Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kamide, Hideki; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Hayafune, Hiroki; Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Maeda, Seiichiro; Sagayama, Yutaka; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; et al.
Jisedai Genshiro Ga Hiraku Atarashii Shijo; NSA/Commentaries, No.28, p.14 - 36, 2023/10
Developments of next generation nuclear reactors, e.g., Fast Reactor, and High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor, are in progress. They can contribute to markets of electricity and industrial heat utilization in the world including Japan. Here, current status of reactor developments in Japan and also situation in the world are summarized, especially for activities of Generation IV International Forum (GIF), developments of Fast Reactor and High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor in Japan, and SMR movements in the world.
Shibata, Taiju; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Kubo, Shinji; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 398, p.111964_1 - 111964_4, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been promoting the research and development (R&D) of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). R&D on reactor technologies is carried out by using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). The HTTR was resumed without significant reinforcements in 2021. On January 2022, a safety demonstration test under the OECD/NEA LOFC project was carried out. JAEA is promoting R&D on a carbon-free hydrogen production by thermochemical water splitting Iodine-Sulfur process (IS process). JAEA conducts design study for various HTGR systems toward commercialization. A new test program about demonstration of hydrogen production by the HTTR was launched. Steam methane reforming hydrogen production system was selected for the first demonstration by 2030.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
 F from
F from  O
O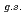 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 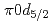 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O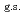 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
 He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation) He
He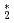 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.65(Physics, Applied)Nishihara, Tetsuo; Yan, X.; Tachibana, Yukio; Shibata, Taiju; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Kubo, Shinji; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; Ueta, Shohei; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2018-004, 182 Pages, 2018/07
Research and development on High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in Japan started since late 1960s. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in cooperation with Japanese industries has researched and developed system design, fuel, graphite, metallic material, reactor engineering, high temperature components, high temperature irradiation and post irradiation test of fuel and graphite, high temperature heat application and so on. Construction of the first Japanese HTGR, High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), started in 1990. HTTR achieved first criticality in 1998. After that, various test operations have been carried out to establish the Japanese HTGR technologies and to verify the inherent safety features of HTGR. This report presents several system design of HTGR, the world-highest-level Japanese HTGR technologies, JAEA's knowledge obtained from construction, operation and management of HTTR and heat application technologies for HTGR.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.; Kubo, Shinji; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Tachibana, Yukio; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2014-031, 30 Pages, 2014/09
In the present study, identification of test items to be validated in the HTTR demonstration test to accomplish a formulation of safety requirement and design consideration for coupling a hydrogen production plant to a nuclear facility as well as confirmation of overall performance of helium gas turbine system. In addition, a plant concept for the heat utilization system to be connected with the HTTR is clarified.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Tachibana, Yukio; Shimakawa, Satoshi; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Yan, X.; Murakami, Tomoyuki; Ohashi, Kazutaka; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2008-019, 57 Pages, 2008/03
The small-sized and safe cogeneration High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) that can be used not only for electric power generation but also for hydrogen production and district heating is considered one of the most promising nuclear reactors for developing countries where sufficient infrastructure such as power grids is not provided. Thus, the small-sized cogeneration HTGR, named High Temperature Reactor 50-Cogeneration (HTR50C), was studied assuming that it should be constructed in developing countries. Specification, equipment configuration, etc. of the HTR50C were determined, and economical evaluation was made. As a result, it was shown that the HTR50C is economically competitive with small-sized light water reactors.
Motojima, Osamu*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Komori, Akio*; Oyabu, Nobuyoshi*; Muto, Takashi*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Ida, Katsumi*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(10), p.S668 - S676, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:73.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The performance of net-current free heliotron plasmas has been developed by findings of innovative operational scenarios in conjunction with an upgrade of the heating power and the pumping/fuelling capability in the Large Helical Device (LHD). Consequently, the operational regime has been extended, in particular, with regard to high density, long pulse length and high beta. Diversified studies in LHD have elucidated the advantages of net-current free heliotron plasmas. In particular, an internal diffusion barrier (IDB) by a combination of efficient pumping of the local island divertor function and core fuelling by pellet injection has realized a super dense core as high as 5 10
10 m
m , which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5% and a discharge duration of 54 min with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW on average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed by highlighting IDB, high-beta and long pulse.
