Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kinase, Akari; Goto, Katsunori*; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-004, 60 Pages, 2024/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3 and stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc, 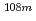 Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Tobita, Minoru*; Goto, Katsunori*; Omori, Takeshi*; Osone, Osamu*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-011, 32 Pages, 2023/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to the study of radioactivity concentration evaluation methods for radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3, JRR-4 and JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 23 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; Konda, Miki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-002, 81 Pages, 2023/05
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Tobita, Minoru*; Konda, Miki; Omori, Takeshi*; Nabatame, Tsutomu*; Onizawa, Takashi*; Kurosawa, Katsuaki*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-007, 40 Pages, 2022/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete, ash, ceramic and brick samples generated from JRR-3, JRR4 and JRTF facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 24 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2020-2021.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2020-2021.
 Sr analysis
Sr analysisHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho*; Konda, Miki; Matsueda, Makoto; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 69(10/11), p.619 - 626, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a Sr adsorption fiber for rapid analysis of  Sr. The prepared Sr adsorption fiber has a Sr-extraction layer that densely retains a Sr-selective extractant, an 18-crown-6 ether derivative, on the fiber surface. Hydrophobic group-containing polymer chains embedded onto the surface of the fiber allow to form a hydrophobic phase, incorporating Sr-selective extractants. This unique surface structure provides high adsorption capacity, leading to rapid and highly efficient adsorption of Sr
Sr. The prepared Sr adsorption fiber has a Sr-extraction layer that densely retains a Sr-selective extractant, an 18-crown-6 ether derivative, on the fiber surface. Hydrophobic group-containing polymer chains embedded onto the surface of the fiber allow to form a hydrophobic phase, incorporating Sr-selective extractants. This unique surface structure provides high adsorption capacity, leading to rapid and highly efficient adsorption of Sr . The adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was 3 times higher than commercially available 18-crown-6 ether derivative-impregnated resin (Sr Resin). The equilibrium adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was comparable to the Sr Resin. The retained
. The adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was 3 times higher than commercially available 18-crown-6 ether derivative-impregnated resin (Sr Resin). The equilibrium adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was comparable to the Sr Resin. The retained  Sr was finally determined by a GM counter. The total analysis time including the Sr adsorption and measurement was about 1 hour.
Sr was finally determined by a GM counter. The total analysis time including the Sr adsorption and measurement was about 1 hour.
 Zr determination with isotope dilution ICP-MS
Zr determination with isotope dilution ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ishihara, Ryo*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Hirota, Hideyuki*
Talanta, 185, p.98 - 105, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:30.63(Chemistry, Analytical)Estimating the risks associated with radiation from long-lived fission products (LLFP) in radioactive waste is essential to ensure the long-term safety of potential disposal sites. In this study, the amount of  Zr, a LLFP, was determined by ICP-MS after separating Zr from a spent nuclear fuel solution using a microvolume anion-exchange cartridge (TEDA cartridge). The TEDA cartridge achieved highly selective separation of Zr regardless of its small bed volume of 0.08 cm
Zr, a LLFP, was determined by ICP-MS after separating Zr from a spent nuclear fuel solution using a microvolume anion-exchange cartridge (TEDA cartridge). The TEDA cartridge achieved highly selective separation of Zr regardless of its small bed volume of 0.08 cm . The time taken to complete the Zr separation was 1.2 min with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, which was 10 times faster than that for a conventional anion-exchange resin column. Almost all the other elements were removed, leading to accurate measurement of
. The time taken to complete the Zr separation was 1.2 min with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, which was 10 times faster than that for a conventional anion-exchange resin column. Almost all the other elements were removed, leading to accurate measurement of  Zr. The result connects experimental value to theoretical prediction provided by ORIGEN2, which requires verification. With the measured value, we demonstrated that the theoretical value is reliable enough to estimate radiation risks.
Zr. The result connects experimental value to theoretical prediction provided by ORIGEN2, which requires verification. With the measured value, we demonstrated that the theoretical value is reliable enough to estimate radiation risks.
