Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kuga, Naoya*; Shiiba, Takuro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Kuroiwa, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study aims to verify the accuracy of PHITS in terms of photon and electron transport and provide essential data for its application in clinical dosimetry in high-energy photon beam therapy. Percentage depth dose (PDD), beam profiles, and output factor (OPF) in a water phantom with various field sizes created by a Clinac 21EX linear accelerator were measured using an ionization chamber. Experimental setups were precisely reproduced by PHITS version 3.24, and the percentage differences (%Diff) between the measured and calculated data were evaluated. The average %Diff of PDDs obtained from PHITS and measurement were within 10% and 2% in the build-up and fall-off regions, respectively. For beam profiles, the average %Diff in the plateau region was within 3%; the differences between the calculated and measured distances from the central axis to 50% dose level were within 2 mm. These differences were lower than their tolerance levels. The consistency between the PHITS and EGSnrc was better; their %Diff was within 1% in most cases. The concurrence between the PHITS and measurement shown in this study demonstrates the potential clinical application of PHITS in high-energy photon beam therapy, given its similar dose calculation accuracy compared with EGSnrc.
Shiiba, Takuro*; Kuga, Naoya*; Kuroiwa, Yasuyoshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 128, p.199 - 203, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.27(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We calculated scaled dose point kernels (DPKs) for mono-energetic electron in water (0.015, 0.1, 1.0, and 2.0 MeV) and compact bone (0.010 and 1 MeV) using the latest version of PHITS. Furthermore, we calculated beta-emitting isotopes (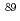 Sr,
Sr,  Y,
Y,  I) DPKs in both water and bone. The simulated results of mono-energetic electron and beta-emitting DPKs were compared with those in literature using different MC codes, such as EGSnrc, GATE6.0, MCNP4C, and FLUKA. All mono-energetic and beta-emitting isotope DPKs calculated using PHITS, both in water and compact bone, were in good agreement with those in literature using other MC codes. The differences were
I) DPKs in both water and bone. The simulated results of mono-energetic electron and beta-emitting DPKs were compared with those in literature using different MC codes, such as EGSnrc, GATE6.0, MCNP4C, and FLUKA. All mono-energetic and beta-emitting isotope DPKs calculated using PHITS, both in water and compact bone, were in good agreement with those in literature using other MC codes. The differences were  4% for all mono-energetic electron and beta-emitting isotope DPKs in both water and bone. PHITS provided reliable mono-energetic electron and beta-emitting isotope scaled DPKs in both water and compact bone for patient-specific dosimetry.
4% for all mono-energetic electron and beta-emitting isotope DPKs in both water and bone. PHITS provided reliable mono-energetic electron and beta-emitting isotope scaled DPKs in both water and compact bone for patient-specific dosimetry.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Kuga, Naoya*
Igaku Butsuri, 35(2), p.180 - 187, 2015/00
PHITS is a general purpose Monte Carlo particle transport simulation code developed through the collaboration of several institutes mainly in Japan. It can analyze the motion of nearly all radiations over wide energy ranges in 3-dimensional matters. It has been used for various applications including medical physics. This paper reviews the recent improvements of the code, such as implementation of EGS5, new photo-nuclear reaction model, and sumtally function. The review of the biological dose estimation method developed on the basis of the microdosimetric function implemented in PHITS is also given.