Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kamiya, Junichiro; Nii, Keisuke*; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Harada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Yutaka; Matsuda, Makoto; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Ida, Yoshiaki*; et al.
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(4), p.344 - 349, 2023/05
no abstracts in English
Nii, Keisuke*; Ida, Yoshiaki*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamaguchi, Takanori*; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Harada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.601 - 604, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Nii, Keisuke*; Ida, Yoshiaki*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamaguchi, Takanori*; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Harada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.334 - 337, 2021/10
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Matsuda, Makoto; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Kako, Eiji*; Domae, Takeshi*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.299 - 302, 2021/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) tandem booster is one of the pioneering superconducting heavy ion linac in the world. It consists of 40 QWRs with an operation frequency of 130 MHz and 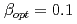 , and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
, and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
Nagano, Hirohiko; Nakayama, Masataka*; Katata, Genki*; Fukushima, Keitaro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Watanabe, Makoto*; Kondo, Toshiaki*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Kubota, Tomohiro*; Tateno, Ryunosuke*; et al.
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 67(5), p.606 - 616, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.07(Plant Sciences)We analyzed the relationships between nitrogen deposition (deposition of nitrate and ammonium ions) and soil microbial properties in a cool temperate forest surrounded by normally fertilized pasture grasslands in northern Japan. The aim of the present study was to gain the primary information on soil microbial response to moderately elevated nitrogen deposition ( 10 kg N ha
10 kg N ha y
y ). We established three experimental plots in the forest edge adjacent to grasslands and other three plots in the forest interior at least 700 m away from the grasslands. During May to November 2018, nitrogen deposition in each plot was measured. In August 2018, litter and soil (0-5 cm depth) samples were collected from all plots to measure net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification rates as indicators of microbial activity, and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and various gene abundances (i.e. bacterial 16S rRNA, fungal ITS, bacterial amoA, and archaeal amoA genes) as indicators of microbial abundance and structure. Nitrogen deposition in the forest edge was 1.4-fold greater than that in the forest interior, even while the maximum deposition was 3.7 kg N ha
). We established three experimental plots in the forest edge adjacent to grasslands and other three plots in the forest interior at least 700 m away from the grasslands. During May to November 2018, nitrogen deposition in each plot was measured. In August 2018, litter and soil (0-5 cm depth) samples were collected from all plots to measure net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification rates as indicators of microbial activity, and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and various gene abundances (i.e. bacterial 16S rRNA, fungal ITS, bacterial amoA, and archaeal amoA genes) as indicators of microbial abundance and structure. Nitrogen deposition in the forest edge was 1.4-fold greater than that in the forest interior, even while the maximum deposition was 3.7 kg N ha . Nitrogen deposition was significantly correlated to the net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification rates and the 16S rRNA and bacterial amoA gene abundances. Microbial community structures were different between litter and soil samples but were similar between the forest edge and interior. Significant correlations of nitrogen deposition to the soil carbon to nitrogen ratio, and the nitrate and ammonium contents were also observed. Thus, our results show that moderately elevated nitrogen deposition in nitrogen-limited forest edges can stimulate microbial activities and abundances in soils.
. Nitrogen deposition was significantly correlated to the net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification rates and the 16S rRNA and bacterial amoA gene abundances. Microbial community structures were different between litter and soil samples but were similar between the forest edge and interior. Significant correlations of nitrogen deposition to the soil carbon to nitrogen ratio, and the nitrate and ammonium contents were also observed. Thus, our results show that moderately elevated nitrogen deposition in nitrogen-limited forest edges can stimulate microbial activities and abundances in soils.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Park, C. H.*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 146(Part A), p.285 - 288, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Herein, the wall shear stress in a double contraction nozzle has been evaluated experimentally to produce a liquid lithium (Li) target as a beam target for intense fusion neutron sources such as the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), the Advanced Fusion Neutron Source (A-FNS), and the DEMO Oriented Neutron Source (DONES). The boundary layer thickness and wall shear stress are essential physical parameters to understand erosion-corrosion by the high-speed liquid Li flow in the nozzle, which is the key component in producing a stable Li target. Therefore, these parameters were experimentally evaluated using an acrylic mock-up of the target assembly. The velocity distribution in the nozzle was measured by a laser-doppler velocimeter and the momentum thickness along the nozzle wall was calculated using an empirical prediction method. The resulting momentum thickness was used to estimate the variation of the wall shear stress along the nozzle wall. Consequently, the wall shear stress was at the maximum in the second convergent section in front of the nozzle exit.
