Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Masuda, Takuya*; Fukumitsu, Hitoshi*; Kondo, Toshihiro*; Naohara, Hideo*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Sakata, Osami*; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117(23), p.12168 - 12171, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:47.24(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of the perfluorosulfonated ionomer (PFSI)/Pt(111) interface in a membrane electrode assembly (MEA)-like configuration of a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell, that is, a vacuum evaporated Pt layer/PEM(Nafion membrane)/PFSI(adhesion Nafion layer)/Pt(111) single crystal, and its bias-induced change were investigated by surface X-ray scattering measurement at an atomic level. Crystal truncation rod measurement shows that PFSI adsorbed on the Pt(111)-(1 1) surface without bias. When the Pt(111) electrode was positively biased to form Pt oxide, the PFSI layer was detached from the Pt surface and oxygen atoms penetrated into the Pt lattice.
1) surface without bias. When the Pt(111) electrode was positively biased to form Pt oxide, the PFSI layer was detached from the Pt surface and oxygen atoms penetrated into the Pt lattice.
 KM1
KM1Okazaki, Nobuo; Tamada, Taro; Feese, M. D.*; Kato, Masaru*; Miura, Yutaka*; Komeda, Toshihiro*; Kobayashi, Kazuo*; Kondo, Keiji*; Blaber, M.*; Kuroki, Ryota
Protein Science, 21(4), p.539 - 552, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:6.67(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Uosaki, Kohei*; Morita, Jun*; Katsuzaki, Tomoko*; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Kondo, Toshihiro*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115(25), p.12471 - 12482, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.16(Chemistry, Physical)Ag/AgCl reaction at the Ag bilayer, which was underpotentially prepared on a Au(111) surface, was investigated using electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM), scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), surface X-ray scattering (SXS), and electrochemical techniques. When the potential was scanned positively from -200 mV, the Cl ion was adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode surface around 0 mV, and then the phase transition of the adsorbed Cl
ion was adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode surface around 0 mV, and then the phase transition of the adsorbed Cl ion layer from random orientation to (
ion layer from random orientation to (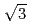

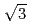 ) structure took place at around +130 mV. The Ag bilayer and Cl
) structure took place at around +130 mV. The Ag bilayer and Cl ions were oxidatively reacted to form the AgCl monolayer with (
ions were oxidatively reacted to form the AgCl monolayer with (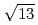

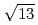 )
)  13.9
13.9 structure around +200 mV, accompanied with the formation of AgCl monocrystalline clusters on the AgCl monolayer surface. The structure of the AgCl monolayer on the Au(111) surface was changed from (
structure around +200 mV, accompanied with the formation of AgCl monocrystalline clusters on the AgCl monolayer surface. The structure of the AgCl monolayer on the Au(111) surface was changed from (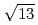

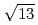 )R13.9
)R13.9 structure to (4
structure to (4 4) structure around +500 mV.
4) structure around +500 mV.
Takahashi, Masamitsu; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Mizuki, Junichiro; Kondo, Toshihiro*; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 22(47), p.474002_1 - 474002_9, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:53.04(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kondo, Makoto; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Motegi, Toshihiro; Emori, Koichi
JAEA-Testing 2009-002, 50 Pages, 2009/08
High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is a test reactor that build on sand layer formed during quaternary era. In principle, nuclear power generation facilities need to be supported on rigid rock formed during tertiary era, and now it is investigated to construct nuclear power generation facilities on sand layer formed during quaternary era for expanding suitable location. For this reason, we installed seismic observation systems in HTTR. And we have performed seismic safety evacuation using measured seismic acceleration in ground and building. This report compiles specifications of seismic observation systems, contents of check for seismic observation systems, check result of seismic observation systems and maintenance of seismic observation systems in HTTR.
