Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linac
particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linacTamura, Jun; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Liu, Y.*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1049, p.168033_1 - 168033_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac is a high-intensity accelerator in which beam loss is a critical issue. In the J-PARC linac, H beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H
beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H
linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H
particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H
linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H particles were separated from the H
particles were separated from the H beam, and the intensity profiles of the H
beam, and the intensity profiles of the H particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H
particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H
particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H
particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(3), p.032802_1 - 032802_12, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.48(Physics, Nuclear)A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is a useful device for performing longitudinal beam tuning using the pointwise longitudinal phase distribution measured at selected points in the beam transportation. To measure the longitudinal phase distribution of a low-energy negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H
) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
 beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitor
beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitorKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011012_1 - 011012_6, 2021/03
The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) is required to measure the bunch size of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.251 - 253, 2020/09
A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) in the low-energy region is being developed in the J-PARC linac to accelerate the high-intensity proton beam with the low emittance. A highly-oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was introduced as the target of the BSM to mitigate the thermal loading. The stable measurement of the BSM was realized thanks to the HOPG target, while the tungsten target was broken by the thermal loading from the high-intensity beam. However, since the longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM using the HOPG target was wider than the expected one, the improvement of tuning parameters is necessary for the BSM. The BSM consists of an electron multiplier, a bending magnet, and a radio-frequency deflector, which should be tuned appropriately. Behavior of these components were investigated and tuned. The longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM after the tuning was consistent with the expected one.
 Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear)Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.74(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Naito, Fujio*; Otani, Masashi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012079_1 - 012079_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)In 2013, the Annular-ring Coupled Structure (ACS) cavities were installed to the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac. Since then, the ACS cavities have been stably running. Although any serious problem induced by the RF window had not yet observed, we decided to replace the RF window of one ACS cavity by the newly manufactured one. The major motivations of the replacement are to check the surface condition of the RF window which have been under operation for nearly five years, to confirm that the new RF window fully meets specifications, and to learn how much time is required for high-power conditioning of the new RF window. By making use of the summer maintenance period of 2018, we carried out the replacement. This was the first experience for us to replace the RF window installed to the ACS cavity in the linac accelerator tunnel. As for the removed RF window, there was no any abnormal warning found with the visual examination. At the resuming of the cavity operation after the maintenance period, we conducted the high-power conditioning in a measured manner. It took around fifty hours so that the targeted peak power was stably input to the cavity through the new RF window. The ACS cavity with the new RF window is now stably operating.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Naito, Fujio*; Otani, Masashi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012080_1 - 012080_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac, negative hydrogen beams are accelerated from 190 MeV to 400 MeV by Annular-ring Coupled Structure (ACS) cavities. The RF input coupler of the ACS21 cavity, which is the twenty-first (the last) accelerating cavity in the order of beam acceleration, had a comparatively larger Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) value than the other ACS cavities. Therefore, we designed and manufactured a rectangular waveguide which has a capacitive iris to adjust the coupling factor of the ACS21 cavity. By making use of the summer maintenance period in 2018, we installed the newly manufactured waveguide to the cavity. Consequently, the VSWR of the ACS21 was successfully decreased to the target value which leads to the critical coupling under the nominal accelerating condition with 50-mA peak beam current.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kosaka, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2543 - 2546, 2019/06
A bunch shape monitor (BSM) is one of the important instruments to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution. For example in the J-PARC linac, three BSMs using the tungsten wire are installed at the ACS section to measure the bunch shapes between the accelerating cavities. However, this conventional BSM is hard to measure the bunch shape of H beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H
beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of
beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of  10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Ao, Hiroyuki*; Naito, Fujio*; Otani, Masashi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1067(5), p.052009_1 - 052009_6, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac, the Annular-ring Coupled Structure (ACS) cavities have been stably operating. To maintain this operation availability, we manufactured three pillbox-type RF windows for the ACS cavities in fiscal year 2015 and 2017. It is desirable to minimize the RF reflection of the RF window to prevent standing waves from exciting between the cavity and the RF window, and not to significantly change the optimized coupling factor between the cavity and the waveguide. To realize the minimization, the relative permittivities of the ceramic disks of the RF windows were evaluated by measuring the resonant frequencies of the pillbox cavity containing the ceramic disk. On the basis of the evaluated relative permittivities, the pillbox-part lengths of the RF windows were determined. The measured Voltage Standing Wave Ratios (VSWRs) of the manufactured RF windows are just about 1.08 and these are applicable for the practical use.