 Sr measurement
Sr measurementHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Konda, Miki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(3), p.189 - 193, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.09(Chemistry, Analytical)A Sr-selective adsorption fiber was prepared for rapid analysis of  Sr content by using radiation-induced emulsion graft polymerization and subsequent chemical modification. A polyethylene fiber with a diameter of 13
Sr content by using radiation-induced emulsion graft polymerization and subsequent chemical modification. A polyethylene fiber with a diameter of 13  m was first immersed in a methanol solution of an epoxy-group-containing vinyl monomer, glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), and polyoxyethylene sorbitol ester (Tween20) as a surfactant for graft-polymerization of GMA. Octadecylamine was then bound to a polymer chain extending from the fiber surface providing hydrophobicity to the polymer chain. Dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6) was finally impregnated onto the polymer chain via a hydrophobic interaction between the octadecyl moiety of the polymer chain and the cyclohexyl moiety of DCH18C6. The fiber surface structure, characterized by DCH18C6 molecules loosely entangled with polymer chains, afforded realizes the rapid and selective adsorption of Sr ions with an adsorption rate approximately 100 times higher than that of a commercially available Sr-selective resin (Sr Resin).
m was first immersed in a methanol solution of an epoxy-group-containing vinyl monomer, glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), and polyoxyethylene sorbitol ester (Tween20) as a surfactant for graft-polymerization of GMA. Octadecylamine was then bound to a polymer chain extending from the fiber surface providing hydrophobicity to the polymer chain. Dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6) was finally impregnated onto the polymer chain via a hydrophobic interaction between the octadecyl moiety of the polymer chain and the cyclohexyl moiety of DCH18C6. The fiber surface structure, characterized by DCH18C6 molecules loosely entangled with polymer chains, afforded realizes the rapid and selective adsorption of Sr ions with an adsorption rate approximately 100 times higher than that of a commercially available Sr-selective resin (Sr Resin).
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Konda, Miki; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Magara, Masaaki
JAEA-Technology 2015-054, 22 Pages, 2016/03
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) with ICP-MS is reliable method for determination of Zr-93, which is one of the long-lived fission products found in spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes. In order to use an isotope standard solution of zirconium as the spike for IDMS, dissolving a commercially available solid isotope standard is indispensable. Prior to the dissolution of the Zr-91 isotope standard, solubility of metal zirconium in a mixture of HNO and HF was evaluated using zirconium metal chips. Then, 2 mg of the Zr-91 isotope standard was dissolved with 0.2 mL of 1 M HNO
and HF was evaluated using zirconium metal chips. Then, 2 mg of the Zr-91 isotope standard was dissolved with 0.2 mL of 1 M HNO -3 v/v% HF mixed solution, followed by adjusting the concentration of Zr-91 to approximately 1,000
-3 v/v% HF mixed solution, followed by adjusting the concentration of Zr-91 to approximately 1,000  g/g. IDMS, in which a natural isotopic abundance standard solution of zirconium was used as the spike, was employed for the determination of the concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. The concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution was (9.6
g/g. IDMS, in which a natural isotopic abundance standard solution of zirconium was used as the spike, was employed for the determination of the concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. The concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution was (9.6 1.0)
1.0)  10
10
 g/g, which is in good agreement with the predicted concentration. This indicates that the Zr-91 metal isotope standard was completely dissolved with sufficient chemical stability. Additionally, no impurities were detected in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. These positive results denote that the Zr-91 isotope standard solution with the preferable quality for IDMS of Zr-93 can be obtained by the proposed dissolution procedures.
g/g, which is in good agreement with the predicted concentration. This indicates that the Zr-91 metal isotope standard was completely dissolved with sufficient chemical stability. Additionally, no impurities were detected in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. These positive results denote that the Zr-91 isotope standard solution with the preferable quality for IDMS of Zr-93 can be obtained by the proposed dissolution procedures.