Kondo, Toshihiro*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Kitamura, Ken*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 13(7), p.1141 - 1145, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:14.88(Electrochemistry)The interfacial structures of Ag bilayer prepared by underpotential deposition on Au(111) were determined by STM and SXS before and after oxidative adsorption and after desorption of a SAM of C SH in alkaline ethanol solution. While no structural change was observed after oxidative formation of C
SH in alkaline ethanol solution. While no structural change was observed after oxidative formation of C SH SAM on the Ag/Au(111) in an ethanol solution containing 20 mM KOH and 0.1 mM C
SH SAM on the Ag/Au(111) in an ethanol solution containing 20 mM KOH and 0.1 mM C SH, some of the Ag atoms in the bilayer were stripped when the SAM was reductively desorbed.
SH, some of the Ag atoms in the bilayer were stripped when the SAM was reductively desorbed.
Saito, Kenji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Kawamata, Takanori; Nemoto, Masumi; Motegi, Toshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-015, 52 Pages, 2009/05
As In-core temperature monitoring system, Type N thermocouples arranged at hot plenum block measures the primary coolant temperature at each hot plenum block in order to monitor the condition of the reactor core during the reactor operation. Type N thermocouples should have a long lifetime with high reliability under the high temperature environment of about 1000 C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
Kondo, Toshihiro*; Morita, Jun*; Hanaoka, Kazuya*; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(35), p.13197 - 13204, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:89.36(Chemistry, Physical)Potential-dependent surface structures of Au(111) and Au(100) single-crystal electrodes in a 50 mM H SO
SO solution were investigated at an atomic level using in situ surface X-ray scattering (SXS) techniques. It was confirmed that both the Au(111) and Au(100) surfaces were reconstructed with an attached submonolayer of an oxygen species, most probably water, at 0 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Results at +0.95 V supported a previously suggested model for both the Au(111) and the Au(100) electrodes that, based on infrared and scanning tunneling microscopy measurements, the surfaces were a (1
solution were investigated at an atomic level using in situ surface X-ray scattering (SXS) techniques. It was confirmed that both the Au(111) and Au(100) surfaces were reconstructed with an attached submonolayer of an oxygen species, most probably water, at 0 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Results at +0.95 V supported a previously suggested model for both the Au(111) and the Au(100) electrodes that, based on infrared and scanning tunneling microscopy measurements, the surfaces were a (1 1) structure with the coadsorbed sulfate anion and hydronium cation (H
1) structure with the coadsorbed sulfate anion and hydronium cation (H O
O ). At +1.05 V, where a small amount of an anodic current flowed, adsorption of a monolayer of oxygen species was observed on both surfaces.
). At +1.05 V, where a small amount of an anodic current flowed, adsorption of a monolayer of oxygen species was observed on both surfaces.
Motegi, Toshihiro; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Saito, Kenji; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Shibutani, Hideki; Ogawa, Satoru; Shinozaki, Masayuki; Mizushima, Toshihiko; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-029, 67 Pages, 2006/06
The plant control performance of the IHX helium flow rate control system, the PPWC helium flow rate control system, the secondary helium flow rate control system, the inlet temperature control system, the reactor power control system and the outlet temperature control system of the HTTR are obtained through function tests and power-up tests. As the test results, the control systems show stable control response under transient condition. Both of inlet temperature control system and reactor power control system shows stable operation from 30% to 100%, respectively. This report describes the outline of control systems and test results.
Saito, Kenji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Tsuchiyama, Masaru*; Ando, Toshio*; Motegi, Toshihiro; Mizushima, Toshihiko; Nakazawa, Toshio
JAERI-Tech 2004-042, 26 Pages, 2004/04
The reactor control system of HTTR is composed of the reactor power control system, the reactor inlet coolant temperature control system, the primary coolant flow rate control system and so on. The reactor control system of HTTR achieves reactor power 30MW, reactor outlet coolant temperature 850 C, reactor inlet coolant temperature 395
C, reactor inlet coolant temperature 395 C under the condition that primary coolant flow rate is fixed. In the Rise-to-Power Test, the performance test of the reactor inlet coolant temperature control system was carried out in order to confirm the control capability of this control system. This report shows the test results of performance test. As a result, the control parameters, which can control the reactor inlet coolant temperature stably during the reactor operation, were successfully selected. And it was confirmed that the reactor inlet coolant temperature control system has the capability of controlling the reactor inlet coolant temperature stably against any disturbances on the basis of operational condition of HTTR.
