Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Inoue, Toshihiko; Ogawa, Miho; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Sato, Soichi; Koyama, Shinichi; Koyama, Tomozo; Nakayama, Shinichi
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2017/00
Decommissioning of TEPCO's 1F is in progress according to the Roadmap. The Roadmap assigned the construction of a hot laboratory and analysis to the JAEA. The hot laboratory, Okuma Analysis and Research Center consists of the three buildings; Administrative building, the Laboratory-1 and Laboratory-2. The Laboratory-1 and Laboratory-2 are hot laboratories. Laboratory-1 is for radiometric analysis of low and medium level radioactive rubble and secondary wastes. The license of the Laboratory-1's implementation was approved by The Secretariat of the Nuclear Regulation Authority and the construction started in April 2017 and plans an operational start in 2020. Laboratory-2 provides concrete cells, steel cells for the analysis of the fuel debris and high level radioactive rubble. The Laboratory-2's major analysis items is reviewed by review meeting organized of cognoscente.
Ito, Masayasu; Ogawa, Miho; Inoue, Toshihiko; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Koyama, Shinichi; Koyama, Tomozo; Nakayama, Shinichi
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2017/00
Laboratory-2 of the Okuma Analysis and Research Center will be used for the technological development of techniques to treat and dispose fuel debris, etc. The specific analytical content and its importance has been discussed by an experts committee in FY 2016. The committee regarded fuel debris retrieval and criticality control related topics as the most important content. As a result, it will be a priority to introduce equipment to perform examination such as shape and size measurement, compositional and nuclide analysis, hardness and toughness test, and radiation dose rate measurement. In addition, since sample will have high dose rates (1 Sv/h or more) at the time of reception, hot cells with enough radiation shielding ability will be used. In the hot cell, the pre-processing will be performed, such as cutting and dissolution of samples. Processed samples will be examined in concrete cells, steel cells, glove boxes and fume hoods. Detail design of Laboratory-2 started on FY 2017.
Sugaya, Yuki; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Akutsu, Hideyuki; Inoue, Toshihiko; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Sato, Soichi; Koyama, Tomozo; Nakayama, Shinichi
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2017/00
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing the research and development facilities, "Okuma Analysis and Research Center", in order to ascertain the properties of radioactive wastes and fuel debris towards the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. This paper outlines the concept of "Laboratory-1" which will analyze low and medium level samples in the Okuma Analysis and Research Center with a focus on the research plan.
Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Kosaka, Ichiro; Hirano, Hiroyasu; Koyama, Tomozo; Kawamura, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 52nd Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling Working Group (HOTLAB 2015) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/09
Due to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in March 2011, the safe and secure implementations of the decommissioning for Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant has been positioned as the urgent tasks in Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has a critical mission of analysing radioactive wastes having generated by the accident for long-term storage and disposal methods. This will be performed in two hot laboratories to be constructed in Okuma Analysis and Research Center at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant site. In one laboratory, radioactive wastes such as rubbles and secondary wastes will be treated, whereas debris such as fuel debris and high dose structural materials will be handled in the other laboratory. The detail considerations for advanced techniques and experimental apparatus to be installed are underway.
Koma, Yoshikazu; Ashida, Takashi; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Sasaki, Toshiki; Yamagishi, Isao; Kameo, Yutaka; Terada, Atsuhiko; Hiyama, Toshiaki; Koyama, Tomozo; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference; Nuclear Energy at a Crossroads (GLOBAL 2013) (CD-ROM), p.736 - 743, 2013/09
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS), TEPCO, was severely damaged with the hydrogen explosions caused by losing their cooling functions due to the earthquake and the tsunami occurred on March 11, 2011. Radioactive wastes generated from the current FINPS and future their decommission and demolition are greater huge amount than those from general reactors and nuclear fuel facilities. Toward accomplishing safe and reasonable management of the wastes, great effort of R&Ds has been strongly required and performed in bringing together the knowledge and experience of all of Japan. This report outlines the current status of the R&Ds performed in JAEA.
