Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Yokoyama, Kenji; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2022/03
In sodium-cooled fast reactors, reactivity feedback is generated by thermal deformation of the core fuel assembly during core temperature rise. To utilize the core deformation reactivity as an inherent safety characteristic and to eliminate excessive conservativeness of core design in the safety evaluation, an evaluation method by coupling analyses of neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structural deformation has been developed. An experiment of unprotected loss-of-flow event in the experimental fast breeder reactor EBR-II was analyzed. The analysis results show that the core deformation reactivity has a negative feedback effect, and that the deformation reactivity is affected not only by the fuel movement but also by the movement of reflectors around the fuel. As a result, the availability of the evaluation method for core deformation reactivity feedback by coupled analysis approach is confirmed.
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
For design optimization of fast reactors, in order to consider the feedback reactivity due to thermal deformation of the core when the core temperature rises, which could not be considered in the conventional design analysis, a neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structure mechanics coupled analysis method has been developed. Neutronics code, plant dynamics code, and structural mechanics code are coupled by a control module in python script. This paper outlines the coupling method of analysis codes and the results of its application to an experiment in an actual plant.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Physics, Nuclear) -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,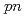 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.72(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
 F from
F from  O
O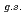 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:74.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 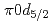 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O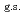 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
 Co
CoLokotko, T.*; Leblond, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Poves, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Authelet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:69.78(Physics, Nuclear)The structures of the neutron-rich  Co isotopes were investigated via (
Co isotopes were investigated via ( ) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the
) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the 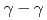 coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the
coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the  Co isotopes.
Co isotopes.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
 Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,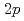 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
,  *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.15(Physics, Nuclear)The nuclear structure of the  Ni nucleus was investigated by (
Ni nucleus was investigated by ( ,
,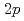 ) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt
) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt  rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by
rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by 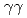 and
and 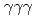 coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
 =28 and
=28 and  =50; Spectroscopy of
=50; Spectroscopy of 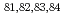 Zn
ZnShand, C. M.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; G
k, Zs.*; G rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 773, p.492 - 497, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:87.36(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Yokoyama, Sumi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hayashida, Toshiyuki*; Tsujimura, Norio; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Nabatame, Kuniaki*; Oguchi, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Kazuko*; Kawaura, Chiyo*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 37(3), p.659 - 683, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:82.15(Environmental Sciences)Since the International Commission on Radiological Protection recommended reducing the occupational equivalent dose limit for the lens of the eye in 2011, there have been extensive discussions in various countries. This paper reviews the current situations in radiation protection of the ocular lens and the discussions on the potential impact of the new lens dose limit in Japan. Topics include historical changes to the lens dose limit, the current situations in occupational lens exposures (e.g., in medical workers, nuclear workers, and Fukushima nuclear power plant workers) and measurements, and the current status of biological studies and epidemiological studies on radiation cataracts. Our focus is on the situations in Japan, but we believe such information sharing will be useful in many other countries.
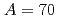 isobars from the
isobars from the 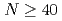 island of inversion
island of inversionMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, T.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 765, p.328 - 333, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:91.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)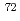 Ni
NiMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; Lorusso, G.*; Patel, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(3), p.034328_1 - 034328_14, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:85.25(Physics, Nuclear)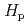 (3) be made?
(3) be made?Akahane, Keiichi*; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Ichiji, Takeshi*; Iwai, Satoshi*; Oguchi, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Kazuko*; Kawaura, Chiyo*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tsujimura, Norio; et al.
Hoken Butsuri, 50(4), p.257 - 261, 2015/12
In a mixed field of photon and beta radiations, the same dose assigned to skin is normally assigned to the dose to the lens of the eye as a conservative estimate of H (3). In exceptional cases that a very high beta dose might be imparted of the same order with the dose limit, however, the conservatively biased dose must be too limiting, and thereby an accurate estimate of beta
(3). In exceptional cases that a very high beta dose might be imparted of the same order with the dose limit, however, the conservatively biased dose must be too limiting, and thereby an accurate estimate of beta 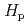 (3) is desirable. This article presents a practical proposal of when and how the dosimetry of beta
(3) is desirable. This article presents a practical proposal of when and how the dosimetry of beta 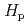 (3) should be made.
(3) should be made.
 Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chain
Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chainBenzoni, G.*; Morales, A. I.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; Gargano, A.*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 751, p.107 - 112, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics) S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Sato, Isamu; Maeda, Koji; Suto, Mitsuo; Osaka, Masahiko; Usuki, Toshiyuki; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(4), p.580 - 587, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Penetration behavior of radionuclides such as  Cs into dried concrete material, dried mortar material and epoxy paint for a few dozen days was observed using a solution containing fission products extracted from irradiated fuels to obtain fundamental information on the radionuclide penetration rate and depth. Hardly any radionuclides could penetrate into the epoxy paint. The radionuclide solution penetrated into concrete and mortar materials to a depth of a few millimeters for a few dozen days. The penetration behavior observed near the surface of concrete and mortar materials was similar to the diffusion of nuclides in media such as water-saturated concrete, bentonite and cement materials.
Cs into dried concrete material, dried mortar material and epoxy paint for a few dozen days was observed using a solution containing fission products extracted from irradiated fuels to obtain fundamental information on the radionuclide penetration rate and depth. Hardly any radionuclides could penetrate into the epoxy paint. The radionuclide solution penetrated into concrete and mortar materials to a depth of a few millimeters for a few dozen days. The penetration behavior observed near the surface of concrete and mortar materials was similar to the diffusion of nuclides in media such as water-saturated concrete, bentonite and cement materials.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
JAEA-Testing 2014-001, 29 Pages, 2014/05
The penetration tests with solution containing radioactive nuclides were experimented to understand basic data for floor and wall materials of Fukushima Daiichi reactor buildings. The solution prepared from irradiated fuels was used as solution containing radioactive nuclides. The solution was applied to surface of epoxy paint, dried concrete and mortar used as specimens. Dose-rate profiles of direction of depth were given by radiation measurement and grinding of the specimens. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for epoxy paint specimens were not clearly observed and the penetration depths would be within 0.4 mm. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for dried concrete specimens proceeded. The penetration rates were substantially decreased when 16 days have elapsed from start. The dose rates of penetrated dried concrete specimens were reduced to background by grinding-2.0 mm.  -ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
-ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
Tsukada, Yuki*; Shiraki, Atsuhiro*; Murata, Yoshinori*; Takaya, Shigeru; Koyama, Toshiyuki*; Morinaga, Masahiko*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 401(1-3), p.13 - 16, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The correlation of defect energies with precipitation of the ferromagnetic phase near M C
C carbide during creep tests at high temperature in Type 304 austenitic steel was examined by estimating the defect energies near the carbide, based on micromechanics. As one of the defect energies, the precipitation energy was calculated by assuming M
carbide during creep tests at high temperature in Type 304 austenitic steel was examined by estimating the defect energies near the carbide, based on micromechanics. As one of the defect energies, the precipitation energy was calculated by assuming M C
C carbide to be a spherical inclusion. The other defect energy, creep dislocation energy, was calculated based on dislocation density data obtained from transmission electron microscopy observations of the creep samples. The dislocation energy density was much higher than the precipitation energy density in the initial stage of the creep process, when the ferromagnetic phase started to increase. Creep dislocation energy could be the main driving force for precipitation of the ferromagnetic phase.
carbide to be a spherical inclusion. The other defect energy, creep dislocation energy, was calculated based on dislocation density data obtained from transmission electron microscopy observations of the creep samples. The dislocation energy density was much higher than the precipitation energy density in the initial stage of the creep process, when the ferromagnetic phase started to increase. Creep dislocation energy could be the main driving force for precipitation of the ferromagnetic phase.
 C
C carbide and ferromagnetic phases during creep deformation in Type 304 steel
carbide and ferromagnetic phases during creep deformation in Type 304 steelTsukada, Yuki*; Shiraki, Atsuhiro*; Murata, Yoshinori*; Takaya, Shigeru; Koyama, Toshiyuki*; Morinaga, Masahiko*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 401(1-3), p.154 - 158, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A phase-field method was applied to the simulation of simultaneous nucleation and growth of both M C
C carbide and ferromagnetic
carbide and ferromagnetic  phases during the creep process in Type 304 steel. The defect energy of the creep dislocations near the carbides, which increases during creep, was integrated into the nucleation driving force for the
phases during the creep process in Type 304 steel. The defect energy of the creep dislocations near the carbides, which increases during creep, was integrated into the nucleation driving force for the  phase. The simulation used in this study accurately reproduced changes in the amounts of the precipitated phases as a function of creep time. Furthermore, we examine the effect of the dislocation density on precipitation of the
phase. The simulation used in this study accurately reproduced changes in the amounts of the precipitated phases as a function of creep time. Furthermore, we examine the effect of the dislocation density on precipitation of the  phase, and show that the phase-field method is useful for examining the stochastic and kinetic phenomenon of phase transformation.
phase, and show that the phase-field method is useful for examining the stochastic and kinetic phenomenon of phase transformation.