Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hagiwara, Kenta*; Ochi, Kotaro; Koike, Yuya*
Radioisotopes, 70(4), p.227 - 237, 2021/05
Behavior of radioactive caesium in river water and sediment in Tama river was investigated during 2012-2016. Concentrations of radioactive caesium in river water and sediment were decreased with time exponentially. Concentrations of suspended radioactive caesium, and radioactive caesium in sediment temporarily increased when sediments were resuspended due to rain. On the other hand, dissolved radioactive caesium was not easily impacted by this factor. Sequential extraction, elemental and crystal phase analysis were performed on the sediments and examined the chemical state of radioactive caesium as well as the adsorption mechanism. Radioactive caesium in sediment was present in a stable chemical form, and there is possibility that radioactive caesium was incorpolated in biotite.
Fujii, Kengo*; Ochi, Kotaro; Obuchi, Atsushi*; Koike, Yuya*
Journal of Environmental Management, 217, p.157 - 163, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:75.51(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Daiichi-Nuclear Power Plant accident, environmental recovery was a major issue because a considerable amount of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash was highly contaminated with radioactive cesium. In this study, MSWI fly ash was sampled in Fukushima Prefecture, and the physicochemical properties of radioactive cesium in MSWI fly ash were evaluated by particle size classification and the Japanese leaching test No. 13 (JLT-13). The results obtained from the classification of fly ash indicated that the activity concentration of radioactive cesium and the content of the coexisting matter (i.e., chloride, potassium, and sylvite) temporarily change in response to the particle size of fly ash. X-ray diffraction results indicated that water-soluble radioactive cesium exists as CsCl because of the cooling process and that insoluble cesium is bound to the inner sphere of amorphous matter.
 W-
W- Re generator using PZC
Re generator using PZCKurihara, Yuichi*; Nogawa, Norio*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Koike, Yuya*; Morikawa, Naotake*; Ijiri, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kono, Takahiko; Ogino, Haruyuki*; Fujiwara, Keiko*; Moriya, Koichi*; Fujimichi, Yuki*; Koike, Yuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
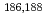 Re-MAG3 and
Re-MAG3 and 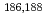 Re-[(CO)
Re-[(CO) (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nogawa, Norio*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Koike, Yuya*; Morikawa, Naotake*; Ijiri, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 W-
W- Re generator using PZC and synthesis of
Re generator using PZC and synthesis of  Re and
Re and  Re-DMSA
Re-DMSANogawa, Norio*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Koike, Yuya*; Morikawa, Naotake*; Ijiri, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ichihashi, Jun*; Kasari, Mitsuki*; Ochi, Kotaro; Koike, Yuya*
no journal, ,
In this study, we sampled a core soil using a core sampler (0-30 cm) at Kawasaki. A sequential extraction procedure was used to characterize radiocesium in each layer of soil. We selected six sampling points in cosideration of the vegetation. Four soils were collected at 900 cm range area. Core sample (0-30 cm) was devided into 5 cm layer and put in U-8 container, respectively. From measurement results, the vertival distribuition of radiocesium in core soil was 2.5 Bq kg
range area. Core sample (0-30 cm) was devided into 5 cm layer and put in U-8 container, respectively. From measurement results, the vertival distribuition of radiocesium in core soil was 2.5 Bq kg (0-5 cm), 22.3 Bq kg
(0-5 cm), 22.3 Bq kg (5-10 cm), 3.4 Bq kg
(5-10 cm), 3.4 Bq kg (10-15 cm), 0.3 Bq kg
(10-15 cm), 0.3 Bq kg (15-20 cm), 0.8 Bq kg
(15-20 cm), 0.8 Bq kg (20-25 cm), 1.0 Bq kg
(20-25 cm), 1.0 Bq kg (25-30 cm). It is indicated that radiocesium penetrate to deeper layer at Kawasaki.
(25-30 cm). It is indicated that radiocesium penetrate to deeper layer at Kawasaki.
Kono, Takahiko; Ogino, Haruyuki*; Koike, Yuya*; Fujiwara, Keiko*; Shimada, Kazumasa*; Tani, Kotaro*; Fujimichi, Yuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 W-
W- Re generator using PZC
Re generator using PZCKurihara, Yuichi*; Nogawa, Norio*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Koike, Yuya*; Morikawa, Naotake*; Ijiri, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English