Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Plompen, A. J. M.*; Cabellos, O.*; De Saint Jean, C.*; Fleming, M.*; Algora, A.*; Angelone, M.*; Archier, P.*; Bauge, E.*; Bersillon, O.*; Blokhin, A.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 56(7), p.181_1 - 181_108, 2020/07
被引用回数:321 パーセンタイル:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)本論文では、核分裂と核融合のための統合評価済み核データファイルのバージョン3.3(JEFF-3.3)について説明する。中性子との反応が重要な核種の U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Na,
Na,  Ni, Cr, Cu, Zr, Cd, Hf, Au, Pb, Biについて、新しい核データ評価結果を示す。JEFF-3.3には、核分裂収率, 即発核分裂スペクトル, 核分裂平均中性子発生数の新しいデータが含まれる。更に、放射崩壊, 熱中性子散乱, ガンマ線放出, 中性子による放射化, 遅発中性子, 照射損傷に関する新しいデータも含まれている。JEFF-3.3は、TENDLプロジェクトのファイルで補完しており、光子, 陽子, 重陽子, 三重陽子,
Ni, Cr, Cu, Zr, Cd, Hf, Au, Pb, Biについて、新しい核データ評価結果を示す。JEFF-3.3には、核分裂収率, 即発核分裂スペクトル, 核分裂平均中性子発生数の新しいデータが含まれる。更に、放射崩壊, 熱中性子散乱, ガンマ線放出, 中性子による放射化, 遅発中性子, 照射損傷に関する新しいデータも含まれている。JEFF-3.3は、TENDLプロジェクトのファイルで補完しており、光子, 陽子, 重陽子, 三重陽子,  He核, アルファ粒子による反応ライブラリについては、TENDL-2017から採用した。また、不確かさの定量化に対する要求の高まりから、多くの共分散データが新しく追加された。JEFF-3.3を用いた解析の結果と臨界性, 遅発中性子割合, 遮蔽, 崩壊熱に対するベンチマーク実験の結果を比較することにより、JEFF-3.3は幅広い原子核技術の応用分野、特に原子力エネルギーの分野において優れた性能を持っていることが分かった。
He核, アルファ粒子による反応ライブラリについては、TENDL-2017から採用した。また、不確かさの定量化に対する要求の高まりから、多くの共分散データが新しく追加された。JEFF-3.3を用いた解析の結果と臨界性, 遅発中性子割合, 遮蔽, 崩壊熱に対するベンチマーク実験の結果を比較することにより、JEFF-3.3は幅広い原子核技術の応用分野、特に原子力エネルギーの分野において優れた性能を持っていることが分かった。
Ma, F.; Kopecky, S.*; Alaerts, G.*; 原田 秀郎; Heyse, J.*; 北谷 文人; Noguere, G.*; Paradela, C.*; 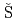 alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35(3), p.478 - 488, 2020/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:22.14(Chemistry, Analytical)The use of Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis to characterize homogeneous samples not fulfilling good transmission geometry conditions is discussed. Analytical expressions for such samples have been derived and implemented in the resonance shape analysis code REFIT. They were validated by experiments at the time-of-flight facility GELINA using a set of metallic natural copper samples. The expressions were used to derive sample characteristics by a least squares adjustment to experimental transmission data. In addition, the resonance parameters of Cu for energies below 6 keV, which are reported in the literature and recommended in evaluated data libraries, were verified. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
河野 俊彦*; Cho, Y. S.*; Dimitriou, P.*; Filipescu, D.*; 岩本 信之; Plujko, V.*; Tao, X.*; 宇都宮 弘章*; Varlamov, V.*; Xu, R.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 163, p.109 - 162, 2020/01
被引用回数:80 パーセンタイル:99.62(Physics, Nuclear)We report our coordinated efforts to address these data needs such as radiation shielding design and radiation transport analyses, and present the results of the new evaluations of more than 200 nuclides included in the new updated IAEA Photonuclear Data Library, where the photon energy goes up to 200 MeV. We discuss the new assessment method and make recommendations to the user community in cases where the experimental data are discrepant and the assessments disagree. In addition, in the absence of experimental data, we present model predictions for photon-induced reaction cross section on nuclides of potential interest to medical radioisotope production.