 Np content in spent nuclear fuel
Np content in spent nuclear fuelAsai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ishihara, Ryo*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Hirota, Hideyuki*
Analytical Chemistry, 88(6), p.3149 - 3155, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:26.70(Chemistry, Analytical)Neptunium-237 ( Np) is one of the major long-lived radionuclides found in spent nuclear fuel. To evaluate the long-term safety of a HLW repository, the
Np) is one of the major long-lived radionuclides found in spent nuclear fuel. To evaluate the long-term safety of a HLW repository, the  Np content in spent nuclear fuel must be determined. In this study, micro-volume anion-exchange porous polymer disk-packed cartridges were prepared for Am-Np separation, which is required prior to the measurement of
Np content in spent nuclear fuel must be determined. In this study, micro-volume anion-exchange porous polymer disk-packed cartridges were prepared for Am-Np separation, which is required prior to the measurement of  Np with ICP-MS. Disks with a volume of 0.08 cm
Np with ICP-MS. Disks with a volume of 0.08 cm were cut out from porous sheets having triethylenediamine (TEDA)-containing polymer chains densely attached on the pore surface. The resulting TEDA-introduced disk cartridge was applied to a spent nuclear fuel sample. The chemical yield of Np was 90.4%, which is sufficiently high for ICP-MS measurement of
were cut out from porous sheets having triethylenediamine (TEDA)-containing polymer chains densely attached on the pore surface. The resulting TEDA-introduced disk cartridge was applied to a spent nuclear fuel sample. The chemical yield of Np was 90.4%, which is sufficiently high for ICP-MS measurement of  Np. Compared with the conventional separation technique using commercially available anion-exchange resin columns, the time required to adsorb, wash and elute Np using the TEDA-introduced disk cartridge was reduced by 75%.
Np. Compared with the conventional separation technique using commercially available anion-exchange resin columns, the time required to adsorb, wash and elute Np using the TEDA-introduced disk cartridge was reduced by 75%.
 Sr; Study of safe Sr adsorption with no nitric acid
Sr; Study of safe Sr adsorption with no nitric acidKonda, Miki; Horita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Np in spent nuclear fuel
Np in spent nuclear fuelAsai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ishihara, Ryo*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Hirota, Hideyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi
no journal, ,
Various Zr isotopes generated by U fission are found in spent fuel and HLW. Among them,  Zr which has a long half-life of 1.5
Zr which has a long half-life of 1.5 10
10 y has a potential to contribute to radiation dose over an extended period of time after the implementation of HLW disposal. The inventory estimation of
y has a potential to contribute to radiation dose over an extended period of time after the implementation of HLW disposal. The inventory estimation of  Zr in HLW confirmed by measured data is the key to realize a safe and cost-efficient disposal. In this study, a simple and robust analytical technique for the determination of
Zr in HLW confirmed by measured data is the key to realize a safe and cost-efficient disposal. In this study, a simple and robust analytical technique for the determination of  Zr based on ion-exchange chromatography combined with ICP-MS was developed. Interference-free measurement was achieved by a single anion-exchange step, removing Sr, Nb, and Mo which would cause spectral interferences. Additionally, major component U and radioactive components, such as Cs, Ba, and Pu, were also removed concurrently. Concentration of
Zr based on ion-exchange chromatography combined with ICP-MS was developed. Interference-free measurement was achieved by a single anion-exchange step, removing Sr, Nb, and Mo which would cause spectral interferences. Additionally, major component U and radioactive components, such as Cs, Ba, and Pu, were also removed concurrently. Concentration of  Zr was readily calculated with measured isotope ratios of
Zr was readily calculated with measured isotope ratios of  Zr/
Zr/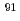 Zr in the sample and natural Zr-spiked sample with sufficient accuracy.
Zr in the sample and natural Zr-spiked sample with sufficient accuracy.
