Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishida, Tsuyoshi; Nakashima, Shinichi; Kondo, Shinji; Hayashibara, Kenichi; Yamada, Shigeki*; Okamoto, Ryo*; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-44-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
 -gas exposure at high temperatures
-gas exposure at high temperaturesTakeda, Yusuke; Iida, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Shinji*; Matsuo, Tadatoshi*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hirade, Tetsuya
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 25, p.011023_1 - 011023_3, 2019/03
In this study, we prepared samples under two different conditions, (1) 810 C, for 600 min, and (2) 850
C, for 600 min, and (2) 850 C, for 720 min. A depth-profile analysis of the surfaces of the samples is conducted through Doppler broadening (DB) measurements of positron annihilation
C, for 720 min. A depth-profile analysis of the surfaces of the samples is conducted through Doppler broadening (DB) measurements of positron annihilation  rays using a slow positron beam. It was indicated that many of positrons annihilated in defects near the surface. According to the TEM image, there are nano-crystal grains near the surface and then positrons can diffuse in the grains and annihilate in defects at the grain boundaries. Furthermore, DB measurements indicated that there is a depth dependence on the chemical composition where positrons annihilate. EDS spectroscopy measurements also indicated that there is a depth dependence of impurities such as Vanadium. These results indicated change of the chemical composition at the grain boundaries.
rays using a slow positron beam. It was indicated that many of positrons annihilated in defects near the surface. According to the TEM image, there are nano-crystal grains near the surface and then positrons can diffuse in the grains and annihilate in defects at the grain boundaries. Furthermore, DB measurements indicated that there is a depth dependence on the chemical composition where positrons annihilate. EDS spectroscopy measurements also indicated that there is a depth dependence of impurities such as Vanadium. These results indicated change of the chemical composition at the grain boundaries.
 -gas exposure at high temperatures
-gas exposure at high temperaturesTakeda, Yusuke; Iida, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Shinji*; Matsuo, Tadatoshi*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hirade, Tetsuya
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 791(1), p.012022_1 - 012022_4, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:39.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Titanium alloy is widely used for applications such as golf club heads and structural materials for aircrafts. The surface can be exceedingly hardened by nitriding treatment that initiates defects, but there are some difficulties on use of titanium nitride because the layer can be exfoliated by stress. Therefore, we prepared samples in two different treatment conditions, (1) 810 C 600 min and (2) 850
C 600 min and (2) 850 C 720 min and performed depth profile analysis of Doppler broadening of positron annihilation
C 720 min and performed depth profile analysis of Doppler broadening of positron annihilation  -rays (DB) for these samples. According to a calculation of nitrogen diffusion depth, the nitride layer should be only about 0.05-0.1
-rays (DB) for these samples. According to a calculation of nitrogen diffusion depth, the nitride layer should be only about 0.05-0.1 m. However, the depth profile analysis of the DB measurement indicated that the defects introduced by nitriding treatment extended to a depth of 0.5
m. However, the depth profile analysis of the DB measurement indicated that the defects introduced by nitriding treatment extended to a depth of 0.5 m.
m.
 Si
Si observed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy
observed by X-ray absorption spectroscopyNakai, Hirohito*; Ebihara, Takao*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(12), p.124712_1 - 124712_5, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The temperature and magnetic field dependences of Yb valence were observed in the heavy fermion compoundYbRh Si
Si by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The measurements revealed that the Yb valence decreases with decreasing temperature in the range from 200 to 2 K and increases with increasing magnetic field in the range from 0 to 33 T without showing an abrupt change in the Yb valence. The Yb valence is in the range from 2.92 to 2.96 depending on temperature and magnetic field. With respect to the valence being 2.92 at 0 T and 2.93 at 33 T in 2 K, YbRh
by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The measurements revealed that the Yb valence decreases with decreasing temperature in the range from 200 to 2 K and increases with increasing magnetic field in the range from 0 to 33 T without showing an abrupt change in the Yb valence. The Yb valence is in the range from 2.92 to 2.96 depending on temperature and magnetic field. With respect to the valence being 2.92 at 0 T and 2.93 at 33 T in 2 K, YbRh Si
Si is a valence fluctuation compound and does not reach the integer trivalent state at high magnetic field. These results endorse the conventional knowledge that the valence of Yb is very close to the integer value of 3+, decreases with decreasing temperature, and becomes closer to 3+ with increasing magnetic field.
is a valence fluctuation compound and does not reach the integer trivalent state at high magnetic field. These results endorse the conventional knowledge that the valence of Yb is very close to the integer value of 3+, decreases with decreasing temperature, and becomes closer to 3+ with increasing magnetic field.
