Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
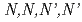 -tetraoctyl diglycolamide solvent induced by hydrogen ion beam
-tetraoctyl diglycolamide solvent induced by hydrogen ion beamNakahara, Masaumi; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Yamagata, Ryohei*; Yamada, Naoto*; Koka, Masashi*
QST-M-52; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2023, P. 47, 2025/03
The development of an extractant and a separation process have been studied to recover Am and Cm from high-level liquid waste. To strip Am and Cm from loaded solvent effectively, the evaluation for complex structures is attempted with ion beam induced luminescence. In this study, Sm as a simulated material of minor actinide in the 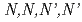 -tetraoctyl diglycolamide were irradiated by the H
-tetraoctyl diglycolamide were irradiated by the H ion beam, and the ion beam induced luminescence spectra of Sm complexes were measured to evaluate the structures of Sm complexes.
ion beam, and the ion beam induced luminescence spectra of Sm complexes were measured to evaluate the structures of Sm complexes.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Yamagata, Ryohei*; Yuri, Yosuke*; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishizaka, Tomohisa*; Koka, Masashi*; Yamada, Naoto*; Hagura, Naoto*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 554, p.165449_1 - 165449_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ion beam induced luminescence analysis of lanthanide complexes in the organic solvents for minor actinides recovery process was carried out to investigate the structures of complexes. In this study, hydrogen ion beam obtained from the single-ended accelerator and argon ion beam obtained from the azimuthally varying field cyclotron were used in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application in National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology. In the experiments, ion beam induced luminescence spectra of lanthanide complexes in the organic solvents were measured, and the relationship between the obtained spectra and the structures of complexes was studied.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishizaka, Tomohisa*; Yuri, Yosuke*; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Yamagata, Ryohei*; Yamada, Naoto*; Koka, Masashi*; Kada, Wataru*; et al.
QST-M-47; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2022, P. 64, 2024/03
An extraction chromatography method has been studied to recover minor actinides from high-level liquid waste. For effective elution of minor actinides in an adsorbent, the structures of complexes are attempted to be evaluated with ion beam induced luminescence. In this study, Eu complexes in the adsorbent were irradiated by Ar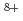 ion beam, and the ion beam induced luminescence spectra of Eu complexes were measured to evaluate the structures of Eu complexes.
ion beam, and the ion beam induced luminescence spectra of Eu complexes were measured to evaluate the structures of Eu complexes.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishizaka, Tomohisa*; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Yamagata, Ryohei*; Yamada, Naoto*; Koka, Masashi*; Kada, Wataru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 542, p.144 - 150, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.63(Instruments & Instrumentation)The structures of Eu complexes in the adsorbents prepared with various extractants were evaluated by ion beam induced luminescence analysis in an extraction chromatography for minor actinides recovery. The luminescence of Eu was measured with a proton beam obtained from the single-ended accelerator and an argon ion beam obtained from the azimuthally varying field cyclotron in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application in National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology. In this study, it was confirmed that the spectral shape of Eu complexes in the adsorbents varied depending on the kinds of extractants, and the correlation between the change in the spectra and the structures of Eu complexes was investigated.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Yamagata, Ryohei*; Yamada, Naoto*; Koka, Masashi*; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishizaka, Tomohisa*; Kada, Wataru*; Hagura, Naoto*
QST-M-39; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2021, P. 62, 2023/02
In an extraction chromatography method for minor actinides recovery, analysis for the structure of complex in a silica-based adsorbent has been studied to separate minor actinides efficiently. In this study, Eu was used as simulated material of minor actinides, and silica-based adsorbents containing Eu complex were prepared. The ion beam induced luminescence spectra of Eu complexes in silica-based adsorbents were measured, and the basic data for the structures of Eu complexes were obtained.
