Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Ide, Shunsuke; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Suzuki, Takahiro; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shiraishi, Junya; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403131_1 - 2403131_4, 2012/09
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 4, p.051_1 - 051_7, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:141 Percentile:97.50(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Bialek, J.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yutaka; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1512 - 1523, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:63.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design of modification of JT-60U, JT-60SA, has been optimized in viewpoint of plasma control, and operation regimes have been evaluated. Upper and lower divertors with different geometry are prepared for flexibility of plasma shape control. The beam lines of negative-ion NBI are shifted downward for off-axis current drive, in order to obtain a weak/reversed shear plasma. The feedback control coils along the port hole in the stabilizing plate are found effective to suppress the resistive wall mode (RWM) and sustain high 
 close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
 = 2.4 MA,
= 2.4 MA, 
 = 4.4,
= 4.4, 
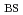 = 0.70,
= 0.70, 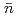
 /
/
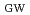 = 0.86, H
= 0.86, H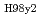 = 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration (
= 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration ( = 2.65). High
= 2.65). High 
 , high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
, high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kizu, Kaname; Kurita, Genichi; Masaki, Kei; Matsukawa, Makoto; Miura, Yukitoshi; Sakurai, Shinji; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.541 - 547, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)JT-60SA is positioned as the ITER satellite tokamak to conduct research elements to support and supplement ITER towards DEMO under the joint collaboration of Japan and EU. After the discussions in JA-EU Satellite Tokamak Working Group in 2005, the heating power is increased up to 41MW, 100s to ensure the ITER support research. With such increased heating power, the prospective plasma performances are analysed by the equilibrium and transport analysis codes. Operation window of a fully non-inductive current drive is extended to high density region. Simultaneous achievement of high equivalent Q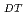 and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.892 - 899, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:86.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The concept for a compact DEMO reactor named "SlimCS" is presented. Distinctive features of the concept is low aspect ratio ( = 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low-
= 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low- , i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
, i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kurita, Genichi; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 47(4), p.297 - 304, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.79(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Stability of a peeling, a ballooning, and a peeling-ballooning modes, which relate to edge-localized modes (ELMs), are investigated numerically with the linear ideal magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stability code MARG2D. Effects of "sharpness" on the stability of the peeling-ballooning mode are examined, where the sharpness is defined in terms of the curvature at the top or bottom of the outermost flux surface. It is found that the stability limit of the pressure gradient significantly improves as the sharpness increases even when the ellipticity and the triangularity are unchanged. The sharpness is an important parameter for high performance H-mode operations with high pedestal pressure.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kurita, Genichi; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Stabilities of peeling, ballooning and peeling-ballooning modes, which relate to edge-localized modes (ELMs), are investigated numerically with the linear ideal magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stability code MARG2D. Effects of "sharpness" on the stability of the peeling-ballooning mode are examined, where the sharpness is defined in terms of the curvature at the top and bottom of the outermost flux surface. It is found for the first time that the stable pressure gradient significantly improves as the sharpness increases even when the ellipticity and the triangularity are unchanged. The sharpness is an important parameter for high performance H-mode operations with high pedestal pressure.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Ozeki, Takahisa; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kurita, Genichi; Isayama, Akihiko; Koide, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
This is the first experimental result which demonstrates the dependence of critical RWM onset of plasma rotation and beta on initial plasma rotation with the variation of the angular momentum input and without magnetic braking. In the JT-60U with newly ferretic wall installed, it is possible to produce high beta plasma tightly coupled with the wall (b/a=1.2) above 



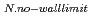 . In near-zero plasma rotation, the RWM started to grow at
. In near-zero plasma rotation, the RWM started to grow at 
 =
= 
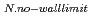 and with finite plasma rotation, the plasma pressure survives up to much higher
and with finite plasma rotation, the plasma pressure survives up to much higher 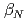 level than that with small rotation. The observed critical beta onset
level than that with small rotation. The observed critical beta onset 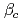 and the RWM growth rate
and the RWM growth rate 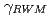 are discussed along with theoretical predictions using experimentally observed q-, pressure-, and rotation profiles. The critical rotation of RWM on JT-60U is less one-second times lower than previous report of other tokamaks.
are discussed along with theoretical predictions using experimentally observed q-, pressure-, and rotation profiles. The critical rotation of RWM on JT-60U is less one-second times lower than previous report of other tokamaks.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Koide, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Kurita, Genichi; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 98(5), p.055002_1 - 055002_4, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:124 Percentile:94.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The plasma rotation necessary for stabilization of resistive wall modes (RWMs) is investigated by controlling the toroidal plasma rotation with external momentum input by injection of tangential neutral beams. The observed threshold is 0.3 % of the Alfv n velocity and much smaller than the previous experimental results obtained with magnetic braking. This low critical rotation has a very weak
n velocity and much smaller than the previous experimental results obtained with magnetic braking. This low critical rotation has a very weak  dependence as the ideal wall limit is approached. These results indicate that for large plasmas such as in future fusion reactors with low rotation, the requirement of the additional feedback control system for stabilizing RWM is much reduced.
dependence as the ideal wall limit is approached. These results indicate that for large plasmas such as in future fusion reactors with low rotation, the requirement of the additional feedback control system for stabilizing RWM is much reduced.
Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Kurita, Genichi; Ozeki, Takahisa; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(1), p.95 - 103, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:36.80(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Ideal MHD instabilities can become resistive wall modes (RWMs) which grows with the time sale of the skin time of the wall due to a finite wall resistivity. Since the RWM could limit the achievable beta-value, the understanding of the RWM physics and the stabilization mechanism is urgent issue for the steady-state high-beta plasma. For this reason, we have carried out the RWM experiment where the plasma-wall separation was systematically scanned in the JT-60U ohmic plasmas. These results show that the RWM growth rates become smaller with decreasing the plasma-wall separation. This means that the plasma-wall separation is effective for the stabilizing the RWM.
Tsuda, Takashi; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.1149 - 1152, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The current density is expected to be negative in the central region of the tokamak when the amplitude of bootstrap current or off-axis current drive is large enough and a negative one-turn voltage exists. However, a flat current profile with almost zero value has been observed in experiments. The current profile with Current Hole has a tendency to be unstable to double tearing mode and we investigate the role of double tearing mode on the formation of Current Hole with RMHD simulation.
Tsuda, Takashi; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S83 - S86, 2006/12
The current density is expected to be negative in the central region of the tokamak when the amplitude of bootstrap current or off-axis current drive is large enough. However, a flat current profile with almost zero value has been observed in experiments even under the situation with negative one-turn voltage exists in the central region of plasma. Double tearing mode (DTM) can be unstable for the current profile with a "current hole" and some MHD activities are observed in JET before the formation of the current hole. On the contrary, no MHD activity is observed in the JT-60 experiment. Here, we study the condition of appearance of DTM and investigate the stability of DTM and the interaction between DTM (n=1 perturbation) and "Current Hole" with resistive RMHD simulations.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Bakhtiari, M.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kurita, Genichi; Takechi, Manabu; Kasai, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(11), p.966 - 971, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:46.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Matsukawa, Makoto; Tamai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kizu, Kaname; Sakurai, Shinji; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Ando, Toshinari; Miura, Yushi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 16(2), p.914 - 917, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.11(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.