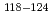 Sn and the
Sn and the  -ray strength function method
-ray strength function methodUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Kamata, Masaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Kondo, Takeo*; Ito, Osamu*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Lui, Y.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 84(5), p.055805_1 - 055805_6, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:89.64(Physics, Nuclear)Photoneutron cross sections were measured for 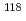 Sn,
Sn, 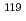 Sn,
Sn, 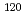 Sn,
Sn, 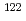 Sn, and
Sn, and 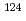 Sn near neutron threshold with quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton scattering
Sn near neutron threshold with quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton scattering  -rays. A systematic analysis of the present photoneutron data and existing neutron-capture data is made using the
-rays. A systematic analysis of the present photoneutron data and existing neutron-capture data is made using the  -ray strength function on the basis of the HFB+QRPA model of E1 strength supplemented with a pygmy dipole resonance, which was deduced from a previous study on
-ray strength function on the basis of the HFB+QRPA model of E1 strength supplemented with a pygmy dipole resonance, which was deduced from a previous study on 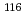 Sn and
Sn and 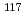 Sn. Radiative neutron capture cross sections for two radioactive nuclei,
Sn. Radiative neutron capture cross sections for two radioactive nuclei, 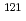 Sn and
Sn and 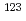 Sn, are deduced through the
Sn, are deduced through the  -ray strength function method.
-ray strength function method.
 SF method
SF methodUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Kondo, Takeo*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Okamoto, Akiyuki*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.255 - 259, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Ito, Osamu*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Kondo, Takeo*; Kamata, Masaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.362 - 364, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics) SF method to palladium
SF method to palladiumUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Arteaga, D. P.*; Daoutidis, I.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Kondo, Takeo*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Kamata, Masaki*; Ito, Osamu*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.450 - 452, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics) -rays and data reduction by a least-squares method
-rays and data reduction by a least-squares methodIto, Osamu*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Kondo, Takeo*; Kamata, Masaki*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(5), p.834 - 840, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:92.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)Photoneutron cross section measurements were made for Au in the entire energy range of the ( ,n) channel based on a direct neutron-counting technique with quasi-monochromatic
,n) channel based on a direct neutron-counting technique with quasi-monochromatic  -rays produced in inverse Compton-scattering of laser photons with relativistic electrons. The data were analyzed with a least-squares method to deduce photoneutron cross sections. The analysis significantly reduced experimental uncertainties compared with those resulted from the photon difference method. The result is compared with the previous data by direct neutron-counting with
-rays produced in inverse Compton-scattering of laser photons with relativistic electrons. The data were analyzed with a least-squares method to deduce photoneutron cross sections. The analysis significantly reduced experimental uncertainties compared with those resulted from the photon difference method. The result is compared with the previous data by direct neutron-counting with  -rays produced in positron annihilation in flight and by photoactivation with bremsstrahlung. The present data are in good agreement with the previous data near neutron threshold, while there remain some discrepancies between the present and the previous data above 10 MeV.
-rays produced in positron annihilation in flight and by photoactivation with bremsstrahlung. The present data are in good agreement with the previous data near neutron threshold, while there remain some discrepancies between the present and the previous data above 10 MeV.
Hasegawa, Makoto; Kondo, Hitoshi; Kamei, Gento; Hirano, Fumio; Mihara, Morihiro; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Ueda, Hiroyoshi*; Oi, Takao*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-003, 47 Pages, 2011/02
In 2009, NUMO and JAEA set up a technical commission to investigate the reasonable TRU waste disposal following a cooperation agreement between these two organizations. In this report, the calculation result of radionuclide transport for a TRU waste geological disposal system was described, by using the TIGER code and the GoldSim code at identical terms. Comparing the calculation result, a big difference was not seen. Therefore, the reliability of both codes was able to be confirmed. Moreover, the influence on the disposal site design (Disposal capacity: 19,000 m ) was examined when 10% of the amount of TRU waste increased. As a result, it was confirmed that the influence of the site design was very little based on the concept of the Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan.
