Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Okada, Hajime; Shimomura, Takuya; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Tanoue, Manabu; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Yogo, Akifumi; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 1, p.015095_1 - 015095_5, 2014/03
We present the design and characterization of a high-contrast, petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser system. Two saturable absorbers and low-gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier in the double CPA laser chain have improved the temporal contrast to 1.4 10
10 on the subnanosecond time scale at 70 terawatt level. Final uncompressed broadband pulse energy is 28 J, indicating the potential for reaching peak power near 600 terawatt. We also discuss our upgrade to over petawatt level at a 0.1 Hz repetition rate briefly.
on the subnanosecond time scale at 70 terawatt level. Final uncompressed broadband pulse energy is 28 J, indicating the potential for reaching peak power near 600 terawatt. We also discuss our upgrade to over petawatt level at a 0.1 Hz repetition rate briefly.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 42(2), p.160 - 162, 2014/02
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical and other applications. We have measured the proton yield from thin-foil targets irradiated with a high-intensity Ti:sapphire laser (J-KAREN) at JAEA. The longitudinal extent of the preformed plasma protruding from the front surface of the target is reduced by decreasing the duration of the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) before the main pulse. The maximum proton energy in the target normal direction increases when the size of the preformed plasma is controlled.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Shimomura, Takuya; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Tanoue, Manabu; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Applied Sciences (Internet), 3(1), p.214 - 250, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:50(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)This paper reviews techniques for improving the temporal contrast and spatial beam quality in an ultra-intense laser system that is based on chirped-pulse amplification (CPA). We describe the design, performance, and characterization of our laser system, which has the potential for achieving a peak power of 600 TW. We also describe applications of the laser system in the relativistically dominant regime of laser-matter interactions and discuss a compact, high efficiency diode-pumped laser system.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Tanoue, Manabu; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
Optics Letters, 37(16), p.3363 - 3365, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:85.86(Optics)We demonstrate the temporal contrast enhancement in a petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser system. An extra saturable absorber, introduced downstream a low gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier, has improved the temporal contrast in the system to 1.4 10
10 on the sub-nanosecond time scale at 70 TW power level. We have achieved 28 J of uncompressed broadband output energy with this system, indicating the potential for reaching peak powers near 600 TW.
on the sub-nanosecond time scale at 70 TW power level. We have achieved 28 J of uncompressed broadband output energy with this system, indicating the potential for reaching peak powers near 600 TW.
Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sagisaka, Akito*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Kando, Masaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Optics Letters, 37(14), p.2868 - 2870, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:95.88(Optics)Using high contrast (10 :1) and high intensity (10
:1) and high intensity (10 W/cm
W/cm ) laser pulse with the duration of 40 fs from OPCPA/Ti:Sapphire laser, a 40 MeV proton bunch is obtained, which is a record for laser pulse with energy less than 10 J. The efficiency for generation of protons with kinetic energy above 15 MeV is 0.1%.
) laser pulse with the duration of 40 fs from OPCPA/Ti:Sapphire laser, a 40 MeV proton bunch is obtained, which is a record for laser pulse with energy less than 10 J. The efficiency for generation of protons with kinetic energy above 15 MeV is 0.1%.
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(4), p.048003_1 - 048003_2, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.93(Physics, Applied)A proton beam driven by a repetitive high-intensity-laser is utilized to induce a  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be nuclear reaction. The total activity of
Be nuclear reaction. The total activity of  Be are evaluated by two different methods. The activity obtained measuring the decay
Be are evaluated by two different methods. The activity obtained measuring the decay  -rays after 1912 shots at 1 Hz is 1.7
-rays after 1912 shots at 1 Hz is 1.7 0.2 Bq. This is in good agreement with 1.6
0.2 Bq. This is in good agreement with 1.6 0.3 Bq evaluated from the proton energy distribution measured using a time-of-flight detector and the nuclear reaction cross-sections. We conclude that the production of activity can be monitored in real time using the time-of-flight-detector placed inside a diverging proton beam coupled with a high-speed signal processing system.
0.3 Bq evaluated from the proton energy distribution measured using a time-of-flight detector and the nuclear reaction cross-sections. We conclude that the production of activity can be monitored in real time using the time-of-flight-detector placed inside a diverging proton beam coupled with a high-speed signal processing system.
Kondo, Takeo*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Okamoto, Akiyuki*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Shima, Tatsushi*; Horikawa, Ken*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 659(1), p.462 - 466, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:89.17(Instruments & Instrumentation)We measured pulse-height spectra of 16.7 MeV laser-Compton scattering photons with a 6" 5" NaI(Tl) detector for blank and three lead materials of 75.8, 50.9, and 25.9% transmissions at the NewSUBARU facility to investigate how the original Poisson distribution of the pulsed photons is modified after passing through thick-target materials. We present a well-prescribed method of determining the number of incident photons within 3.5% accuracy based on the response of the NaI(Tl) detector to the pulsed photon beams.
5" NaI(Tl) detector for blank and three lead materials of 75.8, 50.9, and 25.9% transmissions at the NewSUBARU facility to investigate how the original Poisson distribution of the pulsed photons is modified after passing through thick-target materials. We present a well-prescribed method of determining the number of incident photons within 3.5% accuracy based on the response of the NaI(Tl) detector to the pulsed photon beams.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kawase, Keigo*; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Koga, J. K.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(6), p.066401_1 - 066401_3, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.79(Physics, Applied)Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 637(1, Suppl.), p.S141 - S144, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)We report the present status of the sub-MeV X-ray generation via Compton backscattering by using 150-MeV electron beam and the Nd:YAG laser. In particular, we show the result of the X-ray generation experiment and of the laser pulse compression for increasing the X-ray flux.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
NIFS-PROC-85, p.30 - 33, 2011/02
The experiment of proton generation is performed for developing the laser-driven ion source. We observe proton signals in the laser-plasma interaction by using a thin-foil target. To get higher energy protons the size of the preformed plasma is reduced by changing the laser contrast level. In the high-contrast laser pulse case the maximum energy of the protons generated at rear side of the target increases.