 Np in spent nuclear fuel using anion-exchange porous polymeric filter
Np in spent nuclear fuel using anion-exchange porous polymeric filterAsai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ishihara, Ryo*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Hirota, Hideyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
A large amount of contaminated rubble was generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS). For safe decommissioning of F1NPS, it is important to evaluate the composition and concentration of radionuclides in the rubble. To characterize the rubble collected at F1NPS, radiochemical analysis was conducted. From the rubble collected from reactor buildings,  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Se,
Se,  Sr,
Sr,  Tc,
Tc,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu, 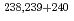 Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm were detected. The radioactivity concentrations of
Cm were detected. The radioactivity concentrations of  Co,
Co,  Sr and
Sr and  Pu are correlated that of
Pu are correlated that of  Cs. The radioactive ratio of
Cs. The radioactive ratio of  Co/
Co/ Cs,
Cs,  Sr/
Sr/ Cs and
Cs and  Pu/
Pu/ Cs were similar between the rubble collected from 1st floor and 5th floor of unit 1 reactor building. This result implied that regardless of sampling location in reactor building, the radioactive ratios of
Cs were similar between the rubble collected from 1st floor and 5th floor of unit 1 reactor building. This result implied that regardless of sampling location in reactor building, the radioactive ratios of  Co/
Co/ Cs,
Cs,  Sr/
Sr/ Cs and
Cs and  Pu/
Pu/ Cs were consistent.
Cs were consistent.
Horita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Konda, Miki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
High activity concentrations of  Sr, which greatly exceed the regulatory limit (30 Bq/L), are detected in contaminated waters sampled in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. However, analytical method for
Sr, which greatly exceed the regulatory limit (30 Bq/L), are detected in contaminated waters sampled in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. However, analytical method for  Sr associated with time-consuming procedure causes delay in understanding the current status of
Sr associated with time-consuming procedure causes delay in understanding the current status of  Sr contamination. In this study, we have prepared a Sr adsorption fiber (Sr Fiber) based on radiation-induced graft polymerization technique to achieve a rapid adsorption of Sr ions. Dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 ether that has high affinity for Sr was impregnated in the hydrophobic interfacial phase provided by hydrophobic polymer chains attached on the fiber surface through graft polymerization. The time required to reach the Sr adsorption equilibrium for the Sr Fiber is approximately 180 times shorter than that for a commercially available Sr adsorbent (Sr Resin), showing that the Sr Fiber has a potential to efficiently reduce the analytical time of
Sr contamination. In this study, we have prepared a Sr adsorption fiber (Sr Fiber) based on radiation-induced graft polymerization technique to achieve a rapid adsorption of Sr ions. Dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 ether that has high affinity for Sr was impregnated in the hydrophobic interfacial phase provided by hydrophobic polymer chains attached on the fiber surface through graft polymerization. The time required to reach the Sr adsorption equilibrium for the Sr Fiber is approximately 180 times shorter than that for a commercially available Sr adsorbent (Sr Resin), showing that the Sr Fiber has a potential to efficiently reduce the analytical time of  Sr.
Sr.
 Sr in contaminated water using Sr adsorptive fiber
Sr in contaminated water using Sr adsorptive fiberKonda, Miki; Horita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Matsueda, Makoto; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ishihara, Ryo*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Hirota, Hideyuki*
no journal, ,
 Zr is a long-lived fission product which can be found in spent nuclear fuel and HLW. The estimation of the
Zr is a long-lived fission product which can be found in spent nuclear fuel and HLW. The estimation of the Zr content is indispensable to achieve a safety disposal of HLW because
Zr content is indispensable to achieve a safety disposal of HLW because  Zr is predicted to be one of the major contributors to radiation dose. However, only a few measured
Zr is predicted to be one of the major contributors to radiation dose. However, only a few measured  Zr values have been reported, leading to a high demand for development of an efficient analytical method. Our group has been prepared a new porous filter cartridge which has densely bound ion-exchanger onto the pore surface of the filter, enabling a high-capacity and rapid adsorption. In order to apply this filter cartridge to a pretreatment for the
Zr values have been reported, leading to a high demand for development of an efficient analytical method. Our group has been prepared a new porous filter cartridge which has densely bound ion-exchanger onto the pore surface of the filter, enabling a high-capacity and rapid adsorption. In order to apply this filter cartridge to a pretreatment for the  Zr measurement with ICP-MS, an elution profiles of Zr and the other coexisting elements were examined. According to the resultant separation conditions, Zr in a spent nuclear fuel sample was successfully separated. The measured
Zr measurement with ICP-MS, an elution profiles of Zr and the other coexisting elements were examined. According to the resultant separation conditions, Zr in a spent nuclear fuel sample was successfully separated. The measured  Zr content is 98.2
Zr content is 98.2  5.1 ng, which agrees with the theoretical value.