) was examined when 10% of the amount of TRU waste increased. As a result, it was confirmed that the influence of the site design was very little based on the concept of the Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan.
 -ray strength function method and its application to
-ray strength function method and its application to  Pd
PdUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*; Kondo, Takeo*; Ito, Osamu*; et al.
Physical Review C, 82(6), p.064610_1 - 064610_5, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:88.18(Physics, Nuclear)The  -ray strength function method (
-ray strength function method ( SF method) is devised to indirectly determine radiative neutron capture cross sections for radioactive nuclei. This method is applied here to the
SF method) is devised to indirectly determine radiative neutron capture cross sections for radioactive nuclei. This method is applied here to the  Pd case. Photoneutron cross sections were measured for
Pd case. Photoneutron cross sections were measured for 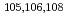 Pd near neutron threshold with quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton-scattering
Pd near neutron threshold with quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton-scattering  -ray beams. These photoneutron cross sections as well as the reverse radiative neutron capture cross sections for
-ray beams. These photoneutron cross sections as well as the reverse radiative neutron capture cross sections for 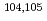 Pd are used to provide constraints on the
Pd are used to provide constraints on the  Pd(n,
Pd(n, )
) 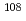 Pd cross section.
Pd cross section.
 Zr near threshold
Zr near thresholdUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Kondo, Takeo*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Ito, Osamu*; Kamata, Masaki*; Io, Masanori*; Kususe, Koichi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.447 - 449, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)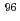 Zr; A Systematic experimental study of photoneutron and radiative neutron capture cross sections for zirconium isotopes
Zr; A Systematic experimental study of photoneutron and radiative neutron capture cross sections for zirconium isotopesUtsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*; Kondo, Takeo*; Ito, Osamu*; et al.
Physical Review C, 81(3), p.035801_1 - 035801_5, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:87.05(Physics, Nuclear)This manuscript presents photoneutron cross sections for 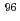 Zr. Combining the present data with the previously published Zr data, we investigated the
Zr. Combining the present data with the previously published Zr data, we investigated the  -ray strength function for zirconium isotopes systematically. We present a unified picture of the
-ray strength function for zirconium isotopes systematically. We present a unified picture of the  -ray strength function that consists of the HFB + QRPA model of E1 strength accompanied by an extra M1 strength attributable to giant M1 resonance. It is shown that the
-ray strength function that consists of the HFB + QRPA model of E1 strength accompanied by an extra M1 strength attributable to giant M1 resonance. It is shown that the  -ray strength function reproduces both (g,n) and (n,g) cross sections for Zr isotopes consistently.
-ray strength function reproduces both (g,n) and (n,g) cross sections for Zr isotopes consistently.
Murai, Yuichi*; Oiwa, Hiroshi; Sasaki, Toshio*; Kondo, Masahiko; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamamoto, Fujio*
Measurement Science and Technology, 16(7), p.1459 - 1468, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:83.87(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Air-water two-phase flow in a helically coiled tube is investigated using backlight imaging tomography to elucidate the effect of centrifugal acceleration on phase distribution and interfacial structure. Superficial velocities up to 6m/s in 20mm-diameter tube are tested. We focused on a slug flow regime in which centrifugal acceleration dominates the flow. The interfacial structure is visualized in six directions using a set of originally designed mirror-mounted water jackets. A temporal expansion image is made from line-sampled images, and is used to reconstruct phase distribution through a linear backward projection algorithm. The present topography measurement showed various new features of gas-liquid two-phase flow in a helically coiled tube, such as a wall-covering effect in the case of high superficial velocity.
