Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
G tz, M.*; G
tz, M.*; G tz, S.*; Kratz, J.-V.*; Ballof, J.*; D
tz, S.*; Kratz, J.-V.*; Ballof, J.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Mokry, C.*; Renisch, D.*; Runke, J.*; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Mokry, C.*; Renisch, D.*; Runke, J.*; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 109(3), p.153 - 165, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We report on a novel two-chamber approach for the synthesis of volatile complexes that allows spatial decoupling of thermalization and gas-phase carbonyl complex synthesis. Neutron induced fission on  U and spontaneous fission of
U and spontaneous fission of  Cm were employed for the production of the fission products. These were stopped inside a gas volume behind the target and flushed with an inert-gas flow into a second chamber. This was flushed with carbon monoxide to allow the gas-phase synthesis of carbonyl complexes. Parameter studies of the transfer from the first into the second chamber as well as on the carbonyl complex formation and transport processes have been performed. High overall efficiencies of more than 50% were reached rendering this approach interesting for studies of superheavy elements. Our results show that carbonyl complex formation of thermalized fission products is a single-atom reaction, and not a hot-atom reaction.
Cm were employed for the production of the fission products. These were stopped inside a gas volume behind the target and flushed with an inert-gas flow into a second chamber. This was flushed with carbon monoxide to allow the gas-phase synthesis of carbonyl complexes. Parameter studies of the transfer from the first into the second chamber as well as on the carbonyl complex formation and transport processes have been performed. High overall efficiencies of more than 50% were reached rendering this approach interesting for studies of superheavy elements. Our results show that carbonyl complex formation of thermalized fission products is a single-atom reaction, and not a hot-atom reaction.
Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064602_1 - 064602_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:98.01(Physics, Nuclear)A search for production of the superheavy elements with atomic numbers 119 and 120 was performed in the  Ti+
Ti+ Bk and
Bk and  Ti+
Ti+ Cf fusion-evaporation reactions, respectively, at the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA. Over four months of irradiation, neither was detected at cross-section sensitivity levels of 65 and 200 fb, respectively. The non-observation of elements 119 and 120 is discussed within the concept of fusion-evaporation reactions including various theoretical predictions on the fission-barrier heights of superheavy nuclei in the region of the island of stability.
Cf fusion-evaporation reactions, respectively, at the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA. Over four months of irradiation, neither was detected at cross-section sensitivity levels of 65 and 200 fb, respectively. The non-observation of elements 119 and 120 is discussed within the concept of fusion-evaporation reactions including various theoretical predictions on the fission-barrier heights of superheavy nuclei in the region of the island of stability.
Nagame, Yuichiro*; Sato, Tetsuya; Kratz, J. V.*
Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology (Internet), 52 Pages, 2020/09
This article gives a brief summary of the recent progress in the synthesis of new elements as well as heavy nuclei far from the stability line and in the studies of exotic nuclear decay properties including nuclear fission of heavy nuclei and chemical characterization of heavy actinides and transactinides. Experimental techniques of single-atom detection after in-flight separation with electromagnetic separators have made a breakthrough in discovery of new heavy isotopes. Development of automated rapid chemical separation apparatuses performing one atom-at-a-time chemistry has also considerably contributed to the progress of chemical studies of the transactinides. Some key experiments exploring new frontiers of the production and chemical characterization of heavy actinides and transactinides using state-of-the-art techniques are demonstrated. A short historical perspective of actinide and transactinide elements and some prospects of extending nuclear and chemical studies of heavy elements in the future are briefly presented.
 Ca+
Ca+ Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)
Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054306_1 - 054306_16, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:90.91(Physics, Nuclear)We have performed an experiment to synthesize the element 117 (Ts) with the  Ca+
Ca+ Bk fusion reaction. Four
Bk fusion reaction. Four  -decay chains attributed to the element 117 were observed. Two of them were long decay chains which can be assigned to the one originating from the
-decay chains attributed to the element 117 were observed. Two of them were long decay chains which can be assigned to the one originating from the  decay of
decay of 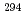 Ts. The other two were short decay chains which are consistent with the one originating from the
Ts. The other two were short decay chains which are consistent with the one originating from the  decay of
decay of 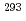 Ts. We have compared the present results with the literature data, and found that our present results mostly confirmed the literature data, leading to the firm confirmation of the synthesis of the element 117.
Ts. We have compared the present results with the literature data, and found that our present results mostly confirmed the literature data, leading to the firm confirmation of the synthesis of the element 117.
 and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCA
and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCALens, L.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 106(12), p.949 - 962, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Online gas-solid adsorption studies with single atom quantities of Hg, Tl, and Pb on SiO and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO
and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO
or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO
surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Beerwerth, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(44), p.14609 - 14613, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:69.46(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
 Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrier
Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrierG tz, M.*; G
tz, M.*; G tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D
tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th
llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch
rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 961, p.1 - 21, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.01(Physics, Nuclear)The kinematics of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Nagame, Yuichiro; Kratz, J. V.*; Sch del, M.*
del, M.*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07007_1 - 07007_8, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.05001_1 - 05001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.9(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We measured ionization efficiencies of fermium, einsteinium, mendelevium, and lawrencium by using a newly developed gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of the elements have not been determined so far due to their low production rates and/or their short half-lives. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potentials of these actinide elements have been successfully determined.
Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.
 -fission and recoil-
-fission and recoil- -
- -fission events observed in the reaction
-fission events observed in the reaction  Ca +
Ca +  Am
AmForsberg, U.*; Rudolph, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Fahlander, C.*; Gates, J. M.*; Golubev, P.*; Gregorich, K. E.*; Gross, C. J.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Fahlander, C.*; Gates, J. M.*; Golubev, P.*; Gregorich, K. E.*; Gross, C. J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 953, p.117 - 138, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:94.56(Physics, Nuclear)Alpha-decay chains observed in the element-115 production reactions of  Ca +
Ca +  Am were investigated using a new data set consisting of our recently reported data obtained at GSI and previously reported ones at Dubna and LBNL. Short decay chains of recoil-
Am were investigated using a new data set consisting of our recently reported data obtained at GSI and previously reported ones at Dubna and LBNL. Short decay chains of recoil- -(
-( )-fission type, fourteen of which were observed, and some of which were interpreted as the 2-neutron evaporation products
)-fission type, fourteen of which were observed, and some of which were interpreted as the 2-neutron evaporation products 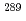 Mc, have been reassigned. It is plausible that most of them were assigned to the 3-neutron evaporation products
Mc, have been reassigned. It is plausible that most of them were assigned to the 3-neutron evaporation products 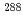 Mc whose decay chain would on the way have branches of EC decays followed by fission.
Mc whose decay chain would on the way have branches of EC decays followed by fission.
 and W(CO)
and W(CO)
Usoltsev, I.*; Eichler, R.*; Wang, Y.*; Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 104(3), p.141 - 151, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:95.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Conditions of the production and decomposition of hexacarbonyl complexes of short-lived Mo and W isotopes were investigated to study thermal stability of the heaviest group 6 hexacarbonyl complex Sg(CO) . A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO)
. A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO) and W(CO)
and W(CO) , indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO)
, indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO) could be determined with this technique.
could be determined with this technique.
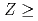 104 in liquid phase
104 in liquid phaseNagame, Yuichiro; Kratz, J. V.*; Sch del, M.
del, M.
Nuclear Physics A, 944, p.614 - 639, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.68(Physics, Nuclear)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
Nature, 520(7546), p.209 - 211, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:97.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We successfully measured ionization efficiencies of lawrencium (Lr,  =103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
=103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
Even, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(3), p.2457 - 2466, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.56(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid In situ synthesis of metal carbonyl complexes has been demonstrated using short-lived isotopes produced in nuclear fission and fusion reactions. The short-lived isotopes with high recoil energy directly react with carbon-monoxides and form carbonyl complexes. Only highly volatile complexes were fast transported in a gas stream to counting and chemistry devices. Short-lived Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, W, Re, Os, and Ir were found to form volatile carbonyl complexes, while no volataile complex of Hf and Ta were detected. This technique has been applied to a chemical investigation of the superheavy element Sg (atomic number 106), and will be applicable to various fields of nuclear science with short-lived transition metal isotopes.
 gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)
gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1253 - 1257, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.13(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a surface-ionization ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr,
gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, 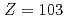 ). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of
). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of  Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Rudolph, D.*; Forsberg, U.*; Golubev, P.*; Sarmiento, L. G.*; Yakushev, A.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Gates, J. M.*; Gregorich, K. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Gates, J. M.*; Gregorich, K. E.*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1185 - 1190, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.25(Chemistry, Analytical)Thirty correlated  -decay chains of element 115 were observed, which were consistent with previous observations interpreted as the decay chain of
-decay chains of element 115 were observed, which were consistent with previous observations interpreted as the decay chain of 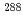 115. GEANT4 Monte-Carlo simulations were performed to reproduce high-resolution
115. GEANT4 Monte-Carlo simulations were performed to reproduce high-resolution  -photon coincidence results, which allows one to propose Q
-photon coincidence results, which allows one to propose Q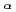 values and excitation schemes of the superheavy nuclei with unprecedented precision.
values and excitation schemes of the superheavy nuclei with unprecedented precision.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 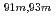 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
Science, 345(6203), p.1491 - 1493, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:83.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A new superheavy element complex, a seaborgium carbonyl, has been successfully synthesized, and its adsorption property has been studied using a cryo-thermochromatography and  -detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived
-detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived  Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of
Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of  50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO)
50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO) . This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
. This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.