Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10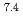 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takano, Masahide; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.1002 - 1012, 2023/08
Onuki, Toshihiko*; Ye, J.*; Kato, Tomoaki; Liu, J.; Takano, Masahide; Kozai, Naofumi; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Environmental Science; Processes & Impacts, 25(7), p.1204 - 1212, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.37(Chemistry, Analytical)To elucidate chemical forms of Cs and I in microparticles produced via the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident and released into the atmosphere, we analyzed Cs and I in condensed vaporized particles (CVP) produced by melting experiments using nuclear fuel components containing CsI with concrete. CVPs consisted of many round particles containing Cs and I of diameters less than several tens of micrometers. Two kinds of particles were present: one containing large amounts of Cs and I, suggesting the presence of CsI, and the other containing small amounts of Cs and I with large Si contents. Most of CsI from both particles were dissolved in water. On the contrary, some fractions of Cs remained from the latter particles. These results suggest that Cs was incorporated in CVPs along with Si to form water low-soluble CVPs
Onuki, Toshihiko*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Satou, Yukihiko; Kitagaki, Toru; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(3), p.384 - 396, 2023/07
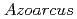 sp. DN11 and its potential use for removal of radioiodine from contaminated aquifers
sp. DN11 and its potential use for removal of radioiodine from contaminated aquifersSasamura, Seiya*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Kozai, Naofumi; Amachi, Seigo*
Frontiers in Microbiology (Internet), 14, p.1162788_1 - 1162788_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:71.89(Microbiology)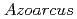 sp. DN11 previously isolated from gasoline-contaminated groundwater contained a gene cluster involved in bacterial iodate (IO
sp. DN11 previously isolated from gasoline-contaminated groundwater contained a gene cluster involved in bacterial iodate (IO
 ) respiration. This study determined if strain DN11 performed iodate respiration and assessed its potential use to remove and sequester radioactive iodine (
) respiration. This study determined if strain DN11 performed iodate respiration and assessed its potential use to remove and sequester radioactive iodine ( I) from subsurface contaminated aquifers. Strain DN11 grew anaerobically with iodate as the sole electron acceptor. After the growth of strain DN11 on iodate, silver-impregnated zeolite was added to the spent medium to remove iodide from the aqueous phase. In the presence of 200
I) from subsurface contaminated aquifers. Strain DN11 grew anaerobically with iodate as the sole electron acceptor. After the growth of strain DN11 on iodate, silver-impregnated zeolite was added to the spent medium to remove iodide from the aqueous phase. In the presence of 200  M iodate as the electron acceptor, more than 98% of iodine was successfully removed from the aqueous phase. These results suggest that strain DN11 is potentially helpful for bioaugmentation of
M iodate as the electron acceptor, more than 98% of iodine was successfully removed from the aqueous phase. These results suggest that strain DN11 is potentially helpful for bioaugmentation of  I-contaminated subsurface aquifers.
I-contaminated subsurface aquifers.
Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Mori, Masanobu*; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A; Chemistry, 438, p.114548_1 - 114548_6, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:34.89(Chemistry, Physical)Removal of iodine from water contaminated by nuclear accidents or the release of radioactive waste is complicated and costly because iodine exists in a variety of forms in the water. We investigated the unification of iodine species by photocatalysis as a pretreatment for removing radioactive iodine species from water. The effect of the TiO crystal phase of Pt-TiO
crystal phase of Pt-TiO and solution pH on the photocatalytic redox reactions of iodide (I
and solution pH on the photocatalytic redox reactions of iodide (I ), iodate (IO
), iodate (IO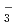 ), and
), and 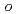 -iodobenzoic acid were evaluated. The choice of TiO
-iodobenzoic acid were evaluated. The choice of TiO crystalline phase and pH allowed the mixture of iodine species to be unified to only I
crystalline phase and pH allowed the mixture of iodine species to be unified to only I or IO
or IO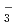 . Regardless of the type of Pt-TiO
. Regardless of the type of Pt-TiO , the iodine in o-iodobenzoic acid was mineralized to I
, the iodine in o-iodobenzoic acid was mineralized to I under alkaline conditions. Because the iodine species can be unified to a single species by selecting the photocatalyst and the solution pH, this photocatalytic treatment could be applied to remove iodine species with high efficiency.
under alkaline conditions. Because the iodine species can be unified to a single species by selecting the photocatalyst and the solution pH, this photocatalytic treatment could be applied to remove iodine species with high efficiency.

