Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
Electrochemical study of mendelevium (Md) with flow electrolytic column chromatography is presented. The  Md isotope was produced in the
Md isotope was produced in the  Cm(
Cm( B, 4
B, 4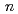 ) reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator. In applying a negative voltage on the column electrode, Md was eluted with 0.1 M HCl. This behavior is quite similar to that of Sr
) reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator. In applying a negative voltage on the column electrode, Md was eluted with 0.1 M HCl. This behavior is quite similar to that of Sr and Eu
and Eu , clearly indicating that most stable Md
, clearly indicating that most stable Md is reduced to Md
is reduced to Md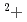 . We determined the redox potential of Md to be approximately -0.18 V versus a standard hydrogen electrode.
. We determined the redox potential of Md to be approximately -0.18 V versus a standard hydrogen electrode.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Oe, Kazuhiro; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
Redox potential of mendelevium (Md) was determined with flow electrolytic chromatography. Mendelevium-255 with a half-life of 27 min was produced in the  Cm(
Cm( B, 4
B, 4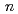 ) reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator. Reaction products transported by a KCl/He gas-jet method were collected on a chemistry apparatus. After removing KCl with HDEHP column chromatography, elution behavior of Md in 0.10 M HCl was investigated with a flow electrolytic column apparatus at the applied potentials between -0.3 and -0.6 V vs. a Ag/AgCl reference electrode. At -0.3 V, elution behavior of Md was the same as that of
) reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator. Reaction products transported by a KCl/He gas-jet method were collected on a chemistry apparatus. After removing KCl with HDEHP column chromatography, elution behavior of Md in 0.10 M HCl was investigated with a flow electrolytic column apparatus at the applied potentials between -0.3 and -0.6 V vs. a Ag/AgCl reference electrode. At -0.3 V, elution behavior of Md was the same as that of 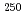 Bk
Bk , showing that the stable Md
, showing that the stable Md was not reduced to the divalent state. At -0.6 V, elution of Md was quite similar to that of Sr
was not reduced to the divalent state. At -0.6 V, elution of Md was quite similar to that of Sr , demonstrating that Md
, demonstrating that Md was successfully reduced to Md
was successfully reduced to Md . From the behavior of Md against the applied potentials, we evaluated its redox potential to be -0.40
. From the behavior of Md against the applied potentials, we evaluated its redox potential to be -0.40 0.03 V.
0.03 V.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Takahiro*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
no journal, ,
The redox behavior of mendelevium (Md) was studied with flow electrolytic chromatography. The  Md isotope produced in the
Md isotope produced in the  Cm(
Cm( B, 4n)
B, 4n) Md reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator was used in the electrolytic reduction experiment with the flow electrolytic column apparatus in 0.1 M HCl. It was clearly observed that, applying appropriate potentials on the chromatography column, the most stable Md
Md reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator was used in the electrolytic reduction experiment with the flow electrolytic column apparatus in 0.1 M HCl. It was clearly observed that, applying appropriate potentials on the chromatography column, the most stable Md is reduced to Md
is reduced to Md . The redox potential of the Md
. The redox potential of the Md = Md
= Md + e
+ e couple was determined to be -0.16
couple was determined to be -0.16  0.05 V vs. a normal hydrogen electrode.
0.05 V vs. a normal hydrogen electrode.
Sch del, M.; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
del, M.; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,