Inoue, Naoko; Kaji, Naoya; Suda, Kazunori; Kawakubo, Yoko; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Koyama, Tomozo; Kuno, Yusuke; Senzaki, Masao
Proceedings of INMM 51st Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/07
Shibata, Atsuhiro; Oyama, Koichi; Yano, Kimihiko; Nomura, Kazunori; Koyama, Tomozo; Nakamura, Kazuhito; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Homma, Shunji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 46(2), p.204 - 209, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:43.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new reprocessing system with 2-stage crystallization process has been developed. In the first stage of the system, U and Pu are recovered from dissolver solution by U-Pu co-crystallization. Laboratory scale experiments were carried out with U and Pu mixed solution and irradiated fuel dissolver solution to obtain fundamental data on U-Pu co-crystallization process. Pu co-crystallized with U, but crystallization yields of Pu were lower than those of U. FPs were separated from U and Pu by co-crystallization, and decontamination factors of Cs and Eu to U in crystal were over 100.
Homma, Shunji*; Ishii, Junichi; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koyama, Tomozo; Koga, Jiro*; Matsumoto, Shiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(6), p.510 - 517, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:57.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)U-Pu co-crystallization reprocessing system is proposed for LWR fuels and its flowsheet study is carried out. This reprocessing system is based on the experimental evidence indicating that hexavalent plutonium is co-crystallized with uranyl nitrate. The system consists of five steps: dissolution of spent fuel, Pu oxidation, U-Pu co-crystallization, dissolution of the crystals, and U crystallization. The system does not require organic solvent, expecting the enhancement of safety and cost-effectiveness. The system requires a recycling of the mother liquor from the U-Pu co-crystallization step to recover almost entire amount of U and Pu. The appropriate recycle ratio is determined for LWR fuels, such that the satisfactory decontamination is achieved. The mother liquor from the U re-crystallization step contains U and Pu. The flowsheet study shows that the constant ratio of Pu to U in the mother liquor can be controlled even though the composition of the spent fuel is different.
Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koyama, Tomozo; Homma, Shunji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(6), p.582 - 587, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:74.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Batch crystallization of uranyl nitrate is carried out in order to obtain fundamental data required for the development of reprocessing involving crystallization. Particular attention is paid to the development of a method for predicting the concentrations of uranium and nitric acid in the mother liquor and the amount of uranyl nitrate crystals produced. Initial concentrations of uranyl nitrate and nitric acid are 500-600 g/dm and 4-6 mol/dm
and 4-6 mol/dm , respectively, corresponding to the condition of a dissolver solution of spent fuel. Steady-state mass balance equations including the correlation equation for the equilibrium solubility of uranium nitrate are applied to the prediction. The calculated concentrations of uranium and nitric acid are in close agreement with the experimental ones. The recovery of uranium is accurately predicted by the calculated concentrations, with an error of less than 5%.
, respectively, corresponding to the condition of a dissolver solution of spent fuel. Steady-state mass balance equations including the correlation equation for the equilibrium solubility of uranium nitrate are applied to the prediction. The calculated concentrations of uranium and nitric acid are in close agreement with the experimental ones. The recovery of uranium is accurately predicted by the calculated concentrations, with an error of less than 5%.
Koyama, Tomozo
Genshiryoku eye, 53(9), p.56 - 59, 2007/09
In order to establish improvement of aqueous reprocessing technology in economy and waste reduction, JAEA has been developing "Actinides co-extraction system with direct extraction process using supercritical carbon dioxide" in collaboration with Nagoya University and ARTECH Co.Ltd. as nuclear system research and development application program by MEXT since 2005. Measurement of distribution factors of major fission product elements and confirmation of supercritical fluid behavior have been executed. In JFY 2007, distribution factors will be continuously measured and direct extraction test of unirradiated MOX in normal pressure will be carried out. In JFY 2008-2009, direct extraction test of unirradiated MOX and irradiated fuel will be executed using supercritical carbon dioxide in a glovebox and a cell.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Koma, Yoshikazu; Kamiya, Masayoshi; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(3), p.373 - 381, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:86.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)Actinides recovery was attempted by the simplified solvent extraction process using TBP as an extractant for U, Pu and Np co-recovery and the SETFICS process for Am and Cm recovery with a view to decreasing the environmental impact. Uranium, Pu and Np co-recovery was conducted under the condition with high nitric acid concentration in the feed solution or scrubbing solution. High nitric acid concentration in the feed solution availed to the Np oxidation not only in the feed solution, but also at the extraction section. This oxidation reaction permitted the Np extraction with U and Pu. In the SETFICS process, a TRUEX solvent of 0.2M CMPO/1.4M TBP was employed to increase the loading of metals. In place of sodium nitrate, HAN was applied to this experimental flow sheet for "salt-free" concept. This experiment was succeeded in Am and Cm product. On high-loading flow sheet, the flow rate of aqueous effluents and spent solvent was expected to decrease in 47% and 54%, respectively.
