Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Uzawa, Akiko*; Takase, Nobuhiro*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Noguchi, Miho; Koda, Kana*; Ozaki, Masakuni*; Yamashita, Kei*; Li, H.*; Kase, Yuki*; et al.
Mutation Research; Genetic Toxicology And Environmental Mutagenesis, 756(1-2), p.146 - 151, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:63.98(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology) -Al
-Al O
O on the oxidation of xylene in air at low temperature under electron-beam irradiation
on the oxidation of xylene in air at low temperature under electron-beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, 4(1), p.65 - 70, 2010/03
The catalytic effect of Pt/Al O
O and Ag/Al
and Ag/Al O
O on the oxidation of xylene in air was studied at a constant temperature of 373 K, when they were combined with electron-beam (EB)-induced non-thermal plasmas (NTPs). The presence of a catalyst bed was found to enhance the oxidation of the irradiation products of xylene. However, the degree of catalytic oxidation was different depending on the type of loaded metal and the position of the catalyst bed. Compared with a Al
on the oxidation of xylene in air was studied at a constant temperature of 373 K, when they were combined with electron-beam (EB)-induced non-thermal plasmas (NTPs). The presence of a catalyst bed was found to enhance the oxidation of the irradiation products of xylene. However, the degree of catalytic oxidation was different depending on the type of loaded metal and the position of the catalyst bed. Compared with a Al O
O bed, a Pt/Al
bed, a Pt/Al O
O bed in the NTP space suppressed oxidation, while an Ag/Al
bed in the NTP space suppressed oxidation, while an Ag/Al O
O bed downstream of the NTP space enhanced it. Under low temperature conditions, Pt/Al
bed downstream of the NTP space enhanced it. Under low temperature conditions, Pt/Al O
O was not a suitable catalyst for the oxidation of organics in combination with the NTP process. On the other hand, the Ag/Al
was not a suitable catalyst for the oxidation of organics in combination with the NTP process. On the other hand, the Ag/Al O
O catalyst was a preferable catalyst for the NTP-induced oxidation of organics under such low temperature conditions.
catalyst was a preferable catalyst for the NTP-induced oxidation of organics under such low temperature conditions.
 Surface in the oxidation of xylene in air using an electron beam irradiation/catalytic process
Surface in the oxidation of xylene in air using an electron beam irradiation/catalytic processHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
Applied Catalysis A; General, 357(2), p.244 - 249, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:36.58(Chemistry, Physical)Catalytic oxidation of xylene in air was performed under electron beam (EB) irradiation using pure TiO as well as TiO
as well as TiO loaded with Ag, Pt, Au, and Mn to clarify the role of loaded metal in the enhancement of oxidation of xylene and its irradiation byproducts to CO
loaded with Ag, Pt, Au, and Mn to clarify the role of loaded metal in the enhancement of oxidation of xylene and its irradiation byproducts to CO in EB-induced non-thermal plasma. EB irradiation experiments were performed with the catalyst bed placed in both irradiated and non-irradiated spaces. The highest conversion percentage of decomposed xylene to CO
in EB-induced non-thermal plasma. EB irradiation experiments were performed with the catalyst bed placed in both irradiated and non-irradiated spaces. The highest conversion percentage of decomposed xylene to CO was obtained by irradiation/catalytic oxidation using an Ag/TiO
was obtained by irradiation/catalytic oxidation using an Ag/TiO bed placed in a non-irradiated space. The greater enhancement of CO
bed placed in a non-irradiated space. The greater enhancement of CO production on an Ag/TiO
production on an Ag/TiO pellet surface compared to that on other metal-loaded TiO
pellet surface compared to that on other metal-loaded TiO pellet surfaces was due to the synergetic effect of strong adsorption of the byproducts on the Ag loaded on TiO
pellet surfaces was due to the synergetic effect of strong adsorption of the byproducts on the Ag loaded on TiO and production of active oxygen from decomposition of O
and production of active oxygen from decomposition of O in the presence of Ag.