Yoshikawa, Shinji; Tamayama, Kiyoshi; Suzuki, Ryosuke*; Kondo, Koki*; Nakai, Satoshi*; NAKAI, Satoshi*
The 23rd International Conference on Termoelectric, 0 Pages, 2004/12
A prototype system for thermoelectric power generation using the Heusler Fe2 VAI alloy has been studied as a potential heat recovery system from a liquid metal cooled fast breeder reactor. The modules consisting of 180 pairs using Fe2VAi cast alloy were mouted on 1.8 m long of the outer surface of a stainless tube (O.D. 34mm) which is internally heated by flowing liquid sodium (484-670K, 2-8 1/min). The element has a shape of a long cuboid, where one small rectangular end was thermally contacted with the tube surface and the other end was directly cooled by forced air flow to form a counter-type heat exchanger. The internal electric resistances of the modules were nearly same, however, the electromotive force varied widely because of the difference of thermal resistance between the module and tube surface. The output power generated from this prototype system was evaluated to be about 4.2 W/m assuming that all the circumference of the pipe surface is covered by the elements.
Nanayama, Futoshi*; Yamaguchi, Tatsuhiko*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Tsuji, Tomohiro*; Ikeda, Michiharu*; Kondo, Yasuo*; Miwa, Michiko*; Sugiyama, Shinji*; Kimura, Kazunari*
no journal, ,
The characteristics of the post-LGM incised valley fills and the depositional sequence were examined the SKM core collected in the Sukumo coastal lowland, where is expected to huge seismic subsidence due to the Nankai Trough great earthquakes. Our sedimentological, radiocarbon dating and paleoenvironmental results are as bellows. Sediments of the SKM core clearly show a succession influenced by post-glacial sea level change. The Matsuda River incised valley was formed in LGM and filled by fluvial sand and gravels in late Pleistocene. After the postglacial transgression, sea level reached -30 m (a.s.l.) at 9.8 ka and the incised valley changed to an estuary environment. The sea level continued to rise and it became an inner bay mud bottom environment, and reaching a maximum water depth was at 7.5 ka. The 7.3 ka Kikai caldera eruption in southern Kyushu caused heavy K-Ah ash fall in southwestern Shikoku, and then large-scale lahars frequently occurred immediately after the ash fall because of the vicinity of volcanic source. After ash fall, the K-Ah secondary sediments rapidly deposited on the inner bay environment and caused forced regression. After 7.0 ka, the growth of the delta became active ahead of the other regions, which may be due to the large K-Ah ash fall. At 5 ka, the sea level reached + 2.5 m (a.s.l.) estimated by the Sukumo midden and this altitude is recognized as the Holocene marine limit in this area. The information on relative sea level change during the past 10000 years has revealed that the Sukumo Bay area has not subsided due to seismic crustal deformation.
Takeda, Yusuke; Iida, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Shinji*; Matsuo, Tadatoshi*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
The impact stress exfoliates a Nitride surface layer on Titanium alloy prepared in some conditions. So we prepared specimens in two different conditions, (1) 810 C, 600min and (2) 850
C, 600min and (2) 850 C, 720min, and performed depth profile analysis of their surfaces with Doppler broadening measurements of positron annihilation
C, 720min, and performed depth profile analysis of their surfaces with Doppler broadening measurements of positron annihilation  -rays (DB) that is sensitive for defects by Slow Positron beams. Although the specimens (2) is harder than (1) according to the Vickers Hardness test, DB results indicated that defect layer of specimen (1) is thicker than (2). It means that the defect layer thickness was not the cause of surface hardening. Furthermore, chemical elements at the positron annihilation sites could be analyzed qualitatively by DB and the change of the composition appeared in deeper region than the defect layer. The defect layer depth does not match the depth where chemical composition changes by DB appeared. TEM and EDS observation showed different tendency from the results by DB. It is because positrons probe specific sites, and the combination of these methods will be a strong tool to investigate surface structures.
-rays (DB) that is sensitive for defects by Slow Positron beams. Although the specimens (2) is harder than (1) according to the Vickers Hardness test, DB results indicated that defect layer of specimen (1) is thicker than (2). It means that the defect layer thickness was not the cause of surface hardening. Furthermore, chemical elements at the positron annihilation sites could be analyzed qualitatively by DB and the change of the composition appeared in deeper region than the defect layer. The defect layer depth does not match the depth where chemical composition changes by DB appeared. TEM and EDS observation showed different tendency from the results by DB. It is because positrons probe specific sites, and the combination of these methods will be a strong tool to investigate surface structures.