Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Furuta, Hiroshige*; Sato, Kaoru; Nishide, Akemi*; Kudo, Shinichi*; Saigusa, Shin*
Health Physics, 121(5), p.471 - 483, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Environmental Sciences)Low dose radiation induced "health effects" containing cancer risk for a Japanese radiation worker cohort is epidemiologically evaluated using the personal dose equivalent (Hp(10)). On the other hand, Hp(10) is not recommended for epidemiological evaluation of cancer risks, since the Hp(10) is widely used for radiological protection purposes. In addition, the cancer risk depends on organ doses rather than Hp(10). Thus, we developed a new method for estimating organ doses from Hp(10) of radiation workers. The developed method enables epidemiological analysis against Japanese radiation workers by considering the response characteristics of personal dosimeters, exposure geometry and energy, and body size of radiation workers in Japan. In the future, we will reconstruct organ dose conversion factor and will evaluate the risk of cancer mortality and morbidity using the organ dose in Japan.
Furuta, Hiroshige*; Tsujimura, Norio; Nishide, Akemi*; Kudo, Shinichi*; Saigusa, Shin*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(3), p.371 - 383, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.56(Environmental Sciences) SO
SO /HNO
/HNO mixed solution
mixed solutionLi, Z.*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Sato, Nozomi; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Pershina, V.*; et al.
del, M.; Pershina, V.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 100(3), p.157 - 164, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Ago, Tomonori*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; Harada, Kentaro*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Honda, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.205 - 207, 2008/06
Future synchrotron light sources based on the energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) are expected to be capable of producing super-brilliant and/or ultra-short pulses of synchrotron radiation. Our Japanese collaboration team is making efforts for realizing an ERL-based hard X-ray source. We report recent progress in our R&D efforts.
Yoshikawa, Hiroshi; Sakaki, Hironao; Sako, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Hiroki; Shen, G.; Kato, Yuko; Ito, Yuichi; Ikeda, Hiroshi*; Ishiyama, Tatsuya*; Tsuchiya, Hitoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Accelerator and Large Experimental Physics Control Systems (ICALEPCS '07) (CD-ROM), p.62 - 64, 2007/10
J-PARC is a large scale facility of the proton accelerators for the multi-purpose of scientific researches in Japan. This facility consists of three accelerators and three experimental stations. Now, J-PARC is under construction, and LINAC is operated for one year, 3GeV synchrotron has just started the commissioning in this October the 1st. The completion of this facility will be next summer. The control system of accelerators established fundamental performance for the initial commissioning. The most important requirement to the control system of this facility is to minimize the activation of accelerator devices. In this paper, we show that the performances of each layer of this control system have been achieved in the initial stage.
Sugo, Yumi; Izumi, Yoshinobu*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Nishijima, Shigehiro*; Sasaki, Yuji; Kimura, Takaumi; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Kudo, Hiroshi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 76(5), p.794 - 800, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:97.53(Chemistry, Physical)The radiolytic behavior of 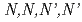 -tetraoctyldiglycolamide,
-tetraoctyldiglycolamide, 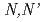 -dimethyl-
-dimethyl-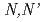 -dioctyl-2-(3'-oxapentadecyl)malonamide, and
-dioctyl-2-(3'-oxapentadecyl)malonamide, and 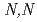 -dioctylhexanamide in
-dioctylhexanamide in  -dodecane was investigated by irradiation with
-dodecane was investigated by irradiation with  -rays and electron pulses. The results showed
-rays and electron pulses. The results showed  -dodecane has a sensitization effect on the radiolysis of these amides, owing mainly to a charge transfer from radical cations of
-dodecane has a sensitization effect on the radiolysis of these amides, owing mainly to a charge transfer from radical cations of  -dodecane to the amide molecules in the primary process observed in pulse radiolysis.
-dodecane to the amide molecules in the primary process observed in pulse radiolysis.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kudo, Kenji; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Rindo, Hiroshi; Watabe, Kozo; Tomii, Hiroyuki; Shiraishi, Kunio; Yagi, Naoto; Fukushima, Tadashi; Zaitsu, Tomohisa
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/07
Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) played a leading role in basic research in the field of atomic energy research and development, while Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) did a major role in FBR cycle development and high level waste disposal. Following the Government's decision in December 2001, JAERI and JNC was merged as of October 1st, 2005. The new organization, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), is an institute for comprehensive R&D for atomic energy, and is the largest research and development institute among Governmental R&D organizations. Its missions are basic research on atomic energy, R&D for nuclear fuel cycle, decommissioning of own facilities and disposal of waste, contribution to safety and non-proliferation, etc. The JAEA owns a number of nuclear facilities: research reactors such as JRR-2 and Joyo, prototype reactors such as ATR "Fugen" and FBR "Monju", fuel cycle plants such as Uranium Enrichment Demonstration Plant at Ningyo-Toge, MOX fuel plants at Tokai, Reprocessing Plant at Tokai, and Hot Laboratories such as JRTF and FMF. As a part of preparation of the mergence, JNC and JAERI have jointly developed a comprehensive cost estimation method for decommissioning, based on decommissioning and refurbishing experiences of JAERI and JNC. This method involves more estimation parameters from typical decommissioning activities than before, so as to make it more reliable. JAERI and JNC have estimated the total cost for decommissioning by using this method, and concluded that the cost would be 600 billion yen (approx. 5 billion USD).
