Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koike, Fumihiro*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kato, Takako*; Morita, Shigeru*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Sudo, Shigeru*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.202 - 211, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:83.55(Physics, Applied)Atomic ionic states and transition properties of elements with atomic numbers Z ranging from 50 to 80 are discussed as these are important to the understanding of plasmas containing such heavy elements. As such, data productions and the current status of theoretical calculations in this field are discussed. Further, recent spectroscopic measurements and respective theoretical analyses for W, Gd, and Nd are provided.
Morita, Shigeru*; Dong, C. F.*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Hasuo, Masahiro*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Nakamura, Nobuyuki*; Oishi, Tetsutaro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.143 - 152, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:99.13(Physics, Applied)Tungsten spectra have been observed from Large Helical Device (LHD) and Compact electron Beam Ion Trap (CoBIT) in wavelength ranges of visible to EUV. The tungsten spectra from LHD are well analyzed based on the knowledge from CoBIT tungsten spectra. The C-R model code has been developed to explain the UTA spectra in details. Radial profiles of EUV spectra from highly ionized tungsten ions have been measured and analyzed by impurity transport simulation code with ADPAK atomic database code to examine the ionization balance determined by ionization and recombination rate coefficients. The ablation cloud of the impurity pellet is directly measured with visible spectroscopy.
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6(Sp.1), p.2401145_1 - 2401145_4, 2011/12
Atomic processes and radiation from multiple charged ions in plasmas are of the interest in the investigation of plasma wall interaction and transport of impurity ions in the fusion devices. The emission from multiple charged ions is also investigated for the development of extreme ultra violet light (EUVL) sources at 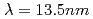 . Efficient emission through the 4d-4f + 4p-4d transition array is obtained from tin ions. An optimization of pumping conditions of laser produced plasma sources is carried out theoretically and experimentally. We also investigate an extension of the plasma light sources to short wavelength to
. Efficient emission through the 4d-4f + 4p-4d transition array is obtained from tin ions. An optimization of pumping conditions of laser produced plasma sources is carried out theoretically and experimentally. We also investigate an extension of the plasma light sources to short wavelength to 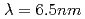 using Gd and Tb plasmas. We discuss requirements to the atomic structure, rate coefficient and collisional radiative codes to determine ion abundance and level population as a function of plasma temperature and density, to calculate the radiation intensity as well as emission spectrum.
using Gd and Tb plasmas. We discuss requirements to the atomic structure, rate coefficient and collisional radiative codes to determine ion abundance and level population as a function of plasma temperature and density, to calculate the radiation intensity as well as emission spectrum.
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*
Applied Physics Letters, 97(23), p.231501_1 - 231501_3, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:52.65(Physics, Applied)Emission spectrum and conversion efficiency of laser produced terbium plasmas are investigated theoretically on the basis of computational atomic data. It is shown that calculation reproduces the main peak of the experimental spectrum at 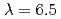 nm, which originates from 4
nm, which originates from 4 -4
-4 transitions of near palladium like ions (Tb
transitions of near palladium like ions (Tb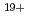 ). Simple model of the isothermal expansion of plasma suggests that efficient emission can be obtained by pumping a plasma with a laser pulse with an intensity approximately one order of magnitude grater than in the case of tin sources at
). Simple model of the isothermal expansion of plasma suggests that efficient emission can be obtained by pumping a plasma with a laser pulse with an intensity approximately one order of magnitude grater than in the case of tin sources at 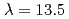 nm.
nm.
Sasaki, Akira; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Ohashi, Hayato*; Tanuma, Hajime*
Journal of Applied Physics, 107(11), p.113303_1 - 113303_11, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:82.26(Physics, Applied)Atomic processes in Sn plasmas are investigated for application to extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) light sources used in microlithography. An atomic model of Sn is developed on the basis of calculated atomic data using the Hebrew University Lawrence Livermore Atomic Code (HULLAC). Resonance and satellite lines from singly and multiply excited states of Sn ions are identified. The wavelengths of the 4 -4
-4 + 4
+ 4 -4
-4 transitions of Sn
transitions of Sn to Sn
to Sn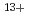 are investigated. Results of calculation are compared with those of the charge exchange spectroscopy, measurement of the emission spectrum of the laser produced plasma EUV source, and the opacity measurement of a radiatively heated Sn sample. A reasonable agreement is observed between calculated and experimental EUV emission spectra. The spectral emissivity and opacity of Sn plasmas are calculated using a full collisional radiative (CR) model as a function of electron temperature and ion density.
are investigated. Results of calculation are compared with those of the charge exchange spectroscopy, measurement of the emission spectrum of the laser produced plasma EUV source, and the opacity measurement of a radiatively heated Sn sample. A reasonable agreement is observed between calculated and experimental EUV emission spectra. The spectral emissivity and opacity of Sn plasmas are calculated using a full collisional radiative (CR) model as a function of electron temperature and ion density.
