Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koga, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Kazunori*; Takagi, Tsuyohiko; Hamano, Tomoharu
FAPIG, (196), p.8 - 15, 2020/01
The prototype fast breeder reactor Monju has already started (from June 2017) the unloading operation period (about 5.5 years: until the end of 2022) of the fuel assembly, which is the first stage of decommission. Among them, the first "Processing of fuel assembly" operation (86 in total) was conducted from August 2018 to January 2019 as the first handling of the fuel assembly. Fuji Electric provided technical support, such as dispatching technicians throughout the period, in cooperation with Japan Atomic Energy Agency for the "Processing of fuel assembly" operation, and contributed to the completion of the operation while experiencing various troubles. This manuscript introduces the contents of the first "Processing of fuel assembly" operation and the overview of the trouble status. This manuscript is a sequel to FAPIG No.194 "Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor Monju Decommissioning and Unloading Operation of the Fuel Assembly from the Core", please refer to it.
Koga, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Kazunori*; Hamano, Tomoharu; Takagi, Tsuyohiko
FAPIG, (194), p.6 - 11, 2018/02
The prototype fast breeder reactor "Monju" was decided to decommission by Japanese government on 21 December 2016. After that, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) submitted "Monju decommissioning basic plan" to MEXT (Charge ministry) on 13 June 2017, then the unloading operation period (about 5.5 years) of the fuel assembly, which is the first stage of decommission, has started. Fuji Electric is proceeding with various preparations in cooperation with JAEA for the safe work of the unloading operation. This manuscript introduces the outline of preparation situation such as maintenance and inspection for the unloading operation.
Ashida, Takashi; Ito, Hideaki; Miyamoto, Kazuyuki*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki; Koga, Kazuhiro*; Ohara, Norikazu*; Ino, Hiroichi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(4), p.210 - 222, 2016/12
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, it was confirmed that the top of the irradiation test sub-assembly of material testing rig named "MARICO-2" had been broken and bent onto the in-vessel storage rack as an obstacle and had damaged the upper core structure (UCS). As the result, for Joyo restart, it was necessary to replace the damaged UCS and to retrieve the bent sub-assembly. This paper describes in-vessel repair techniques performed in the retrieval work of the obstacle inside of the reactor vessel. The devices which were prepared for this work demonstrated expected performance under the environmental conditions of an SFR such as high temperature and radiation dose, and the work was completed in 2014. The successful operation of this retrieval work of the damaged component inside of a reactor vessel will contribute to the development of in-service inspections and repair technics in an SFR.
Koga, Kazuhiro*; Ohara, Norikazu*; Ino, Hiroichi*; Kondo, Katsumi*; Ito, Hideaki; Ashida, Takashi; Nakamura, Toshiyuki
FAPIG, (190), p.3 - 8, 2015/07
no abstracts in English
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.68(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 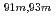 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Kato, Atsushi; Obata, Hiroyuki*; Uzawa, Masayuki*; Koga, Kazuhiro*; Chishiro, Ryo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(4), p.437 - 447, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)A simplified fuel handling system design for the demonstration JSFR has been proposed. FaCT phase I results of key technology evaluations on a pantograph fuel handling machine, a fuel transfer pot with two core component positions, dry spent fuel cleaning and minor actinide-bearing fresh fuel shipping cask are being developed. Experimental and analytical efforts have shown that key technologies to develop simplified fuel handling system are matured enough to proceed large scale sodium experiments and conceptual design study for the demonstration JSFR.
Shibata, Takanori; Koga, Shojiro*; Terasaki, Ryo*; Inoue, Takashi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Umeda, Naotaka; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02A719_1 - 02A719_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.70(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the NBI for large fusion devices, production of uniform negative ion beam is one of important issues. A physical model is proposed to understand the non-uniformity. It has been qualitatively shown that the non-uniform beam intensity is due to the following process; (1) formation of non-uniform EEDF, (2) localized production of hydrogen atoms/ions (H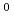 /H
/H ) due to (1), (3) non-uniform flux of H
) due to (1), (3) non-uniform flux of H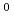 /H
/H to the PG and (4) localized surface production of negative ions. However, in the past studies, the EEDF was assumed as two temperature Maxwellian distribution from measurements. Thus effects of high energy electrons are not taken into account precisely. In the present research, local EEDF is calculated by the 3D Monte-Carlo kinetic model which takes into account the spatial and magnetic configurations of the real negative ion source. The numerical result show that high energy component of the EEDF enhances the spatial non-uniformity in the production rate of H
to the PG and (4) localized surface production of negative ions. However, in the past studies, the EEDF was assumed as two temperature Maxwellian distribution from measurements. Thus effects of high energy electrons are not taken into account precisely. In the present research, local EEDF is calculated by the 3D Monte-Carlo kinetic model which takes into account the spatial and magnetic configurations of the real negative ion source. The numerical result show that high energy component of the EEDF enhances the spatial non-uniformity in the production rate of H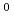 /H
/H .
