Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.78(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 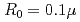 m.
m.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
 Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear)Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Matsunaka, Kazuaki*; Ishida, Hiroki*; Ho, H. Q.; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Kenzhina, I.*; Chikhray, Y.*; Kondo, Atsushi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2019-008, 12 Pages, 2019/07
As a summer holiday practical training 2018, the feasibility study for nuclear design of a nuclear battery using HTTR core was carried out. As a result, it is become clear that the continuous operations for about 30 years at 2 MW, about 25 years at 3 MW, about 18 years at 4 MW, about 15 years at 5 MW are possible. As an image of thermal design, the image of the nuclear battery consisting a cooling system with natural convection and a power generation system with no moving equipment is proposed. Further feasibility study to confirm the feasibility of nuclear battery will be carried out in training of next fiscal year.
Ono, Masato; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Kondo, Toshinari; Kojima, Keidai; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 4(2), p.020906_1 - 020906_8, 2018/04
On March 11th, 2011, the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake of magnitude 9.0 occurred. When the great earthquake occurred, the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) had been stopped under the periodic inspection and maintenance of equipment and instruments. A comprehensive integrity evaluation was carried out for the HTTR facility because the maximum seismic acceleration observed at the HTTR exceeded the maximum value of design basis earthquake. The concept of comprehensive integrity evaluation is divided into two parts. One is the "visual inspection of equipment and instruments". The other is the "seismic response analysis" for the building structure, equipment and instruments using the observed earthquake. All equipment and instruments related to operation were inspected in the basic inspection. The integrity of the facilities was confirmed by comparing the inspection results or the numerical results with their evaluation criteria. As the results of inspection of equipment and instruments associated with the seismic response analysis, it was judged that there was no problem for operation of the reactor, because there was no damage and performance deterioration. The integrity of HTTR was also supported by the several operations without reactor power in cold conditions of HTTR in 2011, 2013 and 2015. Additionally, the integrity of control rod guide blocks was also confirmed visually when three control rod guide blocks and six replaceable reflector blocks were taken out from reactor core in order to change neutron startup sources in 2015.
Adhi, P. M.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kondo, Masatoshi*; Takahashi, Minoru*
Energy Procedia, 131, p.420 - 427, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Energy & Fuels)The ionic conductivity of solid electrolyte may insufficient, and the sensor output signal will deviate from the theoretical one in low temperature. The performance of oxygen sensor with Ag/air reference electrode (RE) and liquid Bi/Bi O
O RE was tested in low-temperature LBE at 300
RE was tested in low-temperature LBE at 300 450
450 C and the charge transfer reactions impedance at the electrode-electrolyte interface was analyzed by electrochemical impedance analysis (EIS). After steady state condition, both of the sensors performed well and can be used at 300
C and the charge transfer reactions impedance at the electrode-electrolyte interface was analyzed by electrochemical impedance analysis (EIS). After steady state condition, both of the sensors performed well and can be used at 300 450
450 C. Bi/Bi/Bi
C. Bi/Bi/Bi O
O RE has lower impedance than Ag/air RE. Therefore, the response time of the oxygen sensor with Bi/Bi/Bi
RE has lower impedance than Ag/air RE. Therefore, the response time of the oxygen sensor with Bi/Bi/Bi O
O RE is faster than the oxygen sensor with Ag/air RE in the low-temperature region.
RE is faster than the oxygen sensor with Ag/air RE in the low-temperature region.
Kondo, Masatoshi*; Okubo, Nariaki; Irisawa, Eriko; Komatsu, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Norito; Tanaka, Teruya*
Energy Procedia, 131, p.386 - 394, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:97.40(Energy & Fuels)The chemical behaviors of lead (Pb) based coolants in the air ingress accident of fast reactors were investigated by means of the thermodynamic considerations and the static oxidation experiments for Pb alloys at various chemical compositions. The results of the static oxidation tests for lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) alloys indicated that Pb was depleted from the alloy due to the preferential formation of PbO in air at 773K. Pb-Bi oxide and Bi O
O were formed after the enrichment of Bi in the alloys due to the Pb depletion. The oxidation rates of the alloys were much larger than that of the steels, and became larger with higher Pb concentration in the alloys. The compatibility of Pb-Bi alloys with stainless steel was worse when the Pb concentration in the alloys became low, since the dissolution type corrosion was promoted by the Bi composition in the alloy. The Pb-Li alloys were oxidized as they formed Li
were formed after the enrichment of Bi in the alloys due to the Pb depletion. The oxidation rates of the alloys were much larger than that of the steels, and became larger with higher Pb concentration in the alloys. The compatibility of Pb-Bi alloys with stainless steel was worse when the Pb concentration in the alloys became low, since the dissolution type corrosion was promoted by the Bi composition in the alloy. The Pb-Li alloys were oxidized as they formed Li PbO
PbO and Li
and Li CO
CO . Then, Li was depleted from the alloy.
. Then, Li was depleted from the alloy.