Goriely, S.*; Dimitriou, P.*; Wiedeking, M.*; Belgya, T.*; Firestone, R.*; Kopecky, J.*; Krti ka, M.*; Plujko, V.*; Schwengner, R.*; Siem, S.*; et al.
ka, M.*; Plujko, V.*; Schwengner, R.*; Siem, S.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 55(10), p.172_1 - 172_52, 2019/10
被引用回数:64 パーセンタイル:92.18(Physics, Nuclear)We report on a coordinated and systematic effort to compile and assess all the existing experimental data on photon strength functions extracted from photoabsorption cross sections in the region of the Giant Dipole Resonance and from neutron-, photon- and charged-particle-induced reactions at energies around or below the neutron separation energy. We also present global empirical and microscopic models that describe the photon strength function in the entire photon energy region and reproduce reasonably well most of the existing experimental data. Finally, we recommend photon strength functions for use in basic sciences and applications. The compilation of experimental photon strengths as well as the recommended model calculations are readily available to the user community from a dedicated database hosted at the IAEA.
土屋 晴文; Ma, F.; 北谷 文人; Paradella, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of 41st ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.374 - 377, 2019/05
From a viewpoint of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, non-destructive assay (NDA) techniques are needed to quantify special nuclear materials (SNMs) in nuclear fuels such as spent fuels and fuel debris. Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) is an NDA technique and it measures the amount of U isotopes in a U O
O sample within 1% accuracy and Pu isotopes in a PuO
sample within 1% accuracy and Pu isotopes in a PuO sample within 5% accuracy. However, NRTA measurements done so far were mainly applied to homogeneous samples with a constant thickness. Spent fuel and especially debris have irregular shapes that affect the NRTA measurements. In order to investigate the influence of irregular-shaped samples, NRTA experiments were done with a copper bar sample with different rotation angles with respect to neutron beams, at a neutron Time-Of-Flight (TOF) facility GELINA (Belgium). Analytical models for irregular shaped samples proposed by Harada et al. (JNST, 2015) were applied to the experimental data. It has been found that the experimental data can be well reproduced by the proposed models. In this presentation, we report how analytical models are applied to a real NRTA experiment with a Cu bar sample and discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system for SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
sample within 5% accuracy. However, NRTA measurements done so far were mainly applied to homogeneous samples with a constant thickness. Spent fuel and especially debris have irregular shapes that affect the NRTA measurements. In order to investigate the influence of irregular-shaped samples, NRTA experiments were done with a copper bar sample with different rotation angles with respect to neutron beams, at a neutron Time-Of-Flight (TOF) facility GELINA (Belgium). Analytical models for irregular shaped samples proposed by Harada et al. (JNST, 2015) were applied to the experimental data. It has been found that the experimental data can be well reproduced by the proposed models. In this presentation, we report how analytical models are applied to a real NRTA experiment with a Cu bar sample and discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system for SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 藤 暢輔; Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