Kuramitsu, Yasuhiro*; Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Kondo, Kiminori; Sakawa, Yoichi*; Mori, Yoshitaka*; Miura, Eisuke*; Tsuji, Kazuki*; Kimura, Kazuya*; Fukumochi, Shuji*; Kashihara, Mamoru*; et al.
Physical Review E, 83(2), p.026401_1 - 026401_6, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An energy distribution function of energetic particles in the universe or cosmic rays is well represented by a power-law spectrum, therefore, nonthermal acceleration is essential to understand the origin of cosmic rays. A possible candidate for the origin of cosmic rays is wakefield acceleration at relativistic astrophysical perpendicular shocks. Substituting an intensive laser pulse for the large amplitude light waves, we performed a model experiment of the shock environments in a laboratory plasma.
Kuramitsu, Yasuhiro*; Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Kondo, Kiminori; Sakawa, Yoichi*; Mori, Yoshitaka*; Miura, Eisuke*; Tsuji, Kazuki*; Kimura, Kazuya*; Fukumochi, Shuji*; Kashihara, Mamoru*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 18(1), p.010701_1 - 010701_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.41(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Substituting an intensive laser pulse for the large amplitude light waves, we performed a model experiment of the shock environments in a laboratory plasma. An intensive laser pulse was propagated in a plasma tube created by imploding a hollow polystyrene cylinder, as the large amplitude light waves propagated in the upstream plasma at an astrophysical shock. Nonthermal electrons were generated, and the energy distribution functions of the electrons have a power-law component with an index of 2.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime*; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.669 - 675, 2010/09
This paper reviews the temporal contrast and spatial beam quality improvement techniques in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped-pulse amplification (CPA). We describe a low gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier that uses high energy, clean pulse seeding and is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 10 -10
-10 relative to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. We also report the use of a diffractive optical element for beam homogenization of a 100 J level Nd:glass green pump laser, achieving a flat-topped spatial profile with a filling factor near 80 %.
relative to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. We also report the use of a diffractive optical element for beam homogenization of a 100 J level Nd:glass green pump laser, achieving a flat-topped spatial profile with a filling factor near 80 %.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.702 - 705, 2010/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. In this study we have tested simultaneous generation of protons and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the thin-foil target. We observed the high-energy proton in the rear side of the target and THz radiation in the reflected direction. Next, high energy protons are observed by reducing the size of preformed plasma.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Orimo, Satoshi; Kondo, Kiminori; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.312 - 315, 2010/08
The beam transport test is carried out through the test beam line of the laser-driven proton accelerator which consists of the phase rotation cavity, PMQ, and bending magnet. The laser system used is J-KAREN at JAEA. The final transmitted bunch duration and transverse profile are well predicted by the PARMILA particle transport code by assuming relatively low initial current of the proton beam. The most probable explanation for this is the space charge neutralization by the laser-plasma-electrons.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 13(7), p.071304_1 - 071304_7, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:79.43(Physics, Nuclear)A laser-driven repetition-rated 1.9 MeV proton beam line composed of permanent quadrupole magnets (PMQs), a radio frequency (rf) phase rotation cavity, and a tunable monochromator is developed to evaluate and to test the simulation of laser-accelerated proton beam transport through an integrated system for the first time. In addition, the proton spectral modulation and focusing behavior of the rf phase rotationcavity device is monitored with input from a PMQ triplet. In the 1.9 MeV region we observe very weakproton defocusing by the phase rotation cavity. The final transmitted bunch duration and transverse profile are well predicted by the PARMILA particle transport code. The transmitted proton beam duration of 6 ns corresponds to an energy spread near 5% for which the transport efficiency is simulated to be 10%. The predictive capability of PARMILA suggests that it can be useful in the design of future higher energy transport beam lines as part of an integrated laser-driven ion accelerator system.
Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2010-002, p.95 - 98, 2010/06
At the previous symposium in Advanced Photon Research, we proposed and demonstrated the laser pulse compression via stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) for increasing the flux of the Compton backscattered X rays. After that, we improved the SBS pulse compression system by introducing the image relay in the laser transport line. As a result, we achieve the stably compressed laser pulse with a duration of 2.1 ns and with an energy of 0.84 J. By installing this system into the Compton backscattered X-ray source, the X-ray flux will be increased 3.2 times for the present system at the KPSI-JAEA.
 ), high-intensity (500 TW) J-KAREN laser system
), high-intensity (500 TW) J-KAREN laser systemKiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2010-002, p.18 - 21, 2010/06
We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30 J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500 TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the final compressed pulse (without pumping the booster amplifier) we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescale, and is near 10
on the sub-nanosecond timescale, and is near 10 on the nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
on the nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanoue, Manabu*; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Wakai, Daisuke*; Sasao, Fumitaka*; Okada, Hajime; et al.
Optics Letters, 35(10), p.1497 - 1499, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:85 Percentile:95.22(Optics)OPCPA (Optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification) operation with low gain by seeding with high energy, clean pulses is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 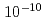 -
-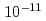 in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77%. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30-Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77%. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30-Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.88 - 90, 2010/05
The concept of a compact ion particle accelerator has become attractive in view of recent progress in laser-driven ion acceleration. We report here the recent progress in the laser-driven proton beam transport at the Photo Medical Research Center (PMRC) at JAEA, which is established to address the challenge of laser-driven ion accelerator development for ion beam cancer therapy.