Ono, Masato; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 2(4), p.044502_1 - 044502_4, 2016/10
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to verify safety evaluation codes to investigate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. The VCS passively removes the retained residual heat and the decay heat from the core via the reactor pressure vessel by natural convection and thermal radiation. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. Through a cold test, which was carried out by non-nuclear heat input from gas circulators with stopping water flow in the VCS, the local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Kawamoto, Taiki; Kondo, Makoto; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Takada, Shoji; Shinozaki, Masayuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(2), p.66 - 69, 2016/06
High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) has the reactivity control system which is accompanied with the Reserved Shutdown System (RSS). The RSS consists of B C/C pellets, guide tube, electric plug, motor which contains brake and reducer, and so on. In accidents when the control rods cannot be inserted, an electric plug is pulled out by motor and the B
C/C pellets, guide tube, electric plug, motor which contains brake and reducer, and so on. In accidents when the control rods cannot be inserted, an electric plug is pulled out by motor and the B C/C pellets fall into the core by gravity. It was revealed that the motor in the RSS drive mechanism did not work as the result of pre-start up checks as described followings: (1) The oil which was separated from a grease of motor reducer flowed down from gap of oil seal, (2) the separated oil penetrated into the brake, (3) the penetrated oil was mixed with abrasion powder released from brake disk, finally, (4) the adhesive mixture blocked the rotation of the motor. A new evaluation method was proposed to detect a sign of the motor sticking. Through the overhaul inspection of all RSS drive mechanisms of HTTR, it was revealed that the proposed method was effective to evaluate the integrity of the RSS drive mechanism.
C/C pellets fall into the core by gravity. It was revealed that the motor in the RSS drive mechanism did not work as the result of pre-start up checks as described followings: (1) The oil which was separated from a grease of motor reducer flowed down from gap of oil seal, (2) the separated oil penetrated into the brake, (3) the penetrated oil was mixed with abrasion powder released from brake disk, finally, (4) the adhesive mixture blocked the rotation of the motor. A new evaluation method was proposed to detect a sign of the motor sticking. Through the overhaul inspection of all RSS drive mechanisms of HTTR, it was revealed that the proposed method was effective to evaluate the integrity of the RSS drive mechanism.
Takada, Shoji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Seki, Tomokazu; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to demonstrate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. The local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
Someya, Yoji; Tobita, Kenji; Yanagihara, Satoshi*; Kondo, Masatoshi*; Uto, Hiroyasu; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hoshino, Kazuo; Nakamura, Makoto; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2033 - 2037, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the replacement period of a fusion power reactor, the assembly of blanket or divertor modules need to be removed from the reactor in order to minimize remote maintenance in the vacuum vessel and to attain a reasonable plant availability. In the hot cell, the modules will be removed from the backplate of the assembly. Here, note that the active cooling must be done by a way that does not cause contamination of the hot cell environment due to dispersion of tritium and tungsten dust. In this sense, the cooling scenario is adopted that the existing pipe of cooling water in the assembly is connected to a different cooling water system in the hot cell. In this scenario, the temperature of the assembly is maintained about 40-100 C. On the other hand, the structural material (RAFM) of the blanket and divertor is not recycled due to its high contact dose rate. It should be crushed into small pieces to reduce volume of the waste and required storage space. Here, the decay heat must be removed by natural convection to keep the temperature below 65
C. On the other hand, the structural material (RAFM) of the blanket and divertor is not recycled due to its high contact dose rate. It should be crushed into small pieces to reduce volume of the waste and required storage space. Here, the decay heat must be removed by natural convection to keep the temperature below 65 C for preventing water evaporation from the mortar. The RAFM is kept in the interim storage during 12 years until the required temperature conditions for mortar are ensured and then is disposed of.
C for preventing water evaporation from the mortar. The RAFM is kept in the interim storage during 12 years until the required temperature conditions for mortar are ensured and then is disposed of.
Kugo, Teruhiko; Ishikawa, Makoto; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Yokoyama, Kenji; Fukaya, Yuji; Maruyama, Hiromi*; Ishii, Yoshihiko*; Fujimura, Koji*; Kondo, Takao*; Minato, Hirokazu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-046, 53 Pages, 2014/03
The present report summarizes the results of a 2-year cooperative study between JAEA and Hitachi-GE in order to contribute to the settlement of the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants which suffered from the severe accident on March 2011. In the present study, the possible scenarios to reach the recriticality events in Fukushima-Daiichi were investigated first. Then, the analytical methodology to evaluate the time-dependent recriticality events has been developed by modelling the reactivity insertion rate and the possible feedback according to the recriticality scenarios identified in the first step. The methodology developed here has been equipped as a transient simulation tool, PORCAS, which is operated on a multi-purpose platform for reactor analysis, MARBLE. Finally, the radiation exposure rates by the postulated recriticality events in Fukushima-Daiichi were approximately evaluated to estimate the impact to the public environment.
Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Ida, Mizuho; Kondo, Hiroo; Miyashita, Makoto; Nakamura, Hiroo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.1299 - 1302, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity (EVEDA) of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) has been started under the Broader Approach Agreement. For the target assembly in the EVEDA Li test loop, two kinds of the back plates, "Integrated type" of SUS316L and "Bayonet type" of F82H, are going to be manufactured and tested. For thermo-structural design of the target assembly, we carried out thermo-structural analysis for these two types of the back plates by using the ABAQUS computer code. In the case of assuming thermal insulation for outer surface of the target assembly, the maximum stress of integrated type was 39.2 MPa, and that of Bayonet type was 340 MPa. These were lower than the permissible stress of their materials, therefore it was evaluated that insulation was effective against decreasing thermal stress.