, which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5% and a discharge duration of 54 min with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW on average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed by highlighting IDB, high-beta and long pulse.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Sakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sano, Naoki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.812 - 819, 2007/09
The objective of this study is to confirm the availability of proposed mitigation methodology against thermal load increase events initiated by the thermochemical water splitting IS process hydrogen production system coupling with the HTTR. JAEA has been performing the development of dynamic simulation code which can evaluate complex phenomena in the HTTR-IS system all at one once to achieve the requirement. The notable feature of the developed code is the APHX module which enables to estimate the IS process thermal load variation considering phase change and chemical reaction behavior assumed in the APHX. In this paper, two cases of dynamic calculation for the thermal load increase events were performed using the newly developed APHX module. The results of the analytical studies clearly show the availability of the developed model for dynamic simulation of the HTTR-IS system and the thermal load increase mitigation methodology.
Motojima, Osamu*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Komori, Akio*; Oyabu, Nobuyoshi*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Muto, Takashi*; Ida, Katsumi*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2007/03
The performance of net-current free Heliotron plasmas has been developed by findings of innovative operational scenarios in conjunction with an upgrade of the heating power and the pumping/fueling capability in the Large Helical Device (LHD). Consequently, the operational regime has been extended, in particular, with regard to high density, long pulse length and high beta. Diversified studies in LHD have elucidated the advantages of net-current free heliotron plasmas. In particular, an Internal Diffusion Barrier (IDB) by combination of efficient pumping of the local island divertor function and core fueling by pellet injection has realized a super dense core as high as 5 10
10 m
m , which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5 % and a discharge duration of 54-min. with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW in average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed with highlighting IDB, high
, which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5 % and a discharge duration of 54-min. with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW in average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed with highlighting IDB, high  and long pulse.
and long pulse.
Goto, Yoshitaka*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Ishimoto, Yuki*; Masaki, Kei; Arai, Takashi; Kubo, Hirotaka; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Miya, Naoyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 357(1-3), p.138 - 146, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:85.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 around the critical pressure
around the critical pressureSettai, Rikio*; Kubo, Tetsuo*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika; Harima, Hisatomo*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(Suppl.), p.167 - 169, 2006/08
We have studied a change of the Fermi surface in an antiferromagnet CeIn via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment under pressure up to 2.9 GPa. In the pressure region P
via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment under pressure up to 2.9 GPa. In the pressure region P
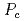 = 2.6 GPa, we have observed a large main Fermi surface named
= 2.6 GPa, we have observed a large main Fermi surface named  , which indicates that the electronic state of 4
, which indicates that the electronic state of 4 electron in CeIn
electron in CeIn changes from localized to itinerant at
changes from localized to itinerant at 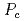 . The cyclotron effective mass
. The cyclotron effective mass 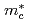 of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced around
of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced around 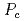 .
.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Kasahara, Seiji; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Terada, Atsuhiko; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Onuki, Kaoru; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 16th World Hydrogen Energy Conference (WHEC-16) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2006/06
High-temperature reactors (HTRs) are particularly attractive due to their wide industrial application from electricity generation to hydrogen production. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency's (JAEA's) HTTR, which is the first HTR in Japan, attained its maximum reactor-outlet coolant temperature and successfully delivered 950 C coolant helium outside its reactor vessel. A hydrogen production system based on the thermochemical water-splitting iodine sulphur (IS) process is planned to be connected to the HTTR in the near future. This will establish the hydrogen production technology with an HTR, including the system integration technology for connection of hydrogen production system to HTRs. It will probably be the world's first demonstration of hydrogen production directly using heat supplied from an HTR. The HTTR-IS system design was launched from a conceptual design in 2005. This paper shows the summary of the HTTR, plan for developing the IS process in JAEA, thermal efficiency evaluation for the HTTR-IS system, etc. The verification of the hydrogen production by the HTTR-IS system by using heat from a nuclear reactor is greatly expected to contribute to the commercialization of nuclear hydrogen in coming hydrogen society.
C coolant helium outside its reactor vessel. A hydrogen production system based on the thermochemical water-splitting iodine sulphur (IS) process is planned to be connected to the HTTR in the near future. This will establish the hydrogen production technology with an HTR, including the system integration technology for connection of hydrogen production system to HTRs. It will probably be the world's first demonstration of hydrogen production directly using heat supplied from an HTR. The HTTR-IS system design was launched from a conceptual design in 2005. This paper shows the summary of the HTTR, plan for developing the IS process in JAEA, thermal efficiency evaluation for the HTTR-IS system, etc. The verification of the hydrogen production by the HTTR-IS system by using heat from a nuclear reactor is greatly expected to contribute to the commercialization of nuclear hydrogen in coming hydrogen society.
