Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Ozaki, Toshinori*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(2), p.023001_1 - 023001_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.47(Physics, Applied)We show that Xe ion irradiation with 80 MeV to GdBa Cu
Cu Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at
Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at 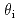 = 45
= 45 , whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (
, whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (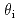 = 0
= 0 ) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density
) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density  .
.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Uraguchi, Yusei*; Suenaga, Momotaro*; Makihara, Takahiro*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Ishikawa, Norito
Physica C, 530, p.72 - 75, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.28(Physics, Applied)In order to clarify the influence of size and spatial distribution of three-dimensional pinning centers (3D-PCs) on hybrid flux pinning, columnar defects (CDs) were installed by using 200 MeV Xe ions along the  -axis direction into quasi-multilayered films consisting of YBa
-axis direction into quasi-multilayered films consisting of YBa Cu
Cu Oy layers and pseudo layers of BaSnO
Oy layers and pseudo layers of BaSnO . The positive effect of the BaSnO
. The positive effect of the BaSnO doping on the hybrid flux pinning stands out for the critical current density
doping on the hybrid flux pinning stands out for the critical current density  around
around 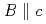 in high magnetic field and/or inclined magnetic field off the
in high magnetic field and/or inclined magnetic field off the  -axis, whereas there is little difference in the
-axis, whereas there is little difference in the  at
at 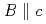 among the same growth temperature samples for low magnetic field. In the case of the in-plane distributed BaSnO
among the same growth temperature samples for low magnetic field. In the case of the in-plane distributed BaSnO nano-dots, the Jc around
nano-dots, the Jc around 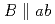 is remarkably enhanced, whereas there is a detrimental effect on the Jc around
is remarkably enhanced, whereas there is a detrimental effect on the Jc around 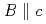 . These imply that the tuning of 3D-PCs is one of the keys to improve the
. These imply that the tuning of 3D-PCs is one of the keys to improve the  at all magnetic field orientations for the hybrid flux pinning.
at all magnetic field orientations for the hybrid flux pinning.
Oks, E.*; Dalimier, E.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Andreev, A.*; Koga, J. K.; Sakaki, Hironao; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 23(25), p.31991 - 32005, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.80(Optics)We present experiments dealing with a femtosecond laser-driven cluster-based plasma, where by analyzing the nonlinear phenomenon of satellites of spectral lines of Ar XVII, we revealed the nonlinear phenomenon of the generation of the second harmonic of the laser frequency. For performing this analysis we developed new results in the theory of satellites of spectral lines. From such lineshape analysis we found, in particular, that the efficiency of converting the short (40 fs) intense (3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm ) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Uraguchi, Yusei*; Kai, Takashi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.6603004_1 - 6603004_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:50.69(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To investigate the effect of discontinuity of 1-D pinning centers on the flux pinning in a wide range of magnetic field directions, discontinuous columnar defects (CDs) and continuous CDs were formed in GdBCO coated conductors using Xe-ion irradiations with 80 and 270 MeV, respectively. An overall shift upward in Jc, for the 80-MeV-irradiated sample compared to the 270-MeV-irradiated one, can be observed in every direction of magnetic field, which is more remarkable as temperature decreases. This implies a synergetic effect of the pinning interaction between the linearity and the discontinuity for the discontinuous CDs.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Koga, J. K.; Mori, Michiaki; Kawase, Keigo*; et al.
RAL-TR-2015-025, P. 22, 2015/00
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 16(9), p.093003_1 - 093003_30, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:80.06(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -values in BaZrO
-values in BaZrO /YBa
/YBa Cu
Cu O
O quasi-multilayered films with columnar defects
quasi-multilayered films with columnar defectsSueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Mitsugi, Fumiaki*; Ikegami, Tomoaki*; Ishikawa, Norito
Physica C, 494, p.153 - 157, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.56(Physics, Applied)BaZrO /YBa
/YBa Cu
Cu Oy quasi-multilayered films, in which the size and the spatial distribution of BaZrO
Oy quasi-multilayered films, in which the size and the spatial distribution of BaZrO nano-particles were controlled, were irradiated using 200 MeV Xe ions along the c-axis direction. Whenthe BaZrO
nano-particles were controlled, were irradiated using 200 MeV Xe ions along the c-axis direction. Whenthe BaZrO nano-particles were larger in size, the flux lines not captured by CDs, such as interstitial fluxlines between CDs and double kinks of flux lines, can be pinned more effectively by the BaZrO
nano-particles were larger in size, the flux lines not captured by CDs, such as interstitial fluxlines between CDs and double kinks of flux lines, can be pinned more effectively by the BaZrO nano-particles, so that the Jc enhances for high magnetic fields and high temperature. In addition, the inverse correlation between Jc and n-value appears at high temperature in increasing magnetic field for the film with correlated rows of the nano-particles which might be curved off the c-axis. These suggest that the hybrid flux pinning depends not only on the combination of one-dimensional (1D) and three-dimensional pinning centers (3D-PCs) but also on the size and the spatial distribution of the 3D-PCs.
nano-particles, so that the Jc enhances for high magnetic fields and high temperature. In addition, the inverse correlation between Jc and n-value appears at high temperature in increasing magnetic field for the film with correlated rows of the nano-particles which might be curved off the c-axis. These suggest that the hybrid flux pinning depends not only on the combination of one-dimensional (1D) and three-dimensional pinning centers (3D-PCs) but also on the size and the spatial distribution of the 3D-PCs.
Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kawase, Keigo*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.159 - 166, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.172 - 180, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)The bow wave induced mechanism of high-order harmonics generation was discovered using simulations and catastrophe theory. This mechanism feasibility was successfully demonstrated in 3D and 2D PIC simulations. The mechanism and the simulations explained high-order harmonics in the XUV spectral region seen in recent experiments with terawatt lasers. Development of new XUV light and X-ray source based on the high-order harmonics generation mechanism is proposed.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.167 - 171, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.30(Physics, Applied)Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 108(13), p.135004_1 - 135004_5, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:90.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We demonstrate a new high-order harmonic generation mechanism reaching the "water window" spectral region in experiments with multi-terawatt femtosecond lasers irradiating gas jets. A few hundred harmonic orders are resolved, giving  J/sr pulses. Harmonics are collectively emitted by an oscillating electron spike formed at the joint of the boundaries of a cavity and bow wave created by a relativistically self-focusing laser in underdense plasma. The spike sharpness and stability are explained by catastrophe theory. The mechanism is corroborated by particle-in-cell simulations.
J/sr pulses. Harmonics are collectively emitted by an oscillating electron spike formed at the joint of the boundaries of a cavity and bow wave created by a relativistically self-focusing laser in underdense plasma. The spike sharpness and stability are explained by catastrophe theory. The mechanism is corroborated by particle-in-cell simulations.
Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; Skobelev, I.*; Gasilov, S.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 49(6), p.06GK03_1 - 06GK03_5, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.25(Physics, Applied)Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kawase, Keigo; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; Daito, Izuru; Kameshima, Takashi; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(23), p.235003_1 - 235003_4, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:93.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Fukuda, Yuji; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Daito, Izuru; Kawase, Keigo; Ma, J. L.*; Chen, L. M.*; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
European Physical Journal D, 55(2), p.465 - 474, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:64.42(Optics)Nonlinear interaction of intense laser beams with plasma causes a number of different regimes of generation of high energy particle beams and of strong radiation with the emitted photon energy from the X-ray to THz frequency range. The review of the first proof-of-principle experiment and the latest progress on the flying mirror is presented. A low frequency EM radiation emission has also been observed in our experiments. The interpretation invokes the relativistic electromagnetic solitons. The solitons are formed in an underdense plasma in the process of the laser pulse frequency downshift. They store a portion of EM wave energy with the polarization inherited from the laser and emit it at the plasma-vacuum interface in a form of the low frequency EM bursts. We present the results of the polarization-resolved measurements.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Chen, L.-M.*; Daito, Izuru; Ogura, Koichi; Homma, Takayuki; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1153, p.274 - 284, 2009/07
Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Fukuda, Yuji; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Daito, Izuru; Kawase, Keigo; Ma, J.-L.; Chen, L.-M.; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Harnessing Relativistic Plasma Waves as Novel Radiation Sources from Terahertz to X-Rays and Beyond (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.7359), p.73590K_1 - 73590K_11, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Optics)Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Daito, Izuru; Ma, J.-L.; Chen, L. M.; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 92(12), p.121110_1 - 121110_3, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:86.20(Physics, Applied)The novel soft X-ray light source using the supersonic expansion of the mixed gas of He and CO , when irradiated by a femtosecond Ti:sapphire laser pulse, is observed to enhance the radiation of soft X-rays from the CO
, when irradiated by a femtosecond Ti:sapphire laser pulse, is observed to enhance the radiation of soft X-rays from the CO clusters. Using this soft X-ray emissions, nanostructure images of 100-nm thick Mo foils in a wide field of view (mm
clusters. Using this soft X-ray emissions, nanostructure images of 100-nm thick Mo foils in a wide field of view (mm scale) with high spatial resolution (800 nm) are obtained with high dynamic range LiF crystal detectors. The local inhomogeneities of soft X-ray absorption by the nanometer-thick foils is measured with an accuracy of less than
scale) with high spatial resolution (800 nm) are obtained with high dynamic range LiF crystal detectors. The local inhomogeneities of soft X-ray absorption by the nanometer-thick foils is measured with an accuracy of less than  3 %.
3 %.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ma, J.-L.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Chen, L. M.; Daito, Izuru; Ogura, Koichi; Homma, Takayuki; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(12), p.123106_1 - 123106_22, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:97 Percentile:42.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Kinoshita, Kenichi*; Watanabe, Takahiro*; Sugahara, Jun*; Ueda, Toru*; Yoshii, Koji*; Kobayashi, Tetsuya*; Halz, N.*; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Sakai, Fumio*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 28(4), p.1133 - 1142, 2000/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:41.05(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ma, J.-L.; Fukuda, Yuji; Chen, L. M.; Daito, Izuru; Ogura, Koichi; Homma, Takayuki; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
no journal, ,