In fields of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, non-destructive assay (NDA) techniques are needed in order to quantify special nuclear materials (SNMs) in nuclear fuels. Among those techniques, active NDA ones would be preferable to passive ones. One candidate of active NDA techniques is neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). In fact, experiments done at GELINA have shown that NRTA has high potential enough to quantify SNMs in complex materials. Currently, such a NRTA system requires a large electron accelerator facility to generate intense neutron sources. In other words, it is very difficult to perform NRTA at various facilities that need to measure SNMs. Thus, downsizing a NRTA system would be one solution of its difficulty. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we develop a prototype with a D-T neutron generator that has a pulse width of 10  s. For this aim, numerical calculations to optimize the compact NRTA system were done. In addition, NRTA measurements with simulated fuel pins were made at neutron time-of-flight facilities such as GELINA. In this presentation, we present results of the numerical calculations and the experimental results. On the basis of those results we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system that would be applicable to SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
s. For this aim, numerical calculations to optimize the compact NRTA system were done. In addition, NRTA measurements with simulated fuel pins were made at neutron time-of-flight facilities such as GELINA. In this presentation, we present results of the numerical calculations and the experimental results. On the basis of those results we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system that would be applicable to SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
Dimitriou, P.*; Belgya, T.*; Cho, Y.-S.*; Filipescu, D.*; Firestone, R.*; Goriely, S.*; 岩本 信之; 河野 俊彦*; Kopecky, J.*; Krticka, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 178, p.06005_1 - 06005_3, 2018/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:74.98(Optics)測定や既存のデータ評価・編集、また基礎科学や応用への利用に向けた巨大双極子共鳴パラメータ等のテーブル作成を基にした光核反応断面積や光子強度関数の開発について報告する。
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
被引用回数:66 パーセンタイル:98.06(Physics, Nuclear)CIELO国際協力では、原子力施設の臨界性に大きな影響を与える重要核種( U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O,
O,  H)の中性子断面積データの精度を改善し、これまで矛盾していると考えられた点を解消することを目的として研究が行われた。多くの研究機関が参加したこのパイロットプロジェクトは、IAEAの支援も受けて、OECD/NEAの評価国際協力ワーキングパーティ(WPEC)のSubgroup 40として組織された。本CIELOプロジェクトは、新たな実験研究や理論研究を行う動機付けとなり、測定データを正確に反映し臨界性の積分テストに優れた新たな一連の評価済みライブラリとして結実した。本報告書は、これまでの研究成果と、本国際協力の次の段階の計画概要をまとめたものである。
H)の中性子断面積データの精度を改善し、これまで矛盾していると考えられた点を解消することを目的として研究が行われた。多くの研究機関が参加したこのパイロットプロジェクトは、IAEAの支援も受けて、OECD/NEAの評価国際協力ワーキングパーティ(WPEC)のSubgroup 40として組織された。本CIELOプロジェクトは、新たな実験研究や理論研究を行う動機付けとなり、測定データを正確に反映し臨界性の積分テストに優れた新たな一連の評価済みライブラリとして結実した。本報告書は、これまでの研究成果と、本国際協力の次の段階の計画概要をまとめたものである。
 Am reactor activation measurements
Am reactor activation measurements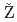 erovnik, G.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Becker, B.*; Fiorito, L.*; 原田 秀郎; Kopecky, S.*; Radulovic, V.*; 佐野 忠史*
erovnik, G.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Becker, B.*; Fiorito, L.*; 原田 秀郎; Kopecky, S.*; Radulovic, V.*; 佐野 忠史*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 877, p.300 - 313, 2018/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:46.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)原子炉中性子スペクトルで照射することにより得られる積分データから中性子断面積を導出する手法に関して、Westcottの記法を用いる断面積導出法の有効性について検討を行った。この結果、本手法で得られる精度は、中性子束エネルギー分布の精度に大きく依存すること、特に、導出される共鳴積分値が大きな影響を受けることを定量的に示した。また、中性子断面積のエネルギー依存性が既知の場合は、その情報を用いてこの影響を補正する手法を提案した。本手法を適用して、 Amの熱中性子捕獲断面積を再解析した結果、720(14)bを得た。
Amの熱中性子捕獲断面積を再解析した結果、720(14)bを得た。
Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; 小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09002_1 - 09002_4, 2017/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:97.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron-induced reactions can be used to study the properties of nuclear materials in the field of nuclear safeguards and security. The elemental and isotopic composition of these materials can be determined by using the presence of resonance structures in the reaction cross sections as fingerprints. This idea is the basis of two non-destructive analytical techniques which have been developed at the GELINA neutron time-of-flight facility of the JRC-IRMM: Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA) and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). A full quantitative validation of the NRTA technique was obtained by determining the areal densities of enriched reference samples used for safeguards applications with an accuracy better than 1%. Moreover, a combination of NRTA and NRCA has been proposed for the characterisation of particle-like debris of melted fuel formed in severe nuclear accidents. In order to deal with the problems due to the diversity in shape and size of these samples and the presence of strong absorbing matrix materials, new capabilities have been implemented in the resonance shape analysis code REFIT. They have been validated by performing a blind test in which the elemental abundance of a combined sample composed of unknown quantities of materials such as cobalt, tungsten, rhodium or gold was determined with accuracies better than 2%.