.
Koga, J. K.; Moribayashi, Kengo; Fukuda, Yuji; Bulanov, S. V.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Kimura, Toyoaki*; Fujikawa, Taketoshi*; et al.
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 43(2), p.025204_1 - 025204_15, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:58.75(Physics, Applied)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Attallah, M. F.*; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Towards electrolytic reduction of Sg, batch-wise electrolytic reduction of carrier-free  Mo and
Mo and 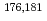 W radiotracers was studied using a flow electrolytic column (FEC). The electrolyzed samples from a FEC were chemically analyzed by solvent extraction with TOA and HDEHP to separate and identify reduced species from the stable Mo(VI) and W(VI) ones based on their different extraction behavior.
W radiotracers was studied using a flow electrolytic column (FEC). The electrolyzed samples from a FEC were chemically analyzed by solvent extraction with TOA and HDEHP to separate and identify reduced species from the stable Mo(VI) and W(VI) ones based on their different extraction behavior.  Mo and
Mo and 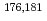 W were applied as radiotracers. We also performed cyclic voltammetry and UV/Vis absorption spectrometry of macro amounts of Mo and W in acidic solutions to obtain information on redox reactions of these elements under given conditions. In the conference, the present status of the preparatory reduction experiments with Mo and W will be presented.
W were applied as radiotracers. We also performed cyclic voltammetry and UV/Vis absorption spectrometry of macro amounts of Mo and W in acidic solutions to obtain information on redox reactions of these elements under given conditions. In the conference, the present status of the preparatory reduction experiments with Mo and W will be presented.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Ogura, Koichi; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Ragozin, E. N.*; Neely, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Asai, Masato; Attallah, M. F.*; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Kaneko, Masashi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Due to short half-lives less than 10 s and extremely low production rates, transactinide elements heavier than seaborgium (Sg) are produced on an atom per hour scale. Therefore, a continuous rapid chemistry assembly is required to study aqueous-phase chemistry of these heaviest elements. In the present study, we started developments of a continuous chemistry assembly. Our first attempt was made in on-line experiments with Mo and W, lighter homologs of Sg, to optimize a chemistry assembly consisting of a newly developed membrane degasser as an interface between gas-jet and aqueous phase, a flow electrolytic column apparatus utilized to control oxidation states of Mo and W ions, and the continuous liquid-liquid extraction apparatus of SISAK for separation. In the conference, present status of the developments will be presented.
Rekimoto, Masafumi; Ando, Masato; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Kato, Atsushi; Hamano, Tomoharu; Shiohama, Yasutaka; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uzawa, Masayuki*; Hara, Hiroyuki*; Yamauchi, Kanau*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Koga, J. K.; Moribayashi, Kengo; Fukuda, Yuji; Bulanov, S. V.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Kimura, Toyoaki; Fujikawa, Taketoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Rekimoto, Masafumi; Hamano, Tomoharu; Shiohama, Yasutaka; Ando, Masato*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Hara, Hiroyuki*; Yamauchi, Kanau*; Eda, Yuhei*; Koga, Kazuhiro*; Tanabe, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Otobe, Tomohito; Koga, J. K.; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
no journal, ,
The interaction between laser and matter has been studied intensively. Recently, new approaches to probe of matter with intense laser are discussed. However, only the analytical approaches have been reported on theoretical studies. We solve the time-dependent Khon-Sham equation with real-time and real-space method and apply to laser-matter interaction for the first time.
Otobe, Tomohito; Koga, J. K.; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
no journal, ,
We show the simulation for interaction between intense laser field and dielectrics by solving Time-dependent Khon-Sham equation which is the fundamental equation of Time-Dependent density functional theory. As a first step, we show that this approach can describe the dielectric breakdown of diamond. As a next step, we shows the change of the dielectric function after the intense laser field. Furthermore, we found that the angular dependence of electron excitation rate has information about the band structure.
Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Moribe, Takeshi; Koga, Kazuhiro*
no journal, ,
In accordance with the revision of "Regulatory guide for seismic design of nuclear power plants", the seismic safety assessment of the prototype fast breeder reactor "Monju" was carried out based on the revised guide. In this report, the sloshing in the fuel pool is simulated by the MPS method and the overflow from the pool is evaluated.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Kitayama, Yuta*; Lerum, H. V.*; Goto, Naoya*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Komori, Yukiko*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Vascon, A.; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ashida, Takashi; Sakata, Hideaki; Miyamoto, Kazuyuki; Nakamura, Toshiyuki; Ito, Hideaki; Tobita, Koichi; Koga, Kazuhiro*; Ohara, Norikazu*; Ino, Hiroichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Ogura, Koichi; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Ragozin, E. N.*; Neely, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,