Yano, Kimihiko; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(3), p.344 - 348, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)The crystallization process has been developed as a part of the advanced aqueous process, NEXT (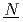 ew
ew 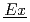 traction System for
traction System for 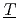 RU recovery) for fast reactor (FR) cycle. In this process, a large part of U is separated from dissolver solution by crystallization as UO
RU recovery) for fast reactor (FR) cycle. In this process, a large part of U is separated from dissolver solution by crystallization as UO (NO
(NO )
) 6H
6H O. The U crystallization test was carried out with real dissolver solution of irradiated FR fuel to investigate the influence of cooling rate on the crystal size and the behavior of fission product (FP) compared with that of Pu(IV). In regard to the influence of the cooling rate, it was obvious that the crystal size was smaller as the cooling rate is faster. Although it was expectable that the decontamination performance was improved by diminishing the specific surface of the crystals, it was suggested that a large crystal produced by crystallization was not always high purity. Concerning the behavior of FPs, Eu behaved similarly to Pu(IV). Cs accompanied with U into the crystals under the condition in this test.
O. The U crystallization test was carried out with real dissolver solution of irradiated FR fuel to investigate the influence of cooling rate on the crystal size and the behavior of fission product (FP) compared with that of Pu(IV). In regard to the influence of the cooling rate, it was obvious that the crystal size was smaller as the cooling rate is faster. Although it was expectable that the decontamination performance was improved by diminishing the specific surface of the crystals, it was suggested that a large crystal produced by crystallization was not always high purity. Concerning the behavior of FPs, Eu behaved similarly to Pu(IV). Cs accompanied with U into the crystals under the condition in this test.
 concentration feed solution and scrubbing solution
concentration feed solution and scrubbing solutionNakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Miyachi, Shigehiko; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo; Aose, Shinichi
JAEA-Research 2006-030, 43 Pages, 2006/06
Concerning the advanced aqueous reprocessing system, the simplified solvent extraction process for U, Pu and Np co-recovery has been investigated. We carried out the counter-current experiment, which aimed for Np oxidation and extraction by high [HNO ] condition. For preventing Np leakage to the raffinate, feed solution and scrubbing solution with high [HNO
] condition. For preventing Np leakage to the raffinate, feed solution and scrubbing solution with high [HNO ] were used, which would bring high [HNO
] were used, which would bring high [HNO ] in the extraction section and efficient Np oxidation and extraction in this section. In addition, high [HNO
] in the extraction section and efficient Np oxidation and extraction in this section. In addition, high [HNO ] in the feed solution could help the pre-oxidation of Np to extractable Np(VI). In the steady state, the Np leakage to the raffinate could be kept under about 1%. The stage efficiencies for these elements were estimated by fitting the concentration profiles calculated by MIXSET-X into the experimental results. The stage efficiency of U, Pu and Np were evaluated 100%, 100% and 98.5% in the extraction section and 95%, 90% and 89% in the stripping section respectively.
] in the feed solution could help the pre-oxidation of Np to extractable Np(VI). In the steady state, the Np leakage to the raffinate could be kept under about 1%. The stage efficiencies for these elements were estimated by fitting the concentration profiles calculated by MIXSET-X into the experimental results. The stage efficiency of U, Pu and Np were evaluated 100%, 100% and 98.5% in the extraction section and 95%, 90% and 89% in the stripping section respectively.
Yano, Kimihiko; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo
Recent Advances in Actinide Science, p.644 - 646, 2006/06
U crystallization is effective to minimize solvent extraction process equipment by separating U from dissolver solution of spent fuel. In order to establish crystallization process for FBR MOX fuel, Pu behavior needs to be investigated with mixed U and Pu solution. Pu valence influence on the decontamination factor (DF) of Pu to U in crystal. Pu(IV) was not crystallized with U and DF was about 30. Although Pu(VI) dose not solely crystallized, it was co-crystallized with U and DF of Pu to U in crystal was about 1.3. The effect of Pu(IV) concentration on crystallization yield of U is small. It had a tendency to decrease crystallization yield of U by that Pu(VI) exists, compared with that calculated by solubility of U in U-HNO -H
-H O system.
O system.