 -, SeO
-, SeO
 -, and SeO
-, and SeO
 -coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphate
-coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphateTokunaga, Kohei; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(8), p.3166 - 3175, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.41(Engineering, Environmental)Coprecipitation of radionuclides with barite has been studied to remove radionuclides from radioactive liquid waste because of its excellent removal efficiency; however, little information exists concerning the stability of the ions coprecipitated with barite. This study systematically investigated the stability of iodate, selenite, and selenate coprecipitated with barite via leaching tests. These oxyanions were gradually leached from the oxyanion-bearing barite into ultrapure water over time. Leaching of the oxyanions significantly increased in leaching solutions containing NaCl (pH5.3), NaNO (pH5.9), and Na
(pH5.9), and Na SO
SO (pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH
(pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH PO
PO solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO
solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
Nagano, Hirohiko*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Tanaka, Sota*; Yomogida, Takumi; Kozai, Naofumi; Koarashi, Jun
Frontiers in Forests and Global Change (Internet), 6, p.1228053_1 - 1228053_9, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Ecology)Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 23, p.14 - 19, 2023/00
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Sumita, Takehiro; Kitagaki, Toru; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(6), p.2785 - 2794, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:63.91(Chemistry, Analytical)Remnant nuclear fuel debris in the damaged nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) has contacted the groundwater containing microorganisms for over ten years. Herein, we report the possibility of bacterial alteration of fuel debris. We investigated the physical and chemical changes of fuel debris simulants (FDS) in the powder and pellet forms via exposure to two ubiquitous bacteria, Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus subtilis. In the experiments using FDS composed of the powders of Fe(0), solid solution of CeO and ZrO
and ZrO , and SiO
, and SiO , Ce, Zr, and Si were hardly dissolved, while Fe was dissolved, a fraction of the dissolved Fe was present in the liquid phase as Fe(II) and Fe(III), and the rest was precipitated as the nano-sized particles of iron (hydr)oxides. In the experiment using P. fluorescens and FDS pellet pieces prepared by melting the Fe(0) particles and solid solution of CeO
, Ce, Zr, and Si were hardly dissolved, while Fe was dissolved, a fraction of the dissolved Fe was present in the liquid phase as Fe(II) and Fe(III), and the rest was precipitated as the nano-sized particles of iron (hydr)oxides. In the experiment using P. fluorescens and FDS pellet pieces prepared by melting the Fe(0) particles and solid solution of CeO and ZrO
and ZrO , the bacteria selectively gathered on the Fe(0) particle surface and made corrosion pits. These results suggest that bacteria in groundwater corrode the iron in fuel debris at FDNPP, change fuel debris into porous one, releasing the nano-sized iron (hydr)oxide particles into the water.
, the bacteria selectively gathered on the Fe(0) particle surface and made corrosion pits. These results suggest that bacteria in groundwater corrode the iron in fuel debris at FDNPP, change fuel debris into porous one, releasing the nano-sized iron (hydr)oxide particles into the water.
Kato, Tomoaki; Kozai, Naofumi; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kaplan, D. I.*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.580 - 589, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study reports the effect of fulvic acids, which is a natural organic substance generally contained in groundwater, on the oxidation states of radioactive iodine anions (iodide and iodate). Iodide and iodate are contained in the contaminated water of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and supposed to be removed by activated carbon (AC) via adsorption. When fulvic acids does not exist in the experimental system, the adsorption of iodide on AC was less than that of iodate and their oxidation states after the adsorption were not changed. When fulvic acids existed, a fraction of the adsorbed iodate was reduced to iodide. This result indicates that the reduction of the adsorbed iodate progresses during the storage of the spent AC.
Eljamal, O.*; Maamoun, I.; Alkhudhayri, S.*; Eljamal, R.*; Falyouna, O.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Sugihara, Yuji*
Journal of Water Process Engineering (Internet), 46, p.102608_1 - 102608_13, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:98.65(Engineering, Environmental)Tanaka, Kazuya; Tani, Yukinori*; Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(2), p.1109 - 1114, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)We investigated the sorption of Pu(IV) on biogenic Mn oxide produced by Mn(II)-oxidizing fungus. The sorption of Pu(IV) on biogenic Mn oxide was similar to that of U(VI) and different from that of Th(IV), possibly due to oxidation of Pu(IV) to Pu(VI). When Pu(IV) was sorbed on hyphae only, it was desorbed into the solution phase over time. Pu(IV) could be solubilized by complexation with organic ligands secreted by fungal cells. In particular, Pu(IV) desorption was observed under circumneutral pH conditions.
Mei, H.; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*; Kozai, Naofumi; Sugiura, Yuki; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 136, p.105178_1 - 105178_8, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.52(Geochemistry & Geophysics) U accumulations in
U accumulations in 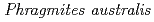 naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophores
naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophoresNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
Minerals (Internet), 11(12), p.1337_1 - 1337_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.11(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mine drainage is a vital water problem in the mining industry worldwide because of the heavy metal elements and low pH. Rhizofiltration using wetland plants is an appropriate method to remove heavy metals from the water via accumulation in the rhizosphere. 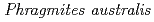 is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,
is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,  has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that
has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that  accumulated Fe, Mn, and
accumulated Fe, Mn, and  U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around
U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around  roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as
roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as 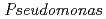 spp. and
spp. and 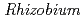 spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several
spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several 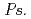 spp. and
spp. and 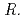 spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as
spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as 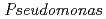 spp. and
spp. and 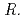 spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of
spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of  , might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in
, might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in  , and
, and 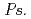 spp. and
spp. and 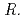 spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
Guido-Garcia, F.; Sakamoto, Fuminori; David, K.*; Kozai, Naofumi; Grambow, B.