Kudo, Hiroshi*; Iwasaki, Wataru*; Uchiyama, Rumi*; Tomita, Shigeo*; Shima, Kunihiro*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Ishii, Satoshi*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Saito, Yuichi; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2, 45(22), p.L565 - L568, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:50.42(Physics, Applied)The first observation of the energy distribution of electrons emitted from solids bombarded by MeV atom clusters is reported. In the backward direction, using graphite and Si bombarded by C
 and Al
and Al
 (n
(n  8), an appreciable suppression of electron emission has been observed at electron energies lower than
8), an appreciable suppression of electron emission has been observed at electron energies lower than  10 eV. Electron yield per atom decreases with increasing n, and becomes less than 50% at n
10 eV. Electron yield per atom decreases with increasing n, and becomes less than 50% at n  3, relative to the case of n = 1. The experimental results cannot be explained in terms of projectile stopping cross sections nor by the clearing-the-way effect. It is probable that the suppressed electron emission is a result of the suppression of the transport or surface transmission of the produced low-energy electrons, rather than of the suppression of ionization.
3, relative to the case of n = 1. The experimental results cannot be explained in terms of projectile stopping cross sections nor by the clearing-the-way effect. It is probable that the suppressed electron emission is a result of the suppression of the transport or surface transmission of the produced low-energy electrons, rather than of the suppression of ionization.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.60(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Kudo, Yusuke; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kizu, Kaname; Ando, Toshinari*; Matsukawa, Makoto; Tamai, Hiroshi; Miura, Yukitoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1005 - 1011, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents dependence of the stress intensity factor, around the defect in the butt joint welding of a superconducting conductor conduit, on a geometrical factor estimated by fracture mechanics analysis. The stress intensity factor can be estimated by the Newman-Raju equation about CICC section, but the effect of the difference between the geometry assumed in the equation and CICC has not been clarified yet. Therefore, the three-dimensional finite element method (3D-FEM) is performed to estimate the geometrical factor. As a result, the Newman-Raju equation is considered to be available for the assessment of the fracture toughness of the conduit of rectangular shape because the maximum stress intensity factor by 3-D FEM is only 3% larger than that by the Newman-Raju equation in the maximum postulated defect.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.60(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
 Xe-fullerene to endohedral
Xe-fullerene to endohedral  Xe-fullerenol to be used in nuclear medicine
Xe-fullerenol to be used in nuclear medicineWatanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Kudo, Hiroshi*; Shimomura, Haruhiko*; Muramatsu, Hisakazu*; Kume, Tamikazu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 266(3), p.499 - 502, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.78(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Sugo, Yumi; Sasaki, Yuji; Kimura, Takaumi; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Kudo, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
Rindo, Hiroshi; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Kudo, Kenji; Saiki, Hideo
Proceedings ANS Topical Meeting on Decommissioning, Decontamination, and Reutilization (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/00
None
 Sn superconducting conductor
Sn superconducting conductorKudo, Yusuke; Sakasai, Akira; Hamada, Kazuya; Takano, Katsutoshi*; Nakajima, Hideo; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.634 - 638, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has a plan to construct a tokamak fusion device called JT-60SC in which superconducting magnet system will be used. The objectives of this study are to clarify applicability of conventional austenitic stainless steel wire for the SS316LN to the conduit material of the Nb3Sn cable-in-conduit conductor for the central solenoid (CS) of JT-60SC. Tensile properties, fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth rate of both as-weld and aged (923 K  240 hours) weld metals were evaluated at 4 K. The measured tensile properties of aged weld metal satisfied the requirement of JT-60SC. Fatigue crack growth property was enough to ensure the required operation cycles of 9.0
240 hours) weld metals were evaluated at 4 K. The measured tensile properties of aged weld metal satisfied the requirement of JT-60SC. Fatigue crack growth property was enough to ensure the required operation cycles of 9.0  10e4. However, fracture toughness of aged weld metal could not be validated due to unstable crack extension. It was concluded that improvement of fracture toughness after aging was required to ensure the structural integrity of the CS conduit.
10e4. However, fracture toughness of aged weld metal could not be validated due to unstable crack extension. It was concluded that improvement of fracture toughness after aging was required to ensure the structural integrity of the CS conduit.
Hiroki, Fumio; Yoshikawa, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Yasunori*; Kudo, Kikuo*
Proceedings of 1st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 29th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.159 - 161, 2004/08
The main purpose of Personnel Protection System (PPS) is to protect people from radiation exposure. From the viewpoint of it, important features of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) are (1) the beam power as high as 1MW, and (2) a lot of beam-line entrances apart from the main control room. The first feature requires the beam interlock function of PPS to be more reliable than ever. The second one is dealt with the access control function of PPS, with which the remote access control from the central control room is enabled. In this paper, we report the beam interlock and access control functions of the PPS.
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.42(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English