Yano, Kimihiko; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/10
The uranium crystallization process has been developed as part of advanced aqueous reprocessing system. In the process, the great part of uranium is separated from the dissolver solution by crystallization as uranyl nitrate hydrate. The uranium crystallization test was carried out with the dissolver solution of irradiated FBR MOX fuel to investigate the influence of cooling rate on the crystal size and the behavior of fission products compared with that of tetravalent plutonium with the real dissolver solution. In regard to the influence of the cooling rate, it was obvious that the crystal size was smaller as the cooling ratio was faster. However, it was suggested that a large crystal produced by crystallization was always not high purity. Concerning the behavior of fission products, europium behaved similarly to tetravalent plutonium. Cesium accompanied with uranium into the crystals under the condition of this test.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Koma, Yoshikazu; Kamiya, Masayoshi; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/10
Concerning the advanced aqueous reprocessing system named NEXT process, the behavior of actinide elements was investigated in main two extraction processes of NEXT process, i.e. the simplified PUREX process for U, Pu and Np recovery, and SETFICS process for Am and Cm recovery.
Sano, Yuichi; Miyachi, Shigehiko; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/10
Dissolution behavior of the irradiated MOX fuel was investigated under high Heavy Metal concentration condition for the feed solution of the crystallization process.
Sano, Yuichi; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo; Fox, D.*; Carrott, M.*; Taylor, R.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/10
Based on the U(VI) back-extraction experiments with the miniaturized single stage centrifugal contactor, effects of the total flowrate, the rotor speed and the temperature on the U(VI) mass transfer efficiency were discussed. The relationship between the U(VI) mass transfer efficiency and the residence time suggested that the U(VI) back-extraction system with the centrifugal contactor could be treated as a perfectly stirred continuous reactor. It is considered that the variations of the mass transfer efficiency were caused by the flow pattern change from the laminar flow to the turbulent flow with increasing of the rotor speed in the centrifugal contactor. In the U(VI) back-extraction under the high rotor speed condition, no significant temperature dependence of the apparent overall transform coefficient was observed. In the U(VI) back-extraction under the low rotor speed condition, temperature dependence of the apparent overall transform coefficient seemed to be larger than under the high rotor speed condition, and it suggested a chemical-step contribution in this system. Such a difference of the temperature dependence of the apparent overall transform coefficient between these experiments might be caused by the change of solvent extraction environments in the centrifugal contactor with the variation of the rotor speed.
Koyama, Tomozo; Sano, Yuichi; Kamiya, Masayoshi; Shibata, Atsuhiro
Program and Abstracts, p.50, P. 50, 2005/02
Small scale hot tests have been conducted with irradiated fuel pins of the experimental Fat Reactor
 Complex for Super-DIREX Process
Complex for Super-DIREX ProcessKamiya, Masayoshi; Miura, Sachiko; Nomura, Kazunori; Koyama, Tomozo; Ogumo, Shinya*; Mori, Yukihide*; Enokida, Yoichi*
CD-ROM, P1-35, 4P., 4 Pages, 2004/00
Super-DIREX is a new reprocessing method which has high economical efficiency. Experimental study of this process was started on the direct extraction of U and Pu from irradiated MOX fuel by the supercritical carbon dioxide (SFCO ) containing TBP-HNO
) containing TBP-HNO complex. This report describes direct extraction of U and Pu with TBP-HNO3 complex at atmospheric pressure, as the first test for irradiated fuel, in order to investigate the applicability of SFCO
complex. This report describes direct extraction of U and Pu with TBP-HNO3 complex at atmospheric pressure, as the first test for irradiated fuel, in order to investigate the applicability of SFCO containing TBP-HNO
containing TBP-HNO complex. In this test, dependency on dissolution temperature, Pu content, fuel/ TBP-HNO
complex. In this test, dependency on dissolution temperature, Pu content, fuel/ TBP-HNO complex ratio and effect of voloxidation were investigated. From these results, TBP-HNO
complex ratio and effect of voloxidation were investigated. From these results, TBP-HNO complex was found to be effective in the respect of the recovery of U and Pu. The number of the process step in dissolution and co-extraction is small, and amount of waste can be reduced. It is applicable to the direct extraction in Super-DIREX.
complex was found to be effective in the respect of the recovery of U and Pu. The number of the process step in dissolution and co-extraction is small, and amount of waste can be reduced. It is applicable to the direct extraction in Super-DIREX.