Ida, Mizuho; Fukada, Satoshi*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Kondo, Hiroo; Miyashita, Makoto; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugiura, Hirokazu*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.1294 - 1298, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA) of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) was started. As a Japanese activity for the target system, EVEDA Lithium Test Loop simulating hydraulic and impurity conditions of IFMIF is under design and preparation for fabrication. Feasibility of thermo-mechanical structure of the target assembly and the replaceable back-plate made of F82H (a RAFM) and 316L (a stainless steel) is a key issue. Toward final validation on the EVEDA loop, diagnostics applicable to a high-speed free-surface Li flow and hot traps to control nitrogen and hydrogen in Li are under tests. For remote handling of target assemblies and the replaceable back-plates activated up to 50 dpa/y, lip weld on 316L-316L by laser and dissimilar weld on F82H-316L are under investigation. As engineering design of the IFMIF target system, water experiments and hydraulic/thermo-mechanical analyses of the back-plate are going.
Nishida, Akemi; Araya, Fumimasa; Kushida, Noriyuki; Kondo, Makoto; Sakai, Michiya*; Shiogama, Yuzo*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.576 - 581, 2011/10
Design evaluation of nuclear facilities would be facilitated by a numerical evaluation system that can evaluate both global and local behaviors under severe seismic loading. A critical part of such a system is the numerical model describing the dynamic physical interactions among component connections, called the elastic-plastic connection model. Here we propose such a model and use it to simulate dynamic interactions using real earthquake and plant data from the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) of the JAEA. We focus on joints connecting the component supports and the building walls, which generally involve fixed/pinned boundary conditions. The results confirmed a reduction in the vibration response and a change in the natural frequencies of individual components under large virtual earthquake loading, which are considered to have resulted from dynamic interactions between the joints connecting the component supports and the building walls.
Hasegawa, Makoto; Kondo, Hitoshi; Kamei, Gento; Hirano, Fumio; Mihara, Morihiro; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Ueda, Hiroyoshi*; Oi, Takao*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-003, 47 Pages, 2011/02
In 2009, NUMO and JAEA set up a technical commission to investigate the reasonable TRU waste disposal following a cooperation agreement between these two organizations. In this report, the calculation result of radionuclide transport for a TRU waste geological disposal system was described, by using the TIGER code and the GoldSim code at identical terms. Comparing the calculation result, a big difference was not seen. Therefore, the reliability of both codes was able to be confirmed. Moreover, the influence on the disposal site design (Disposal capacity: 19,000 m ) was examined when 10% of the amount of TRU waste increased. As a result, it was confirmed that the influence of the site design was very little based on the concept of the Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan.
) was examined when 10% of the amount of TRU waste increased. As a result, it was confirmed that the influence of the site design was very little based on the concept of the Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan.
Kondo, Hiroo; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Nakamura, Hiroo*; Ida, Mizuho; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Miyashita, Makoto*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Kanemura, Takuji; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
The Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity (EVEDA) for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is proceeded as one of the ITER Broader Approach (BA) activities. The EVEDA Li test loop (ELTL) is aimed at validating stability of the Li target and feasibility of a Li purification system as the key issues. In this paper, the design of the ELTL especially of a target assembly in which the Li target is produced by the contraction nozzle is presented.
Nishida, Akemi; Araya, Fumimasa; Kushida, Noriyuki; Kondo, Makoto; Sakai, Michiya*; Shiogama, Yuzo*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2010/10
The objective of this research is to contribute to the seismic design evaluation of nuclear facilities through the construction of a numerical evaluation system which is able to evaluate both global and local behaviors of facilities under severe seismic events. As one of the technology components to realize this objective, we are developing a physical model describing the dynamic interaction characteristics of component connections, called as the elastic-plastic connection model. We focused on the joints of the support structures of the component and the building in nuclear plants which generally designed as fixed/pinned boundaries, and tried to consider their dynamic interaction effects. In this paper, we show the proposal of the elastic-plastic connection model and the application of the model to a numerical simulation using a real plant data. The precision of the model was optimized by adjusting its parameters using the data obtained in the experiment.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.702 - 705, 2010/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. In this study we have tested simultaneous generation of protons and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the thin-foil target. We observed the high-energy proton in the rear side of the target and THz radiation in the reflected direction. Next, high energy protons are observed by reducing the size of preformed plasma.
Kondo, Makoto; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Motegi, Toshihiro; Emori, Koichi
JAEA-Testing 2009-002, 50 Pages, 2009/08
High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is a test reactor that build on sand layer formed during quaternary era. In principle, nuclear power generation facilities need to be supported on rigid rock formed during tertiary era, and now it is investigated to construct nuclear power generation facilities on sand layer formed during quaternary era for expanding suitable location. For this reason, we installed seismic observation systems in HTTR. And we have performed seismic safety evacuation using measured seismic acceleration in ground and building. This report compiles specifications of seismic observation systems, contents of check for seismic observation systems, check result of seismic observation systems and maintenance of seismic observation systems in HTTR.