in the presence of Ag.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Hirota, Koichi
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 29(1), p.69 - 78, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.03(Engineering, Chemical)Electron beam (EB) technology has an advantage for treating dilute environmental pollutants in gases due to high-density population of active species such as radicals and atoms. In general, OH radicals play an important role of initiating the decomposition and removal of such pollutants. It is quite important to understand the behavior of OH radical production for the development of efficient decomposition/removal processes and the comparison with other purification methods. The number of OH radicals produced in humid N at doses of 2.0-10.0 kGy with dose rates of 0.17-2.55 kGy/s under 1-MeV EB irradiation was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO
at doses of 2.0-10.0 kGy with dose rates of 0.17-2.55 kGy/s under 1-MeV EB irradiation was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO , which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. An experiment under conditions where all OH radicals produced react with CO demonstrated that the concentration of CO
, which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. An experiment under conditions where all OH radicals produced react with CO demonstrated that the concentration of CO increased linearly with doses of 0-10 kGy, and the
increased linearly with doses of 0-10 kGy, and the 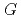 (OH) was estimated as 4.90.
(OH) was estimated as 4.90.
 under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Mizuno, Akira*; Narita, Tadashi*; Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi
IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 44(6), p.1950 - 1956, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:33.47(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Oxidation of xylene and its irradiation-induced organic byproducts in air using Ag-loaded TiO (Ag/TiO
(Ag/TiO ) beds was studied under electron beam (EB) irradiation. The Ag/TiO
) beds was studied under electron beam (EB) irradiation. The Ag/TiO beds were placed in an irradiation or a non-irradiation space in order to identify the oxidation of xylene/its byproducts by EB irradiation, by catalytic process, and by a combination of the two. Placement of the Ag/TiO
beds were placed in an irradiation or a non-irradiation space in order to identify the oxidation of xylene/its byproducts by EB irradiation, by catalytic process, and by a combination of the two. Placement of the Ag/TiO bed to the irradiation space resulted in the suppression of xylene decomposition. On the other hand, production of CO
bed to the irradiation space resulted in the suppression of xylene decomposition. On the other hand, production of CO was observed in the gas phase of the irradiation space and on the surface of the Ag/TiO
was observed in the gas phase of the irradiation space and on the surface of the Ag/TiO pellets placed both in the irradiation and non-irradiation spaces. The concentration of CO
pellets placed both in the irradiation and non-irradiation spaces. The concentration of CO became higher when the layer was placed in the non-irradiation space. The production of CO
became higher when the layer was placed in the non-irradiation space. The production of CO was enhanced by loading of Ag to the TiO
was enhanced by loading of Ag to the TiO pellet surface. The highest concentration of CO
pellet surface. The highest concentration of CO was obtained for Ag/TiO
was obtained for Ag/TiO with Ag contents greater than 5wt%.
with Ag contents greater than 5wt%.
 -Al
-Al O
O bed
bedHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 41(15), p.155202_1 - 155202_7, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.97(Physics, Applied)The oxidation of xylene and its irradiation byproducts in air using a  -Al
-Al O
O bed was studied under electron-beam irradiation to enhance the decomposition of volatile organic compounds in ventilation gases emitted from paint factories. The use of the
bed was studied under electron-beam irradiation to enhance the decomposition of volatile organic compounds in ventilation gases emitted from paint factories. The use of the  -Al
-Al O
O bed enhanced the oxidation of the irradiation byproducts to CO
bed enhanced the oxidation of the irradiation byproducts to CO . Furthermore, the oxidation of the byproducts was accelerated by the placement of the
. Furthermore, the oxidation of the byproducts was accelerated by the placement of the  -Al
-Al O
O bed in an irradiation space, because of the interaction of primary electrons with the surface of
bed in an irradiation space, because of the interaction of primary electrons with the surface of  -Al
-Al O
O pellets. This combined oxidation process enabled a reduction in the energy consumption for non-toxic CO
pellets. This combined oxidation process enabled a reduction in the energy consumption for non-toxic CO formation, and improved the selectivity of CO
formation, and improved the selectivity of CO production.
production.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Shimada, Akihiko; Narita, Tadashi*; Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(5), p.585 - 590, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.27(Chemistry, Physical)The electron beam (EB) oxidation of gaseous xylene in air, appearing as ventilation gases emitted from painting factories, was investigated under various experimental conditions. Thereby the implementation of an ozone decomposition catalyst, MnO , into EB-induced oxidation of xylene/air mixtures strongly contributed in the achievement of a better purification degree.
