. Given the risk evaluation, we believe that expected national actions in Japan are to support individuals who consider taking measures for the own risk perception and control of lifetime risk, rather than to introduce regulations. Comprehensive argument and judgement would also be desired for better public health, based on information on not only radon but also other common modifiable risk factors.
is set, the statistically significant reduction in lung cancer deaths could not be observed. Given the risk evaluation, we believe that expected national actions in Japan are to support individuals who consider taking measures for the own risk perception and control of lifetime risk, rather than to introduce regulations. Comprehensive argument and judgement would also be desired for better public health, based on information on not only radon but also other common modifiable risk factors.
 Be activity concentrations with respect to precipitation
Be activity concentrations with respect to precipitationNarazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 277, p.107432_1 - 107432_7, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Environmental Sciences)Beryllium-7 activity concentrations in the atmosphere and precipitation were continuously measured every day between April 2011 and December 2015 in Dazaifu, western Japan. The measured data were quantitatively analyzed to determine the precipitation-induced variation in  Be activity concentrations. The average concentrations on nonprecipitation and precipitation days were 5.5 and 3.8 mBq/m
Be activity concentrations. The average concentrations on nonprecipitation and precipitation days were 5.5 and 3.8 mBq/m , respectively. This difference of 31% (1.7 mBq/m
, respectively. This difference of 31% (1.7 mBq/m ) on average, was attributable to the washout effect, which was more significant in the summer. Regarding the association between
) on average, was attributable to the washout effect, which was more significant in the summer. Regarding the association between  Be activity concentration and precipitation, the concentration remained at a similar level for the small precipitation amount of
Be activity concentration and precipitation, the concentration remained at a similar level for the small precipitation amount of  5.0 mm/day and showed a decreasing trend (but was insignificant) for the precipitation of 5.0-10.0 mm/day. A significant decrease in the concentration was observed for
5.0 mm/day and showed a decreasing trend (but was insignificant) for the precipitation of 5.0-10.0 mm/day. A significant decrease in the concentration was observed for 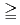 10 mm/day. Furthermore, when precipitation occurred on two successive days, the
10 mm/day. Furthermore, when precipitation occurred on two successive days, the  Be activity concentrations on the second day significantly decreased regardless of precipitation.
Be activity concentrations on the second day significantly decreased regardless of precipitation.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu; Hasan, Md. M.*; Jin, Q.*; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Atmosphere (Internet), 15(6), p.701_1 - 701_12, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:59.73(Environmental Sciences)Building materials such as brick and concrete are known indoor radon ( Rn) and thoron (
Rn) and thoron (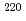 Rn) sources. Most radon and thoron exhalation studies are based on the laboratory testing of pieces and blocks of such materials. To discuss if laboratory findings can be applied to a real-world environment, we conducted intensive in-situ exhalation tests on two solid concrete interior walls of an apartment in Japan for over a year. Exhalation rates of radon (
Rn) sources. Most radon and thoron exhalation studies are based on the laboratory testing of pieces and blocks of such materials. To discuss if laboratory findings can be applied to a real-world environment, we conducted intensive in-situ exhalation tests on two solid concrete interior walls of an apartment in Japan for over a year. Exhalation rates of radon (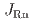 ) and thoron (
) and thoron (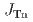 ) were measured by a measurement system, mainly consisting of an accumulation chamber and dedicated monitors. The indoor air temperature (
) were measured by a measurement system, mainly consisting of an accumulation chamber and dedicated monitors. The indoor air temperature ( ) and absolute humidity (
) and absolute humidity (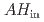 ) were measured in parallel, and the wall-surface temperature and water content were occasionally measured. All data obtained here were investigated to reveal environmental and material-associated factors affecting exhalation from the concrete walls. There were weak correlations between
) were measured in parallel, and the wall-surface temperature and water content were occasionally measured. All data obtained here were investigated to reveal environmental and material-associated factors affecting exhalation from the concrete walls. There were weak correlations between 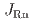 or
or 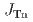 and T or
and T or 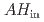 at one tested wall, and moderate correlations of
at one tested wall, and moderate correlations of 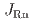 and strong correlations of
and strong correlations of 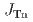 with
with  or
or 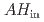 at the other wall. Our findings on
at the other wall. Our findings on 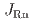 were consistent with those in a previous laboratory work where a concrete sample was subject to various temperatures, although a corresponding laboratory study of
were consistent with those in a previous laboratory work where a concrete sample was subject to various temperatures, although a corresponding laboratory study of 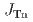 could not be collected. Additionally, moderate or strong correlation between
could not be collected. Additionally, moderate or strong correlation between 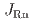 and
and 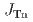 was observed for both tested walls. The comparison of the measured data and theoretical calculations revealed a new issue on how much impact each process of the emanation and migration within concrete pore spaces has on radon and thoron exhalation. This study provides an insight into parameterizing radon and thoron source inputs in modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of indoor radon and thoron.