Chemosphere, 279, p.130511_1 - 130511_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.54(Environmental Sciences)Cesium (Cs) accumulation by Shiitake was investigated to contribute to the elucidation of radiocesium-cycling mechanisms in forest environments. The results demonstrate that Shiitake non-specifically accumulates Cs while accumulating the essential element K and provide evidence that no selective Cs accumulation (or binding) sites exist within the Shiitake fruit body. Furthermore, the present results show that most accumulated Cs quickly leaches out from the dead fruit body with exposure to water. The leached Cs was largely adsorbable on clay minerals, suggesting that the Shiitake fruit body likely contains Cs in the cation form.
Kimura, Tatsuki*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Ikegami, Maiko*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Grambow, B.*; Yoneda, Minoru*
Chemosphere, 276, p.130121_1 - 130121_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.54(Environmental Sciences)The adsorption of cesium (Cs) on biotite and dissolution of Cs from Cs-bearing biotite using a siderophore were investigated aiming to contribute to the elucidation of radiocesium migration mechanisms in the soil environment. Cs was adsorbed on a hardly weathered biotite powder sample. A siderophore was extracted and purified from the bacterial culture medium, and the purified siderophore was used in five consecutive dissolution experiments of the biotite samples. The major components of the biotite (Al, Fe, and Mg) were dissolved almost stoichiometrically, strongly suggesting that the siderophore selectively dissolves the broken edges of the biotite. The Cs adsorbed on the broken edges was dissolved rapidly as the siderophore dissolved the broken edges, and then, the Cs adsorbed on the outer planar surface of the biotite particles was slowly dissolved.
Kozai, Naofumi; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Shimoyama, Iwao; Sekine, Yurina; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 416, p.125965_1 - 125965_9, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:85.54(Engineering, Environmental)Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Takeguchi, Masaki*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shimoyama, Iwao; Kozai, Naofumi; Morooka, Satoshi
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2), p.105114_1 - 105114_12, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:50.83(Engineering, Environmental)Remediating toxic ion contamination is crucial for protecting human health and the environment. This study aimed to provide a powerful strategy for effectively utilizing bone waste from the food production and preparation industries for removal of toxic ions. Here, we show that immersing pig bone in NaHCO solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr
solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr , Cd
, Cd , Pb
, Pb , and Cu
, and Cu . The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
. The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi
Chemosphere, 266, p.129104_1 - 129104_10, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.60(Environmental Sciences)Radioactive iodine ( I) is of great concern owing to its high mobility in the environment and long-term radiotoxicity, but there is a lack of effective techniques for removing iodate (IO
I) is of great concern owing to its high mobility in the environment and long-term radiotoxicity, but there is a lack of effective techniques for removing iodate (IO
 ) from aqueous solution. The aim of this study is to develop a new technique for removing radioactive iodate from contaminated solution by using barite (BaSO
) from aqueous solution. The aim of this study is to develop a new technique for removing radioactive iodate from contaminated solution by using barite (BaSO ). In the present study, we examined the coprecipitation mechanism of iodate by barite at the molecular level for determining optimum conditions for iodate removal. The results showed that iodate was effectively removed from aqueous solution by coprecipitation, even in the presence of competitive anions in solution. Comparing our method with previous studies, iodate removal efficiency by barite was determined to be about two orders of magnitude greater than that by hydrotalcite-like layered double hydroxide at Cl
). In the present study, we examined the coprecipitation mechanism of iodate by barite at the molecular level for determining optimum conditions for iodate removal. The results showed that iodate was effectively removed from aqueous solution by coprecipitation, even in the presence of competitive anions in solution. Comparing our method with previous studies, iodate removal efficiency by barite was determined to be about two orders of magnitude greater than that by hydrotalcite-like layered double hydroxide at Cl concentration of 10 mmol L
concentration of 10 mmol L . Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis indicated that incorporated iodate was strongly bound in the crystal lattice of barite by substituting the sulfate site in the structure when the iodine concentration was low. The charge compensation problem from the IO
. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis indicated that incorporated iodate was strongly bound in the crystal lattice of barite by substituting the sulfate site in the structure when the iodine concentration was low. The charge compensation problem from the IO
 substitution in SO
substitution in SO
 site is achieved by the substitution of Na
site is achieved by the substitution of Na -IO
-IO
 pairs at the nearest Ba
pairs at the nearest Ba site. Therefore, considering high removal efficiency and strong binding of iodate in barite, coprecipitation with barite is a promising material for removing radioactive iodate from various aqueous solutions contaminated with iodate.
site. Therefore, considering high removal efficiency and strong binding of iodate in barite, coprecipitation with barite is a promising material for removing radioactive iodate from various aqueous solutions contaminated with iodate.