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:95.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)CIELO共同研究では中性子断面積データの改善及びこれまでの評価で見られた断面積の不一致を解決することを目的として、原子力の臨界性に大きな影響を与える5核種( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 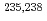 U,
U,  Pu)の中性子断面積を評価している。この国際パイロットプロジェクトでは、経済協力開発機構・原子力機関・核データ評価国際協力ワーキングパーティに設置されたサブグループ40の下でIAEAからのサポートを受けて、実験並びに理論的な研究を活発に実施している。これらの研究を通じて測定データを精度よく反映し、さらに臨界性に関する積分テストで良い結果を示す新しい評価済ライブラリを開発している。
Pu)の中性子断面積を評価している。この国際パイロットプロジェクトでは、経済協力開発機構・原子力機関・核データ評価国際協力ワーキングパーティに設置されたサブグループ40の下でIAEAからのサポートを受けて、実験並びに理論的な研究を活発に実施している。これらの研究を通じて測定データを精度よく反映し、さらに臨界性に関する積分テストで良い結果を示す新しい評価済ライブラリを開発している。

 -ray spectrometer for detecting
-ray spectrometer for detecting  B in debris of melted nuclear fuel
B in debris of melted nuclear fuel小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 原田 秀郎; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 837, p.153 - 160, 2016/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:19.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) has been proposed as a non-destructive analytical method for quantifying Special Nuclear Material (SNM) in the rock- and particle-like debris that is to be removed from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The method is based on Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis combined with Prompt Gamma Ray Analysis (NRCA/PGA). Although quantification of SNM will predominantly rely on NRTA, this will be hampered by the presence of strong neutron-absorbing matrix materials, in particular  B. Results obtained with NRCA/PGA are used to improve the interpretation of NRTA data. Prompt
B. Results obtained with NRCA/PGA are used to improve the interpretation of NRTA data. Prompt  -rays originating from the
-rays originating from the  B(n,
B(n, 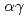 ) reaction are used to assess the amount of
) reaction are used to assess the amount of  B. The 478 keV
B. The 478 keV  -rays from
-rays from  B, however, need to be measured under a high-radiation environment, especially from
B, however, need to be measured under a high-radiation environment, especially from  Cs. In order to meet this requirement, we have developed a well-shaped
Cs. In order to meet this requirement, we have developed a well-shaped  -ray spectrometer consisting of a cylindrical and four rectangular cuboid LaBr
-ray spectrometer consisting of a cylindrical and four rectangular cuboid LaBr scintillators, and a fast data acquisition system.
scintillators, and a fast data acquisition system.
 線分析法
線分析法土屋 晴文; 原田 秀郎; 小泉 光生; 北谷 文人; 呉田 昌俊; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; Mondelaers, W.*; et al.
核物質管理学会(INMM)日本支部第36回年次大会論文集(インターネット), 9 Pages, 2015/12
粒子状の溶融燃料デブリに含まれるウランやプルトニウム同位体を非破壊で定量することを目的に、中性子共鳴濃度分析法(NRD)の技術開発を進めてきた。NRDは、中性子共鳴透過分析法(NRTA)に中性子共鳴捕獲 線分析法(NRCA)、あるいは即発
線分析法(NRCA)、あるいは即発 線分析法(PGA)を組み合わせた技術である。NRDにおけるNRCA/PGAの役割は、主に
線分析法(PGA)を組み合わせた技術である。NRDにおけるNRCA/PGAの役割は、主に Csによる高放射線場においてデブリ中の原子炉や建屋の構造材、ボロンなどの不純物を同定することである。これを実現するため、LaBr
Csによる高放射線場においてデブリ中の原子炉や建屋の構造材、ボロンなどの不純物を同定することである。これを実現するため、LaBr 結晶を用いた新型の
結晶を用いた新型の 線検出器やそれ専用の遮蔽体を開発した。これらの
線検出器やそれ専用の遮蔽体を開発した。これらの 線検出器や遮蔽体を用いて、ベルギーの中性子飛行時間施設GELINAにおいて公開デモ実験を実施した結果、第三者によってブラックボックス内に密封された試料(Hf, Gd, Ni)を同定することに成功した。本発表では、開発した
線検出器や遮蔽体を用いて、ベルギーの中性子飛行時間施設GELINAにおいて公開デモ実験を実施した結果、第三者によってブラックボックス内に密封された試料(Hf, Gd, Ni)を同定することに成功した。本発表では、開発した 線検出器の設計概念と測定原理、及びNRCAデモ実験結果について報告する。
線検出器の設計概念と測定原理、及びNRCAデモ実験結果について報告する。
北谷 文人; 原田 秀郎; 小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文; 呉田 昌俊; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; Mondelaers, W.*; et al.