C under the condition that primary coolant flow rate is fixed. In the Rise-to-Power Test, the performance test of the reactor inlet coolant temperature control system was carried out in order to confirm the control capability of this control system. This report shows the test results of performance test. As a result, the control parameters, which can control the reactor inlet coolant temperature stably during the reactor operation, were successfully selected. And it was confirmed that the reactor inlet coolant temperature control system has the capability of controlling the reactor inlet coolant temperature stably against any disturbances on the basis of operational condition of HTTR.
Hirato, Yoji; Saito, Kenji; Kondo, Makoto; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Motegi, Toshihiro; Tsuchiyama, Masaru*; Ando, Toshio*; Mizushima, Toshihiko; Nakazawa, Toshio
JAERI-Tech 2004-037, 33 Pages, 2004/04
HTTR (High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor) was operated from May 6th, 2003 to June 18th, 2003 to obtain operation data in parallel loaded operation mode and in safety demonstration tests. Operated with the reactor power at 60% of the rated power on May 21st, HTTR was automatically scrammed by a signalof "Primary coolant flow rate of the Primary Pressurized Water Cooler (PPWC): Low". The cause of the shutdown was the primary gas circulator (A) automatically stopped. The primary coolant flow rate of the PPWC decresed and reached the scram set value due to the gas circulator stop. As a result of investigation, it became clear that the cause of the gas circulator stop was malfunction of an auxiliary relay which monitored electric power of a circuit breaker in power line of the gas circulator. The cause of malfunction was deterioration of the relay under high temperature condition because the relay was installed beside an electric part which was heated up by electricity.
Kondo, Toshihiro*; Tamura, Kazuhisa*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uosaki, Kohei*
Electrochimica Acta, 47(19), p.3075 - 3080, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:56.86(Electrochemistry)A nwely designed spectroelectrochemical cell was constructed for surface X-ray scattering (SXS) to study single crystal electrodes. Electrochemical characteristics of a specific face of a single crystal electrode can be investigated in the meniscus mode, adn SXS measurement can be easily carried out using the spectroelectrochemical cell. The usefulness of the present cell was demonstrated by studying the electrochemical deposition of Pd thin layers on Au(111) and Au(001) that require precise amounts of Pd deposits.
Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Tamura, Kazuhisa*; Kondo, Toshihiro*; Uosaki, Kohei*
Shinku, 44(3), P. 375, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Masamitsu; Hayashi, Yukio; Mizuki, Junichiro; Tamura, Kazuhisa*; Kondo, Toshihiro*; Naohara, Hideo*; Uosaki, Kohei*
Surface Science, 461(1-3), p.213 - 218, 2000/08
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:91.97(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Okazaki, Nobuo; Tamada, Taro; Miura, Yutaka*; Feese, M. D.*; Kato, Masaru*; Komeda, Toshihiro*; Takehara, Kyoko*; Kobayashi, Kazuo*; Kondo, Keiji*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The crystal structure of glycosyltrehalose synthase (GTSase) from the hyperthermophilic archaeum Sulfolobus shibatae DSM5389 has been determined to 2.3 A resolution by X-ray crystallography. GTSase converts the glucosidic bond between the last two glucose residues of amylose from an alpha-1,4 bond to an alpha-1,1 bond, making a non-reducing glycosyl trehaloside in the first step of the biosynthesis of trehalose. The structure of GTSase can be divided into five domains. The central domain has the (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold which is conserved in the alpha-amylase family as the catalytic domain. Three invariant catalytic carboxylic amino acids in the alpha-amylase family are also found in GTSase at positions Asp241, Glu269 and Asp460 in the (beta/alpha)8 domain. Our previous study with KM1-GTSase has been shown that the maltooligosaccharides are converted to glycosyltrehalose by an intramolecular transglycosylation mechanism.