Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid reveals that
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid reveals that 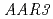 , a gene encoding a DCN1-like protein, regulates responses to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in Arabidopsis roots
, a gene encoding a DCN1-like protein, regulates responses to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in Arabidopsis rootsBiswas, K. K.*; Oura, Chiharu*; Higuchi, Kanako*; Miyazaki, Yuji*; Nguyen, V. V.*; Rahman, A.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Kiyosue, Tomohiro*; Koshiba, Tomokazu*; Tanaka, Atsushi; et al.
Plant Physiology, 145(3), p.773 - 785, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:66.14(Plant Sciences)We screened mutants for root growth resistance to a putative antiauxin, PCIB, which inhibits auxin action by interfering the upstream auxin signaling events. Eleven PCIB-resistant mutants were obtained. Genetic mapping indicates that the mutations are located in at least 5 independent loci including two known auxin-related loci, 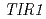 and
and 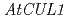 .
. 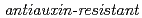 mutants (
mutants (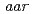 s)
s) 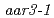 ,
, 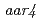 and
and 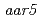 were also resistant to 2,4-D as shown by a root growth assay. Positional cloning of
were also resistant to 2,4-D as shown by a root growth assay. Positional cloning of 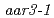 revealed that the
revealed that the 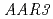 gene encodes a protein with a domain of unknown function (DUF298), which has not previously been implicated in auxin signaling. The protein has a putative nuclear localization signal and shares homology with the DCN-1 protein through the DUF298 domain. The results also indicate that PCIB can facilitate the identification of factors involved in auxin or auxin-related signaling.
gene encodes a protein with a domain of unknown function (DUF298), which has not previously been implicated in auxin signaling. The protein has a putative nuclear localization signal and shares homology with the DCN-1 protein through the DUF298 domain. The results also indicate that PCIB can facilitate the identification of factors involved in auxin or auxin-related signaling.