 -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of  Mg via knockout reactions at intermediate energies
Mg via knockout reactions at intermediate energiesMomiyama, Satoru*; Doornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Niikura, Megumi*; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(3), p.034328_1 - 034328_8, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.71(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 shore of the "island of inversion" and the reduced neutron magicity toward
shore of the "island of inversion" and the reduced neutron magicity toward  O
ODoornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(4), p.041301_1 - 041301_5, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:91.74(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Ne
NeLiu, H. N.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K. A.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 767, p.58 - 62, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:84.56(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Ono, Masato; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 2(4), p.044502_1 - 044502_4, 2016/10
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to verify safety evaluation codes to investigate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. The VCS passively removes the retained residual heat and the decay heat from the core via the reactor pressure vessel by natural convection and thermal radiation. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. Through a cold test, which was carried out by non-nuclear heat input from gas circulators with stopping water flow in the VCS, the local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
 Ne at
Ne at  230 MeV/nucleon
230 MeV/nucleonLee, J.*; Liu, H.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Minomo, Kosho*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2016(8), p.083D01_1 - 083D01_7, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ono, Masato; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Tochio, Daisuke; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2016/06
On March 11th, 2011, the Great East Japan Earthquake of magnitude 9.0 occurred. When the great earthquake occurred, the HTTR had been stopped under the periodic inspection and maintenance of equipment and instrument. In the great earthquake, the maximum seismic acceleration observed at the HTTR exceeded the maximum value in seismic design. The visual inspection of HTTR facility was carried out for the seismic integrity conformation of HTTR. The seismic analysis was also carried out using the observed earthquake motion at HTTR site to confirm the integrity of HTTR. The concept of comprehensive integrity evaluation for the HTTR facility is divided into two parts. One is the inspection of equipment and instrument. The other is the seismic response analysis using the observed earthquake. For the basic inspections of equipment and instrument were performed for all them related to the operation of reactor. The integrity of the facilities is confirmed by comparing the inspection results or the numerical results with their evaluation criteria. As the result of inspection of equipment and instrument and seismic response analysis, it was judged that there was no problem to operate the reactor, because there was no damage and performance deterioration, which affects the reactor operation. The integrity of HTTR was also supported by the several operations without reactor power in cold conditions of HTTR in 2011, 2013 and 2015.
Okumura, Yoshikazu; Gobin, R.*; Knaster, J.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02A739_1 - 02A739_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:35.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)IFMIF is an accelerator based neutron facility having two set of linear accelerators each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams (250mA in total) at 40MeV. The LIPAc (Linear IFMIF Prototype Accelerator) being developed in the IFMIF-EVEDA project consists of an injector, a RFQ accelerator, and a part of superconducting Linac, whose target is to demonstrate 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV. The injector has been developed in CEA Saclay and already demonstrated 140mA/100keV deuterium beam. The injector was disassembled and delivered to the International Fusion Energy Research Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan, and the commissioning has started after its reassembly 2014; the first beam production has been achieved in November 2014. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beam has been produced with a low beam emittance of 0.2  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
 /D
/D ion source for IFMIF (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility)
ion source for IFMIF (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility)Shinto, Katsuhiro; Sen e, F.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Chauvin, N.*; Gobin, R.*; Ichimiya, Ryo; Ihara, Akira; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kasugai, Atsushi; et al.
e, F.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Chauvin, N.*; Gobin, R.*; Ichimiya, Ryo; Ihara, Akira; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kasugai, Atsushi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02A727_1 - 02A727_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)Okumura, Yoshikazu; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; Gobin, R.*; Harrault, F.*; Heidinger, R.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.203 - 205, 2015/09
Under the framework of Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and Euratom, IFMIF/EVEDA project was launched in 2007 to validate the key technologies to realize IFMIF. The most crucial technology to realize IFMIF is two set of linear accelerator each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams up to 40MeV. The prototype accelerator, whose target is 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV, is being developed in International Fusion Research Energy Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan. The injector developed in CEA Saclay was delivered in Rokkasho in 2014, and is under commissioning. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beams and 100keV/90mA/CW duty deuterium ion beams are successfully produced with a low beam emittance of 0.21  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized). Delivery of RFQ components will start in 2015, followed by the installation of RF power supplies in 2015.
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized). Delivery of RFQ components will start in 2015, followed by the installation of RF power supplies in 2015.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Takahashi, Hiroki; Kondo, Keitaro; Kasugai, Atsushi; Gobin, R.*; Sen e, F.*; Chauvin, N.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Marqueta, A.*; et al.
e, F.*; Chauvin, N.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Marqueta, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.493 - 495, 2015/09
Development of the prototype accelerator (LIPAc) for the engineering validation of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) which is an accelerator driven neutron source has been progressed at Rokkasho. The LIPAc is a deuteron linear accelerator consisting of an injector, a radio-frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a superconducting linac. The objective of LIPAc is to produce a CW beam with the energy and current of 9 MeV and 125 mA, respectively. The injector was developed at CEA/Saclay and succeeded to produce CW proton and deuteron beams of 100 keV/140 mA by autumn 2012. After the test at CEA/Saclay, the injector was shipped to the International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Aomori and started to reassemble from the end of 2013. It was successfully produced proton beams in November 2014 at Rokkasho. While the ion source conditioning was done, the beam test was progressed. In this paper, the present status of the LIPAc injector at Rokkasho with some experimental results will be presented.
Takada, Shoji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Seki, Tomokazu; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to demonstrate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. The local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
Shimizu, Atsushi; Furusawa, Takayuki; Homma, Fumitaka; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Masayuki; Kondo, Masaaki; Isozaki, Minoru; Fujimoto, Nozomu; Iyoku, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(11-12), p.1444 - 1451, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has kept up a data-base system of operation and maintenance experiences of the HTTR. The objective of this system is to share the information obtained operation and maintenance experiences and to make use of lessons learned and knowledge into a design, construction and operation managements of the future HTGR. More than one thousand records have been registered into the system between 1997 and 2012. This paper describes the status of the data-base system, and provides suggestions for improvement from four experiences: (1) performance degradation of helium compressors; (2) malfunction of reserved shutdown system in reactivity control system; (3) maintenance experiences of emergency gas turbine generators; and (4) experiences of the Great East Japan Earthquake. These experiences are extracted from the system as important lessons learned to be expected to apply for design, construction and operation managements of future HTGR.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:104 Percentile:94.74(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English