5.1 ng, which agrees with the theoretical value.
 Sr adsorbed on fiber surface; Preparation of 18-crown 6-ether derivative-impregnated Sr adsorption fiber based on the radiation-induced graft polymerization
Sr adsorbed on fiber surface; Preparation of 18-crown 6-ether derivative-impregnated Sr adsorption fiber based on the radiation-induced graft polymerizationHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Konda, Miki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
There has been an increasing importance of the development of rapid separation techniques for  Sr analysis, responding to needs in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. However, conventional
Sr analysis, responding to needs in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. However, conventional  Sr analytical methods require two different separation steps for Sr and Y, respectively, resulting in a long processing time of about one month. In this study, we prepared a Sr adsorptive fiber (Sr fiber) that has a high density Sr adsorption phase on its surface, allowing to highly efficient
Sr analytical methods require two different separation steps for Sr and Y, respectively, resulting in a long processing time of about one month. In this study, we prepared a Sr adsorptive fiber (Sr fiber) that has a high density Sr adsorption phase on its surface, allowing to highly efficient  -ray counting by minimizing the self-attenuation effects. The adsorption capacity of the prepared Sr fiber was about 14 g/mol, which is equivalent to that of a commercially available Sr adsorptive resin (Sr Resin). The selectivity of the Sr fiber was nearly the same as that of the Sr resin. Considering that the Sr fiber has a specific surface area 1000 times smaller than that of the Sr Resin, the Sr ions can be concentrated to 1000 times on its surface, capable of achieving highly-efficient
-ray counting by minimizing the self-attenuation effects. The adsorption capacity of the prepared Sr fiber was about 14 g/mol, which is equivalent to that of a commercially available Sr adsorptive resin (Sr Resin). The selectivity of the Sr fiber was nearly the same as that of the Sr resin. Considering that the Sr fiber has a specific surface area 1000 times smaller than that of the Sr Resin, the Sr ions can be concentrated to 1000 times on its surface, capable of achieving highly-efficient  -ray counting. From these result, we confirmed that Sr fiber has adsorption capacity and selectivity necessary for highly efficient
-ray counting. From these result, we confirmed that Sr fiber has adsorption capacity and selectivity necessary for highly efficient  -ray counting of
-ray counting of  Sr.
Sr.
Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi
no journal, ,
Isotopes of Zr and Mo including both radio and stable isotopes can be found in spent nuclear fuel. Of these isotopes,  Zr and
Zr and  Mo which have long half-lives of 1.61
Mo which have long half-lives of 1.61  10
10 y and 4
y and 4  10
10 y, respectively, are of great importance from the viewpoint of managing high-level radioactive wastes in a long-term basis. In this study, contents of Zr and Mo isotopes in spent nuclear fuel solution were determined by isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The sample solution was prepared by dissolving a Japanese PWR irradiated UO
y, respectively, are of great importance from the viewpoint of managing high-level radioactive wastes in a long-term basis. In this study, contents of Zr and Mo isotopes in spent nuclear fuel solution were determined by isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The sample solution was prepared by dissolving a Japanese PWR irradiated UO fuel with a burnup of 51 GWd/t. The measured contents of
fuel with a burnup of 51 GWd/t. The measured contents of  Zr,
Zr, 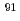 Zr,
Zr, 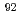 Zr,
Zr,  Zr,
Zr,  Zr, and
Zr, and 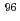 Zr in the sample were agreed well with the predicted values obtained through a burnup calculation code ORIGEN2. For Mo, the contents in the sample were approximately 30% less than the predicted values, indicating that part of Mo exists in the insoluble residue.
Zr in the sample were agreed well with the predicted values obtained through a burnup calculation code ORIGEN2. For Mo, the contents in the sample were approximately 30% less than the predicted values, indicating that part of Mo exists in the insoluble residue.