, into EB-induced oxidation of xylene/air mixtures strongly contributed in the achievement of a better purification degree.
 under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Mizuno, Akira*; Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 28(1), p.25 - 37, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:61.98(Engineering, Chemical)The oxidation of xylene and its irradiation byproducts in air using TiO was studied under electron beam (EB) irradiation for the purification of ventilation gases emitted from paint factories. EB irradiation experiments were performed mainly under two different conditions: a TiO
was studied under electron beam (EB) irradiation for the purification of ventilation gases emitted from paint factories. EB irradiation experiments were performed mainly under two different conditions: a TiO pellet layer was placed in an irradiation or non-irradiation space. The results revealed that xylene was decomposed and CO was formed in the gas phase of the irradiation space irrespective of the presence of the TiO
pellet layer was placed in an irradiation or non-irradiation space. The results revealed that xylene was decomposed and CO was formed in the gas phase of the irradiation space irrespective of the presence of the TiO pellets, while CO
pellets, while CO was produced in the gas phase of the irradiation space and on the surface of the TiO
was produced in the gas phase of the irradiation space and on the surface of the TiO pellets. The total CO
pellets. The total CO concentration increased when the pellet layer was in the non-irradiation space. On the other hand, the concentration of CO
concentration increased when the pellet layer was in the non-irradiation space. On the other hand, the concentration of CO produced on the surface of the TiO
produced on the surface of the TiO pellets in the irradiation space was higher than that in a non-irradiation space.
pellets in the irradiation space was higher than that in a non-irradiation space.
 -Al
-Al O
O
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 catalyst
catalystMatsumoto, Kanae; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Narita, Tadashi*; Kojima, Takuji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Al
-Al O
O under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationMatsumoto, Kanae; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi; Narita, Tadashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 and Ag/TiO
and Ag/TiO
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Mizuno, Akira*; Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Noguchi, Miho; Uzawa, Akiko*; Koda, Kana*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*
no journal, ,
The presence or absence of molecular oxygen dramatically influences the biological effect of low LET radiations. To produce oxygen effect, molecular oxygen must be present during the radiation exposure or at least during the lifetime of the free radicals generated by the radiation. Little study has been done to actually investigate the influence of oxygen after the radiation exposure. The present study was undertaken in order to explore the rejoining activity of DNA-DSB induced by anaerobic X-ray or carbon ion ( 80 keV/
80 keV/ m) irradiations under oxic and hypoxic holdings (37
m) irradiations under oxic and hypoxic holdings (37  C). DNA-DSB in CHO cells were analyzed by a static-field gel electrophoresis. The kinetics of the rejoining could be described by a sum of fast and slow components. The slow component of DNA-DSB induced by X-ray under oxic incubation was faster than that under hypoxic incubation. Furthermore, the percentages of non-reparable DNA damage were 5% and 20% under oxic and hypoxic incubation conditions, respectively. However, no difference between oxic and hypoxic incubation conditions was found for carbon ion irradiation. There results indicate that molecular oxygen influences the rejoining of DNA-DSB after low LET radiation exposure.
C). DNA-DSB in CHO cells were analyzed by a static-field gel electrophoresis. The kinetics of the rejoining could be described by a sum of fast and slow components. The slow component of DNA-DSB induced by X-ray under oxic incubation was faster than that under hypoxic incubation. Furthermore, the percentages of non-reparable DNA damage were 5% and 20% under oxic and hypoxic incubation conditions, respectively. However, no difference between oxic and hypoxic incubation conditions was found for carbon ion irradiation. There results indicate that molecular oxygen influences the rejoining of DNA-DSB after low LET radiation exposure.
 and Ag/TiO
and Ag/TiO under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Kanae; Shimada, Akihiko; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Narita, Tadashi*; Kojima, Takuji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 series catalyst under electron beam irradiation
series catalyst under electron beam irradiationMatsumoto, Kanae; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Narita, Tadashi*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae; Ito, Hisayoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 under electron beam irradiation
under electron beam irradiationMatsumoto, Kanae; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Ito, Hisayoshi; Kojima, Takuji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English