Sasaki, Akira; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Tanuma, Hajime*
High Energy Density Physics, 5(3), p.147 - 151, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:39.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We study the radiative properties of the EUV source to address conditions to achieve an output power and efficiency required for its application to the next generation microlithography. An atomic model is developed based on the atomic data calculated by Hullac code, which is validated through detailed comparisons with experimental emission and a absorption spectra. The atomic model is improved with respect to the wavelength of the strong emission lines, and the number of satellite channels taken into account. As a result, the radiation hydrodynamics model is shown to successfully reproduce the experiments. We show Sn plasma is more efficient than Xe plasma because of the atomic number dependence of the emission wavelength, and the use of CO lasers as a pumping source has an advantage to reduce satellite contribution and to have narrower emission spectrum to obtain higher conversion efficiency.
lasers as a pumping source has an advantage to reduce satellite contribution and to have narrower emission spectrum to obtain higher conversion efficiency.
Sasaki, Akira; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Tanuma, Hajime*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 163, p.012107_1 - 012107_4, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*
Alternative Lithographic Technologies (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.7271), p.727130_1 - 727130_8, 2009/03
We investigate characteristic feature of the atomic radiation from tin plasmas, which allow one to obtain high power EUV emission efficiently. We develop a collisional radiative model of tin ions to calculate steady-state and time dependent ion abundance, level population, and coefficients of radiative transfer of the plasma. The model, which is based atomic data calculated using the Hullac code is refined both theoretically and experimentally. Calculation of the spectral emissivity and opacity are carried out over a wide range of plasma density and temperature, and pumping conditions to obtain high conversion efficiency are discussed.
Sasaki, Akira; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Tanuma, Hajime*
Reza Kenkyu, 36(Suppl.), p.1132 - 1135, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Sasaki, Akira; Tanuma, Hajime*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Shimada, Yoshinori*
Reza Kenkyu, 36(11), p.690 - 699, 2008/11
The critical issue for realization of a laser produced plasma (LPP) extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source is the conversion efficiency (CE) from incident laser power to EUV radiation of 13.5 nm wavelength. From an atomic physics, we show that tin is the most suitable radiation material compared with xenon and lithium. We also show the optimization of laser and target conditions to obtain high CE using a power balance model. We propose a double-pulse irradiation scheme for high CE using a carbon dioxides laser and a droplet target.
Sasaki, Akira; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Tanuma, Hajime*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 112, p.042062_1 - 042062_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.16(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Sasaki, Akira; Nunami, Masanori*; Tanuma, Hajime*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Shimada, Yoshinori*; Fujima, Kazumi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Kato, Takako*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 15(5), p.056708_1 - 056708_11, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:122 Percentile:97.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Sunahara, Atsushi*; Sasaki, Akira; Tanuma, Hajime*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Aota, Tatsuya*; Yamaura, Michiteru*; Shimada, Yoshinori*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(11), p.920 - 926, 2007/11
We study the EUV emission from laser produced Sn plasmas using the 1D and 2D radiation hydrodynamics simulation, for the development of EUV source for the next generation semiconductor lithography. The opacity and emissivity of the plasma used in the simulation are calculated by a detailed atomic model, with the accurate wavelength of emission lines obtained from the detailed spectroscopic measurements. Calculation is shown to reproduce the experimental spectrum and conversion efficiency reasonably, including the effect of photo pumping which modifies the EUV emission spectrum in the case with a long scale length of the plasmas.
Sasaki, Akira; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Fujima, Kazumi*; Kagawa, Takashi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Tanuma, Hajime*
High Energy Density Physics, 3(1-2), p.250 - 255, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:49.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Kagawa, Takashi*; Tanuma, Hajime*
Proceedings of SPIE's International Symposium on Microlithography, Vol.6151, p.61513W_1 - 61513W_8, 2006/03
The atomic processes in the Xe and Sn plasmas are investigated. The wavelength of atomic transitions is shown to have a critical effect in reproducing experiments. The wavelengths of resonance lines in our model are improved through detailed comparison with charge specific spectroscopic measurement. Distribution of satellite lines in the presence of the effect of the configuration interaction (CI) is investigated. The spectral profile of Xe and Sn emission, with determines fraction of usable EUV power, is discussed with respect to its dependence on the plasma temperature, density as well as the optical depth.
Kagawa, Takashi*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sasaki, Akira; Koike, Fumihiro*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.7, p.245 - 248, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Murakami, Masakatsu*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Kagawa, Takashi*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Fujima, Kazumi*; Kawamura, Toru*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 85(24), p.5857 - 5859, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:80.02(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Fujima, Kazumi*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Kawamura, Toru*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Kagawa, Takashi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; More, R.*; Murakami, Masakatsu*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Sasaki, Akira; et al.
Emerging Lithographic Technologies VIII, Proceedings of SPIE Vol.5374, p.405 - 412, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
 ions in comparison with an isoelectronic species Ne
ions in comparison with an isoelectronic species Ne
Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Yamaoka, Hitoshi*; Oura, Masaki*; Hayaishi, T.*; Sekioka, T.*; Agui, Akane; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Koike, Fumihiro*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 35(20), p.4147 - 4153, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:65.36(Optics)no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Maehara, Hiroaki*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Kagawa, Takashi*; Tanuma, Hajime*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English