 ; From localized to itinerant
; From localized to itinerantSettai, Rikio*; Kubo, Tetsuo*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika; Harima, Hisatomo*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 378-380, p.417 - 418, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.16(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have studied a change of the Fermi surface in an antiferromagnet CeIn via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment for the magnetic field along
via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment for the magnetic field along 
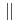 [100] and [111] under pressure at about 2.7 GPa. We have observed a large main spherical Fermi surface named
[100] and [111] under pressure at about 2.7 GPa. We have observed a large main spherical Fermi surface named  , which indicates that the electronic state of 4f electron in CeIn
, which indicates that the electronic state of 4f electron in CeIn changes from localized to itinerant. The cyclotron effective mass
changes from localized to itinerant. The cyclotron effective mass 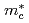 of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced:
of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced: 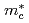
 60
60 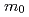 at 2.75 GPa for
at 2.75 GPa for 
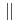 [100].
[100].
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Konoshima, Shigeru; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Ide, Shunsuke; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S39 - S48, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:52.36(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 ; The de Haas-van Alphen study under pressure
; The de Haas-van Alphen study under pressureSettai, Rikio*; Kubo, Tetsuo*; Shiromoto, Tomoyuki*; Honda, Daisuke*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Betsuyaku, Kiyoshi*; Harima, Hisatomo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(11), p.3016 - 3026, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:87.38(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have studied a change of the Fermi surface in an antiferromagnet CeIn via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment under pressure up to 3 GPa. With increasing pressure P, the Neel temperature
via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment under pressure up to 3 GPa. With increasing pressure P, the Neel temperature 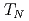 =10 K decreases and becomes zero at a critical pressure Pc
=10 K decreases and becomes zero at a critical pressure Pc  2.6 GPa. In the pressure region
2.6 GPa. In the pressure region  , we have observed a large main Fermi surface named a, which indicates that the electronic state of 4 f electron in CeIn
, we have observed a large main Fermi surface named a, which indicates that the electronic state of 4 f electron in CeIn changes from localized to itinerant at Pc, as observed in the similar antiferromagnets CeRh
changes from localized to itinerant at Pc, as observed in the similar antiferromagnets CeRh Si
Si and CeRhIn
and CeRhIn . The cyclotron effective mass
. The cyclotron effective mass 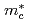 of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced around Pc:
of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced around Pc: 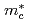
 60
60 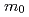 at 2.7 GPa for the magnetic field along the
at 2.7 GPa for the magnetic field along the  100
100 direction.
direction.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Higashijima, Satoru; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Horikawa, Toyohiko*; Kubo, Hirotaka; Miya, Naoyuki; Nishi, Masataka; Konishi, Satoshi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 70(2), p.163 - 173, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish the effective and conventional in-vessel tritium removal method, glow discharge methods, usually used as wall conditioning, have been applied and examined in vacuum vessel of JT-60U for tritium removal characteristics and kinetics. Release rates of all hydrogen isotopes as well as hydrocarbons from JT-60U vacuum vessel induced by Glow Discharge Cleaning (GDC) with He and H were measured. Release characteristics of hydrogen isotopes were classified into three different release processes each of which is well described by a simple exponential decay with time. It was found that H
were measured. Release characteristics of hydrogen isotopes were classified into three different release processes each of which is well described by a simple exponential decay with time. It was found that H GDC showed the superior hydrogen isotope release characteristics than the He GDC, probably because chemical processes, such as isotope exchanges assisted by the chemical sputtering process between discharged hydrogen and hydrogen isotopes plasma facing carbon tiles are enhanced by the H
GDC showed the superior hydrogen isotope release characteristics than the He GDC, probably because chemical processes, such as isotope exchanges assisted by the chemical sputtering process between discharged hydrogen and hydrogen isotopes plasma facing carbon tiles are enhanced by the H glow discharge. Based on the release kinetics observed in the present work, it is estimated that it will take several days to reduce tritium inventory in the surface area of JT-60U to a half by continuous H
glow discharge. Based on the release kinetics observed in the present work, it is estimated that it will take several days to reduce tritium inventory in the surface area of JT-60U to a half by continuous H GDC at 573 K.
GDC at 573 K.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.