Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Zn
Zn probed by muon spin relaxation
probed by muon spin relaxationHigemoto, Wataru; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Saiga, Yuta*; Kosaka, Masashi*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012039_1 - 012039_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.2(Physics, Applied)The cubic compound YbCo Zn
Zn has huge electronic specific heat coefficient and its ground state could be located in the vicinity of the quantum critical point. Indeed, a magnetic long-range order was observed under pressure above 1-2 GPa. To investigate magnetic ground state, we have carried out muon spin relaxation measurements and confirm non-magnetic ground state with fluctuating tiny magnetic moment.
has huge electronic specific heat coefficient and its ground state could be located in the vicinity of the quantum critical point. Indeed, a magnetic long-range order was observed under pressure above 1-2 GPa. To investigate magnetic ground state, we have carried out muon spin relaxation measurements and confirm non-magnetic ground state with fluctuating tiny magnetic moment.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kosaka, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2543 - 2546, 2019/06
A bunch shape monitor (BSM) is one of the important instruments to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution. For example in the J-PARC linac, three BSMs using the tungsten wire are installed at the ACS section to measure the bunch shapes between the accelerating cavities. However, this conventional BSM is hard to measure the bunch shape of H beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H
beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of
beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of  10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
 Si
SiHiraka, Haruhiro*; Oyama, Kenji*; Kosaka, Masashi*; Matsumura, Daiju
AIP Advances (Internet), 8(10), p.101424_1 - 101424_5, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.41(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) C
C
Yamauchi, Hiroki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Kosaka, Masashi*; Matsuoka, Eiichi*; Onodera, Hideya*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.2084 - 2087, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Ga
Ga O
O (x =0, 0.018)
(x =0, 0.018)Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Takahashi, Keiichiro*; Yoshitomi, Keisuke*; Masuda, Kazuya*; Kaneko, Chikafumi*; Homma, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kosaka, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094710_1 - 094710_8, 2012/09
 Ga
Ga O
O (
( = 0, 0.018)
= 0, 0.018)Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Takahashi, Keiichiro*; Yoshitomi, Keisuke*; Masuda, Kazuya*; Kaneko, Chikafumi*; Homma, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kosaka, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094710_1 - 094710_8, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.29(Physics, Multidisciplinary) C
C
Matsumura, Takeshi*; Inami, Toshiya; Kosaka, Masashi*; Kato, Yoshiaki*; Inukai, Takaki*; Ochiai, Akira*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Katano, Susumu*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(10), p.103601_1 - 103601_4, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:62.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Araya, Fumimasa; Hirano, Masashi; ; Matsumoto, Kiyoshi; Yokobayashi, Masao; Kosaka, Atsuo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 34(9), p.879 - 888, 1992/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Araya, Fumimasa; Hirano, Masashi; ; Matsumoto, Kiyoshi; Yokobayashi, Masao; Kosaka, Atsuo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 34(6), p.565 - 575, 1992/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Tadashi; Hirano, Masashi; ; Tanabe, Fumiya; Kosaka, Atsuo
JAERI 1326, 232 Pages, 1992/03
no abstracts in English
Hirano, Masashi; Kosaka, Atsuo
JAERI-M 92-006, 76 Pages, 1992/02
no abstracts in English
Araya, Fumimasa; Hirano, Masashi; ; Matsumoto, Kiyoshi; Yokobayashi, Masao; Kosaka, Atsuo
CSNI-178, p.370 - 384, 1990/00
no abstracts in English
Araya, Fumimasa; ; Hirano, Masashi; Matsumoto, Kiyoshi; Yokobayashi, Masao; Kosaka, Atsuo
1989 Stability Symp., p.1 - 17, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
Araya, Fumimasa; ; Hirano, Masashi; Matsumoto, Kiyoshi; Yokobayashi, Masao; Kosaka, Atsuo
ANS Proc. on 1989 National Heat Transfer Conf., Vol. 4, p.69 - 76, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
 Zn
Zn probed by muon spin relaxation
probed by muon spin relaxationHigemoto, Wataru; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Saiga, Yuta*; Kosaka, Masashi*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*
no journal, ,
A heavy fermion compound YbCo Zn
Zn possess quite large electronic specific heat coefficient at low temperature. We have carried out muon spin relaxation measurement to clarify a magnetic ground state. No static magnetic ordering was observed down to 20mK. Meanwhile, the fluctuating magnetic field was detected. This fact suggests that the compound is located in the vicinity of the quantum critical point.
possess quite large electronic specific heat coefficient at low temperature. We have carried out muon spin relaxation measurement to clarify a magnetic ground state. No static magnetic ordering was observed down to 20mK. Meanwhile, the fluctuating magnetic field was detected. This fact suggests that the compound is located in the vicinity of the quantum critical point.
 O
O in magnetic field
in magnetic fieldMatsuda, Masaaki; Hoshi, Takemichi*; Katori, Hiroko*; Kosaka, Masashi*; Takagi, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
GeCo O
O has the spinel structure, in which the Co
has the spinel structure, in which the Co moments with
moments with  =3/2 are located at the corners of the tetrahedron. It shows an antiferromagnetic ordering with a characteristic wave vector of
=3/2 are located at the corners of the tetrahedron. It shows an antiferromagnetic ordering with a characteristic wave vector of  =(1/2, 1/2, 1/2) below
=(1/2, 1/2, 1/2) below 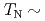 21 K accompanied by a structural phase transition from cubic to tetragonal symmetry. This compound also exhibits a magnetic phase transition at
21 K accompanied by a structural phase transition from cubic to tetragonal symmetry. This compound also exhibits a magnetic phase transition at 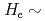 4 T. Magnetic field dependence of some magnetic Bragg peak intensities was measured. For example, the (1/2, 1/2, 1/2) Bragg intensity increases with increasing magnetic field up to 4 T and gradually decreases above 4 T. This characteristic field is consistent with Hc. The field dependence of the intensity probably originates from the combined effects of the redistribution of the magnetic domains and a magnetic phase transition.
4 T. Magnetic field dependence of some magnetic Bragg peak intensities was measured. For example, the (1/2, 1/2, 1/2) Bragg intensity increases with increasing magnetic field up to 4 T and gradually decreases above 4 T. This characteristic field is consistent with Hc. The field dependence of the intensity probably originates from the combined effects of the redistribution of the magnetic domains and a magnetic phase transition.