核物質管理学会(INMM)日本支部第36回年次大会論文集(インターネット), 9 Pages, 2015/12
平成24年度から平成26年度にかけて、粒子状の溶融燃料デブリに含まれるウランやプルトニウム同位体を非破壊で定量する技術として、中性子共鳴濃度分析法(NRD)の開発を進めてきた。NRDは、中性子共鳴透過分析法(NRTA)と中性子共鳴捕獲 線分析法(NRCA)あるいは即発
線分析法(NRCA)あるいは即発 線分析法(PGA)を組み合わせた技術である。NRDにおけるNRTAの役割は、溶融燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質(U, Pu等)の同位体を定量することである。この目的のために飛行時間法(Time of Flight: TOF)を利用した中性子吸収測定を実施する。これについて。ベルギーの中性子飛行時間施設GELINAにて性能評価デモ実験を実施した。その結果、Au, W, Rh, Nb, Cu. Co, Mn, Bをランダムに選択して、封をされたブラックボックス内の試料を定量することに成功した。本発表では、開発したNRTAの測定原理を述べ、実施したデモ実験の詳細を発表する。
線分析法(PGA)を組み合わせた技術である。NRDにおけるNRTAの役割は、溶融燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質(U, Pu等)の同位体を定量することである。この目的のために飛行時間法(Time of Flight: TOF)を利用した中性子吸収測定を実施する。これについて。ベルギーの中性子飛行時間施設GELINAにて性能評価デモ実験を実施した。その結果、Au, W, Rh, Nb, Cu. Co, Mn, Bをランダムに選択して、封をされたブラックボックス内の試料を定量することに成功した。本発表では、開発したNRTAの測定原理を述べ、実施したデモ実験の詳細を発表する。
 erovnik, G.*; Becker, B.*; Belgya, T.*; Genreith, C.*; 原田 秀郎; Kopecky, S.*; Radulovi
erovnik, G.*; Becker, B.*; Belgya, T.*; Genreith, C.*; 原田 秀郎; Kopecky, S.*; Radulovi , V.*; 佐野 忠史*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Trkov, A.*
, V.*; 佐野 忠史*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Trkov, A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 799, p.29 - 36, 2015/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:33.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)冷中性子ビームを用いた測定から、熱中性子捕獲断面積を導出する際の問題点を指摘するとともに、導出する中性子捕獲断面積の系統誤差を低減するための手法について提案するものである。これまでの冷中性子を用いた測定では、標準断面積との相対値より、熱中性子捕獲断面積が導出されてきた。本研究では、冷中性子ビームのエネルギー分布によっては、中性子捕獲断面積のエネルギー依存性が1/v則からずれる核種について、10%以上もの系統的誤差を生じることを明らかとした。中性子捕獲断面積のエネルギー依存性を考慮した断面積導出方法を適用することにより、この系統誤差は補正できることを示した。また、これまでに報告された文献値のいくつかには、冷中性子ビームのサンプル中での自己吸収補正が行われていない問題点があることも指摘した。
土屋 晴文; 小泉 光生; 北谷 文人; 呉田 昌俊; 原田 秀郎; 瀬谷 道夫; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of 37th ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.846 - 851, 2015/08
中性子の共鳴反応を利用した分析手法に、中性子共鳴透過分析法(NRTA)がある。本技術を活用してMA混入核燃料に含まれているウランやプルトニウムを検出・定量するアクティブ中性子非破壊分析法を開発している。さらに、本手法をMA混入核燃料のみならず、高放射線場の中にあるさまざまな物質の定量に適用することを目指している。これまで粒子状の燃料デブリへの適用を目的として、われわれが開発してきた中性子共鳴濃度分析法(NRD)で得た知見を本技術開発に活かす。NRTAにより、透過中性子スペクトルの解析を通じてウランやプルトニウムを同定・定量する。本発表では、NRTAの基礎を紹介するとともに、開発するアクティブ中性子を用いた非破壊測定手法の中でのNRTAの役割を説明する。その上で、NRDの開発で得た知見を紹介するとともに、本技術開発の中でのNRTAの今後の検討項目について議論する。
 -ray analysis for active neutron NDA
-ray analysis for active neutron NDA小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 呉田 昌俊; 瀬谷 道夫; 原田 秀郎; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of 37th ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.852 - 858, 2015/08
Active NDA techniques will draw out more information on the sample objects, in comparison with passive NDA techniques. Elementary particles (such as photons and neutrons) are used to induce nuclear reactions in the sample objects. The materials in the objects are deduced from the measured particles coming out of them. A new development program of active neutron NDA technologies has been started for detection/measurement of nuclear materials using a pulsed neutron source for nuclear security and nuclear non-proliferation; this project includes the basic technological development of NRTA, NRCA/PGA, neutron differential die-away (DDA) and a Delayed Gamma-ray (DG) technique. A system of active neutron NDA has been proposed. In this presentation, we review the methods and techniques on NRCA and PGA, which will be utilized for identifying materials in the objects in active neutron NDA.