was observed for both tested walls. The comparison of the measured data and theoretical calculations revealed a new issue on how much impact each process of the emanation and migration within concrete pore spaces has on radon and thoron exhalation. This study provides an insight into parameterizing radon and thoron source inputs in modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of indoor radon and thoron.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu; Jin, Q.*; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 207, p.111180_1 - 111180_8, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.80(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The impacts of mathematical models and associated parameters on radon ( Rn) and thoron (
Rn) and thoron (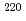 Rn) exhalation rates based on in-situ testing at building interior solid walls were demonstrated to improve data analysis techniques. The results showed that the heterogeneity of their activity concentrations within the measurement system was more significant for thoron than radon. The diurnal variation in indoor radon should be considered for better data quality. In conclusion, a model should be appropriately made and selected under the purposes and accuracy requirements of the exhalation test.
Rn) exhalation rates based on in-situ testing at building interior solid walls were demonstrated to improve data analysis techniques. The results showed that the heterogeneity of their activity concentrations within the measurement system was more significant for thoron than radon. The diurnal variation in indoor radon should be considered for better data quality. In conclusion, a model should be appropriately made and selected under the purposes and accuracy requirements of the exhalation test.
 inferred from muon study
inferred from muon studyKadono, Ryosuke*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Koda, Akihiro*; Ito, Takashi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285503_1 - 285503_13, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.32(Physics, Condensed Matter)Nakajima, Junya; Hirota, Seiko*; Tsuji, Tomoya; Watanabe, Yuki; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kobayashi, Noriko*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(1), p.13 - 20, 2023/04
no abstracts in English
Oishi, Kazuki*; Igarashi, Daisuke*; Tatara, Ryoichi*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Suzuki, Junichi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komaba, Shinichi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012048_1 - 012048_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)
 H
H O
OFujihara, Masayoshi; Hagihara, Masato; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Murai, Naoki; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review B, 107(5), p.054435_1 - 054435_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:37.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The  = 1/2 Heisenberg linear chain antiferromagnet is the simplest spin model; nevertheless it serves as a platform for various quantum many-body phenomena. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of a quasi-one-dimensional antiferromagnet KCuPO
= 1/2 Heisenberg linear chain antiferromagnet is the simplest spin model; nevertheless it serves as a platform for various quantum many-body phenomena. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of a quasi-one-dimensional antiferromagnet KCuPO
 H
H O. A long-range commensurate antiferromagnetic order with ordered moment 0.31(1)
O. A long-range commensurate antiferromagnetic order with ordered moment 0.31(1) 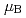 per spin occurs at
per spin occurs at 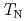 = 11.7(1) K. Above
= 11.7(1) K. Above 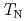 , the inelastic neutron excitation is characterized by a two spinon continuum. The intrachain interaction
, the inelastic neutron excitation is characterized by a two spinon continuum. The intrachain interaction  and interchain interaction
and interchain interaction 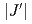 are estimated to be 172 K and 4.25(4) K, respectively; thus the ratio of the
are estimated to be 172 K and 4.25(4) K, respectively; thus the ratio of the 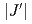 /
/ = 0.0247(3). At lower energies, below
= 0.0247(3). At lower energies, below 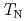 , a spin gap is observed in the dispersive excitations. These results are consistent with characteristics observed in weakly interacting
, a spin gap is observed in the dispersive excitations. These results are consistent with characteristics observed in weakly interacting  = 1/2 Heisenberg chain system.
= 1/2 Heisenberg chain system.
Di Palma, A.; Adamo, P.*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Sakoda, Akihiro; Sato, Kazuhiko; Iijima, Kazuki
Chemosphere, 308, Part 1, p.136179_1 - 136179_13, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.93(Environmental Sciences)The present study shows the use of mosses transplanted in bags, called as moss bags, as biosensors of airborne radioactive dusts in the environment of the evacuated zone of Fukushima. A standardized protocol was applied and three moss species were used. Background sites of Okayama Prefecture were used for comparison. In the Fukushima area, the moss bags were able to accumulate radiocaesium in all exposure sites and periods, with Sphagnum palustre moss acting as the most performant moss. The radiocaesium activity concentrations dectected in mosses were in strong agreement with the Cs deposition levels and decontamination status of each exposure site. The accumulation of soil-derived radiocaesium by moss bags was supported by autoradiography and electron microscopy analyses. The linear dependency of Cs accumulation with the exposure time allowed a radiocaesium quantitative assessment.
 Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg
O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain
chainFujihara, Masayoshi; Jeschke, H. O.*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114408_1 - 114408_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)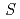 = 1/2 Heisenberg
= 1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd
chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and
O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and  SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the
SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the 
 -
-
 antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions
antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions 
 and
and 
 are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of
are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of 
 is two to three times larger than that of
is two to three times larger than that of 
 , thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of
, thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of 
 . The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K (
. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K ( 0.036
0.036 
 ), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.