Miyazaki, Yasunori; Sano, Yuichi; Okamura, Nobuo; Watanabe, Masayuki; Koka, Masashi*
QST-M-29; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2019, P. 72, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, So; Katai, Yuya*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Kada, Wataru*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 450, p.61 - 65, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:35.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Ono, Shimpei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 404, p.202 - 206, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)Abe, Ryoji*; Nagoshi, Kohei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Takagi, Hideaki*; Shimizu, Nobutaka*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 404, p.173 - 178, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Koka, Masashi; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Yamada, Naoto; Okubo, Takeru; Kada, Wataru*; Kitamura, Akane; Iwata, Yoshihiro*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro
JAEA-Technology 2016-006, 41 Pages, 2016/03
A MeV-class light ion microbeam system has been developed for micro-analysis and micro-fabrication with high spatial resolution at 3-MV single-ended accelerator in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application of Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This report describes the technical improvements for the main apparatus (the accelerator, beam-transport lines, and microbeam system), and auxiliary equipments/ parts for ion beam applications such as Particle Induced X-ray/Gamma-ray Emission (PIXE/PIGE) analysis, 3-D element distribution analysis using PIXE-Computed Tomography(CT), Ion Beam-Induced Luminescence (IBIL) analysis, and Proton Beam Writing with the microbeam scanning, with functional outline of these apparatus and equipments/parts.
Yokoyama, Akihito; Kada, Wataru*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Shimada, Keisuke*; Yokota, Yuya*; Miura, Kenta*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 371, p.340 - 343, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Narisawa, Masaki*; Koka, Masashi; Takeyama, Akinori; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Sato, Takahiro; Hokazono, Hiroki*; Kawai, Taketoshi*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 123(9), p.805 - 808, 2015/09
Yuri, Yosuke; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Koka, Masashi; Yamada, Naoto
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.420 - 423, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Kada, Wataru*; Kambayashi, Yuya*; Miura, Kenta*; Saruya, Ryota*; Kubota, Atsushi*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hanaizumi, Osamu*
Key Engineering Materials, 643, p.15 - 19, 2015/05
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Kada, Wataru*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.4 - 7, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kada, Wataru*; Miura, Kenta*; Kato, Hijiri*; Saruya, Ryota*; Kubota, Atsushi*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.218 - 222, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kada, Wataru*; Kambayashi, Yuya*; Iwamoto, Naoya*; Onoda, Shinobu; Makino, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hoshino, Norihiro*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Kojima, Kazutoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.240 - 245, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)Yokoyama, Akihito; Kada, Wataru*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Yokota, Wataru
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 168, 2015/03
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Akihito; Kada, Wataru*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Yokota, Wataru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 332, p.334 - 336, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)A system is developed for the real-time position detection of single-ions which hits a target with spatial accuracy about 1  m. The system combines highly luminescent, sensitive, scintillators with a high sensitivity luminescence detection system. The real-time detection system contains a Al
m. The system combines highly luminescent, sensitive, scintillators with a high sensitivity luminescence detection system. The real-time detection system contains a Al O
O :Eu scintillator, Eu implanting into
:Eu scintillator, Eu implanting into  -Al
-Al O
O . A single-crystal scintillator has been selected since position resolution of emission for powdery scintillator is limited by a grain size, several micrometers for ZnS for example. When the material is irradiated with an electron or ion beam, the Eu is activated and strong luminescence occurs. The detection system includes an image intensifier tube and an electron multiplier CCD camera. The results show that our system can be sufficiently sensitive to detect the hit of a single-ion in real time through simple improvement in emission intensity of the scintillator.
. A single-crystal scintillator has been selected since position resolution of emission for powdery scintillator is limited by a grain size, several micrometers for ZnS for example. When the material is irradiated with an electron or ion beam, the Eu is activated and strong luminescence occurs. The detection system includes an image intensifier tube and an electron multiplier CCD camera. The results show that our system can be sufficiently sensitive to detect the hit of a single-ion in real time through simple improvement in emission intensity of the scintillator.
Sakai, Takuro; Yasuda, Ryo; Iikura, Hiroshi; Nojima, Takehiro; Koka, Masashi; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Oshima, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 332, p.238 - 241, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have successfully fabricated novel microscopic imaging devices made from UV/EB curable resin using an external scanning proton microbeams. The devices are micro-structured fluorescent plates that consist of an array of micro-pillars that align periodically. The base material used in the pillars is UV/EB curable resin and each pillar contains phosphor grains. The pattern exposures were performed using a proton beam writing technique. The height of the pillars depends on the range of the proton beam. Optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy have been used to characterize the samples. The results show that the fabricated fluorescent plates are expected to be high-spatial-resolution imaging devices.