Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kusumoto, Tamon*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Baba, Kentaro*; Ogawara, Ryo*; Akselrod, M. S.*; Harrison, J.*; Fomenko, V.*; Kai, Takeshi; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Hasegawa, Sumitaka*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 132, p.106256_1 - 106256_4, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)Internal radiation therapy with Cu-64 concentrates energy deposition in tumor cells by virtue of released Auger electrons with low energy. In our previous study, we have attached the solutions at the surface of Fluorescent Nuclear Track Detector (FNTD) and succeeded in measuring the absorbed doses of Auger electrons registered in FNTD. However, because there are several types of radiation emitted from the source, i.e., beta rays, positron etc., the contribution degree of Auger electron to energy concentration remain uncertain. In this study, we quantitatively analyzed the spatial dose distribution in the FNTD based on Monte Carlo simulation with PHITS and GEANT4, and evaluated high dose deposited by Auger electrons. The dose distribution calculated by the PHITS code is exactly equivalent to that by Geant4. Also, the simulations are well agreement with experimental results. If the contribution of Auger electrons is ignored, the significantly high absorbed dose proximal to the source is not properly reduced. These findings demonstrate that Auger electrons work very effectively to kill cancer cells proximal to Cu-64 source while minimizing damage effects on normal cells distal to the source.
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Suzuki, Masatoshi; Kodaira, Tsuneo; Ebisawa, Toru*; ; Tasaki, Seiji*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.951 - 953, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.14(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Hosogane, Tatsuya; Ishikawa, Fumitaka; Kageyama, Tomio; Kayano, Masashi; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Kurano, Mieko*
no journal, ,
For the safe design of MOX fuel, plutonium (Pu) spot analysis is an important control point, thus maximum diameter and Pu content of the Pu spot is defined as MOX fuel specification. Diameter and Pu content of the Pu spot has been analyzed by detecting Pu spot from pictures taken by alpha-autoradiography using commercial imaging analysis software and measure its diameter and content by hand work. Because this method requires a lot of work, automatic detection and measurement system for the Pu spot diameter and Pu content was developed to save workload.
Chiba, Satoshi; Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Projectile charge-changing cross sections for nuclei in galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) on hydrogen play essentially important roles for the study of origin and source composition of GCRs. Previous experimental and theoretical works done so far made much progress on those cross sections. However, there are still uncertainties in much of the cross section data, and therefore the present knowledge of cross sections has not led to successful determination of the GCR source composition. To improve the uncertainties, a novel measurement system of projectile charge-changing cross section using CR-39 plastic nuclear track detectors with excellent position and nuclear charge resolutions has been developed. We carried out measurements of total and partial charge-changing cross sections for Fe and Mg on 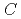 and
and 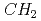 targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
Kodaira, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Hosogane, Tatsuya; Ishikawa, Fumitaka; Kageyama, Tomio; Sato, Mitsuhiro
no journal, ,
The plutonium-thermal use is expected as one of the approach for reuse of spent uranium fuel in nuclear power generation. On the other hand, many kinds of nuclides including Pu with extremely long half-lives are generated in the used fuels, which would be problems for storage and control of radioactive waste. The MOX (Mixed Oxide) consisting of plutonium dioxide enriched with 4-9% Pu and uranium oxide from spent uranium fuel would allow to reduce half-lives of radioactive waste significantly through the nuclear fission. The quality of MOX pellet depends on the homogeneous dispersion of Pu. The region of highly concentrated Pu is sometimes observed as "Pu spot" in the pellet, which has the potential of anomalous combustion localized at that region. The detection of Pu spot and evaluation of its size and concentration are one of the important quality assurance of MOX pellet for the safety use in the nuclear power plant. We have applied CR-39 plastic nuclear track detectors for the measurement of Pu spot inside MOX pellet. CR-39 can image a cross-section of MOX pellet by recording  -particle tracks from Pu in the pellet, like autoradiography. The Pu spot is visibly imaged as a "black spot" due to the dense
-particle tracks from Pu in the pellet, like autoradiography. The Pu spot is visibly imaged as a "black spot" due to the dense  tracks compared to homogeneously dispersed region. Conventionally, the Pu spot measurement has been carried out with manual scanning, which takes much longer times and huge amount of human work. We have developed the automatic detection and measurement system of Pu spot recorded on CR-39 by the image processing with filtering and clustering algorithms. The detection efficiency with CR-39 is achieved to be almost 100% compared with conventional manual scanning result. It provides more information about the number, size and position of Pu spot.
tracks compared to homogeneously dispersed region. Conventionally, the Pu spot measurement has been carried out with manual scanning, which takes much longer times and huge amount of human work. We have developed the automatic detection and measurement system of Pu spot recorded on CR-39 by the image processing with filtering and clustering algorithms. The detection efficiency with CR-39 is achieved to be almost 100% compared with conventional manual scanning result. It provides more information about the number, size and position of Pu spot.