Hirano, Koichiro; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Ito, Takashi; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kawane, Yusuke; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Sato, Yoshikatsu; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.310 - 313, 2016/11
We have used a beam scraper with the incident angle of 65deg to reduce the beam power deposition density in the MEBT between a 324 MHz RFQ and a 50-MeV DTL of the J-PARC linac. The 65 scraper was irradiated by the H
scraper was irradiated by the H beam up to particle number of 1.47E22. We observed a lot of surface projections with several hundred micrometers high in the beam irradiation damage on the scraper by using the laser microscope. In order to study the limits of scrapers, we constructed a new 3 MeV linac at J-PARC. We will conduct the scraper irradiation test at the end of this year.
beam up to particle number of 1.47E22. We observed a lot of surface projections with several hundred micrometers high in the beam irradiation damage on the scraper by using the laser microscope. In order to study the limits of scrapers, we constructed a new 3 MeV linac at J-PARC. We will conduct the scraper irradiation test at the end of this year.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Sugawara, Hirotaka*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '16) (Internet), p.906 - 909, 2016/06
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The required beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present design of this compact, medium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.948 - 950, 2015/09
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The reqired beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present designof this compact, midium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Nemoto, Yasuo; Tamura, Jun; Ito, Takashi; Morishita, Takatoshi; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Sugimura, Takashi*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ao, Hiroyuki*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1101 - 1104, 2015/09
In J-PARC linac, ACS (Annular-ring Coupled Structure) has been operating for one and a half years. Through the long term operation, the ACS cavities have been well conditioned. Therefore, the vacuum pressure of the ACS was reduced to 1 10
10 Pa, which is much lower than the required value, and RF trip rate was steadily decreased. At present, the ACS continues to be stably operating without sacrificing the operating time of the J-PARC accelerator complex. The vacuum leaks caused by the generated crack in the aluminum chain clamps in the ACS beam line have happened five times in the past. To prevent the same situation from occurring, we replaced all the aluminum clamps to the stainless steel clamps. The residual radiation between each ACS cavity is considerably high. It is considered that the CT monitors, which have smaller aperture than that of other instruments in the beam line, contributes to the residual radiation. We are trying to reduce the residual radiation by enlarging the monitor's aperture and by replacing the unused monitors to the titanium ducts in this summer shutdown period.
Pa, which is much lower than the required value, and RF trip rate was steadily decreased. At present, the ACS continues to be stably operating without sacrificing the operating time of the J-PARC accelerator complex. The vacuum leaks caused by the generated crack in the aluminum chain clamps in the ACS beam line have happened five times in the past. To prevent the same situation from occurring, we replaced all the aluminum clamps to the stainless steel clamps. The residual radiation between each ACS cavity is considerably high. It is considered that the CT monitors, which have smaller aperture than that of other instruments in the beam line, contributes to the residual radiation. We are trying to reduce the residual radiation by enlarging the monitor's aperture and by replacing the unused monitors to the titanium ducts in this summer shutdown period.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
 studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringInami, Toshiya; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ishihara, Sumio*; Kondo, Hiroshi*; Nakao, Hironori*; Matsumura, Takeshi*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 67(4), p.045108_1 - 045108_6, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:87.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report resonant inelastic x-ray scattering experiments of the orbitally ordered manganite LaMnO . When incident photon energy is tuned near the Mn
. When incident photon energy is tuned near the Mn  absorption edge, the spectra reveal three features at 2.5 eV, 8 eV and 11 eV. The 8 eV and 11 eV peaks are ascribed to transitions from the O 2
absorption edge, the spectra reveal three features at 2.5 eV, 8 eV and 11 eV. The 8 eV and 11 eV peaks are ascribed to transitions from the O 2 bands to the empty Mn 3
bands to the empty Mn 3 and
and 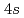 /
/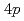 bands, respectively. On the other hand, the 2.5 eV peak is considered an orbital excitation across the Mott gap,
bands, respectively. On the other hand, the 2.5 eV peak is considered an orbital excitation across the Mott gap,  an electron excitation from the effective lower Hubbard band with the
an electron excitation from the effective lower Hubbard band with the 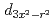 and
and 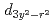 orbital characters to the upper Hubbard band with the
orbital characters to the upper Hubbard band with the 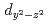 and
and 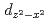 ones. The weak dispersion and characteristic azimuthal angle dependence of this excitation are well reproduced by a theory which includes orbital degeneracy and strong electron correlation.
ones. The weak dispersion and characteristic azimuthal angle dependence of this excitation are well reproduced by a theory which includes orbital degeneracy and strong electron correlation.