呉田 昌俊; 小泉 光生; 大図 章; 古高 和禎; 土屋 敬広*; 瀬谷 道夫; 原田 秀郎; Abousahl, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of 37th ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.111 - 120, 2015/08
原子力機構は、EC-JRCとの国際共同研究による「アクティブ中性子非破壊測定技術開発」に着手した。本研究課題の最終目標は、MA核変換用MA-Pu燃料など高線量核燃料や、核セキュリティ関連装置への適用を目指した核物質測定技術を確立することである。本研究課題では、アクティブ中性子法であるDDA法, NRTA法, PGA/NRCA法, DGS法による核物質測定技術の研究開発を行う。
原田 秀郎; 木村 敦; 北谷 文人; 小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(6), p.837 - 843, 2015/06
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) is a non-destructive analysis method, which can be applied to quantify special nuclear materials (SNM) in small particle-like debris of melted fuel that is formed in severe accidents of nuclear reactors such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. NRD uses neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) to quantify SNM and neutron resonance capture analysis (NRCA) to identify matrix materials and impurities. In order to generalize NRD for the characterization of arbitrary-shaped thick materials, a generalized method to analyze NRTA data has been developed. The method has been applied on data resulting from transmission through non-uniform thick samples with varying areal density of SNM up to 0.253 at/b ( 100 g/cm
100 g/cm ). The investigation shows that NRD could be used to quantify SNM in not only uniform samples made of small particle-like debris but also non-uniform samples made of large rock-like debris with high accuracy by utilizing the generalized analysis method for NRTA.
). The investigation shows that NRD could be used to quantify SNM in not only uniform samples made of small particle-like debris but also non-uniform samples made of large rock-like debris with high accuracy by utilizing the generalized analysis method for NRTA.
Paradela, C.*; Alaerts, G.*; Becker, B.*; 原田 秀郎; Heyse, J.*; 北谷 文人; 小泉 光生; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Moens, A.*; et al.
EUR-27507-EN, 16 Pages, 2015/04
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD), a non-destructive analysis method, is presented. The method has been developed to quantify special nuclear material (SNM) in debris of melted fuel that will be produced during the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. The method is based on Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA). The quantification of SNM relies on the NRTA results. The basic principles of NRD, which are based on well-established methodologies for neutron resonance spectroscopy, are explained. To develop NRD for the characterization of rock- and particle like heterogeneous samples a JAEA/JRC collaboration has been established. As part of this collaboration a NRD demonstration workshop was organized at the TOF facility GELINA of the JRC-IRMM. The results of this workshop are presented. They illustrate the potential of measurements of complex mixtures of different elements. It is demonstrated that the elemental composition of an unknown sample predicted by NRTA deviated on average by less than 2% from the declared value. In addition the potential to identify the presence of light elements by NRCA is shown.