Nanayama, Futoshi*; Yamaguchi, Tatsuhiko*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Tsuji, Tomohiro*; Ikeda, Michiharu*; Kondo, Yasuo*; Miwa, Michiko*; Sugiyama, Shinji*; Kimura, Kazunari*
no journal, ,
The characteristics of the post-LGM incised valley fills and the depositional sequence were examined the SKM core collected in the Sukumo coastal lowland, where is expected to huge seismic subsidence due to the Nankai Trough great earthquakes. Our sedimentological, radiocarbon dating and paleoenvironmental results are as bellows. Sediments of the SKM core clearly show a succession influenced by post-glacial sea level change. The Matsuda River incised valley was formed in LGM and filled by fluvial sand and gravels in late Pleistocene. After the postglacial transgression, sea level reached -30 m (a.s.l.) at 9.8 ka and the incised valley changed to an estuary environment. The sea level continued to rise and it became an inner bay mud bottom environment, and reaching a maximum water depth was at 7.5 ka. The 7.3 ka Kikai caldera eruption in southern Kyushu caused heavy K-Ah ash fall in southwestern Shikoku, and then large-scale lahars frequently occurred immediately after the ash fall because of the vicinity of volcanic source. After ash fall, the K-Ah secondary sediments rapidly deposited on the inner bay environment and caused forced regression. After 7.0 ka, the growth of the delta became active ahead of the other regions, which may be due to the large K-Ah ash fall. At 5 ka, the sea level reached + 2.5 m (a.s.l.) estimated by the Sukumo midden and this altitude is recognized as the Holocene marine limit in this area. The information on relative sea level change during the past 10000 years has revealed that the Sukumo Bay area has not subsided due to seismic crustal deformation.
Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Minami, Yasuo*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Kondo, Kiminori; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zakhovsky, V.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Yamaguchi, Tatsuhiko*; Tsuji, Tomohiro*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Ikeda, Michiharu*; Kondo, Yasuo*; Miwa, Michiko*; Hamada, Yohei*
no journal, ,
Shikoku Island is situated 150 km northwest of the Nankai trough that has developed in response to the convergence of the subducting Philippine Sea Plate and overriding Eurasian Plate. This tectonism causes deformation of the island, megathrust earthquakes, and tsunamis. Shikoku Island experiences coseismic and interseismic deformation. The middle Holocene tectonics of the island are still poorly understood. Relative sea-level (RSL) changes indicated by coastal sediments potentially record seismic uplift and subsidence. To infer RSL changes between 8 and 4 cal. kyr BP, we studied Holocene ostracode assemblages from the SKM drill core in Sukumo, southwest Shikoku Island (Tsuji et al., 2018, JpGU, MIS11-P19), and from six cores in the northern part of the island (Yasuhara et al., 2005, Palaeo3; Yasuhara and Seto, 2006, Paleontol. Res. 10). To estimate paleo-water depth and RSL, we employed the ostracode assemblages and modern analog technique. The SKM core is composed of conglomerate, ash, and mud chiefly. Its geological age was examined, using the  C dating method (Nakanishi et al., 2019, Radiocarbon). The differences in RSL were identified across the island, possibly due to convergence of the Philippine Sea Plate.
C dating method (Nakanishi et al., 2019, Radiocarbon). The differences in RSL were identified across the island, possibly due to convergence of the Philippine Sea Plate.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
no journal, ,
In the J-PARC linac, the optimization of the longitude beam matching in the medium-energy beam transport1 is on-going using the bunch shape monitor (BSM) to improve the beam quality. In the measurement with the BSM, the phase distribution of the beam bunch is indirectly measured using the secondary electron beam produced from the negative hydrogen ion beam. However, when the bunch shape is measured at the center of the beam, it has not been measured yet, because of the limitation of the thermal loading of the secondary electron target. Therefore, the graphene was adopted as the BSM target, because it could resist the high thermal loading. and the performance evaluation was conducted. When the target was set at the center of the beam, the detection of the signal from the graphene target was successful. Therefore, this graphene target can be used for the BSM to measure the high-intensity beam with the low energy.
Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Fumiko*; Sugawara, Hirotaka*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Higashi, Yasuo*; Matsumoto, Noriyuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Kazuhide*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*
no journal, ,