Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Matsuno, Takashi*; Harjo, S.; Akita, Koichi*
Materials & Design, 221, p.110965_1 - 110965_8, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Aihara, Jun; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Tachibana, Yukio
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 9(4), p.21-00424_1 - 21-00424_13, 2022/08
It is important to improve oxidation resistance of fuel for huge oxygen ingress into core to improve safety of high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), because almost volume of cores of HTGRs consist of graphite. In this study, simulated oxidation resistant fuel elements, of which matrix is mixture of SiC and graphite, has been fabricated by hot press method. In order to maintain structural integrity of fuel element under accident conditions, high-strength fuel elements should be developed. In order to identify optimal hot press conditions for preparing high-strength fuel elements, effect of hot press conditions on mechanical strength properties of fuel elements should be evaluated quantitatively. In the present study, response surface model, which represents relationship between hot press conditions and mechanical strength properties, has been constructed by introducing statistical design of experiments (DOE) approaches, and optimal hot press conditions were estimated by model.
Aihara, Jun; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
To maintain the structural integrity of fuel elements for a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) under disaster conditions, strong and oxidation-resistant fuel elements should be further developed. The HTGR fuel elements employ a hot-pressed silicon carbide (SiC)/carbon (C) mixed matrix to improve the oxidative resistance. Hot-press conditions such as pressure, temperature, and duration would be one of the factors that affect the strength of the HTGR fuel elements. To identify the optimal hot-press conditions for preparing the high-strength fuel elements, modelling their effects on the mechanical-strength properties of the HTGR fuel elements should be evaluated quantitatively. In this study, the response surface model, which represents the relationship between the hot-press conditions and the mechanical-strength properties, has been constructed by introducing statistical design-of-experiment approaches.
Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Akita, Koichi*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 820, p.141582_1 - 141582_9, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:62.06(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Yamada, Teruaki*; Akita, Koichi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 83(852), p.17-00072_1 - 17-00072_7, 2017/07
In order to assess the fatigue damage of austenitic stainless steels by electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) method more simply and easily, it should be more preferable to use a commercially available general-purpose EBSD analysis software rather than to employ an in-house developed EBSD analysis programme. In the present study, EBSD measurement was performed for Type 316 austenitic stainless steels subjected to cyclic loading, and the applicability of the EBSD parameter relevant to the pattern quality, which could be obtained by the commercial software, to the fatigue damage assessment was discussed by comparing the other EBSD parameter of the averaged local misorientation (Mave), which could be calculated by the in-house developed programme. As a result, the EBSD parameter relevant to the pattern quality, which signified the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the histogram distribution of the image quality (IQ), was saturated at the beginning stage of the fatigue cycles, while Mave was increased monotonically with the cycles. This suggested that the FWHM of IQ could be useful to detect the initial stage of the fatigue damage, while Mave was suitable for the quantitative evaluation of the fatigue damage. XRD measurement was also carried out for the same samples employed in the EBSD measurement, and the XRD data was compared with the EBSD data to discuss the crystallographic mechanism of the change in the FWHM of IQ. As a result, it was found that the FWHM of the (111) XRD peak correlated well with the FWHM of IQ. Because the (111) plane in fcc metal such as austenitic stainless steel was most preferable for slip system, this implied that the change in the distribution of the pattern quality generated by the fatigue loading could be due to the slip deformation.
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(1), p.120 - 127, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:96.13(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yamada, Teruaki*; Matsushima, Yuki*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Fujita, Ichiro*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 271, p.323 - 326, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the effects of the experimental methodology and the notch angle on the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic nuclear graphites IG-110 and IG-430, the three-point-bending test, which has been recently proposed as the methodology to evaluate the fracture toughness of graphite for high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), was performed using two types of the specimens with different notch angles. The results obtained in this study could be summarized as follows: (1) The values of the fracture toughness of IG-110 and IG-430 measured in this study were 0.890 MPa m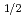 and 1.031 MPa m
and 1.031 MPa m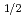 , respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
, respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
Yamada, Teruaki*; Matsushima, Yuki*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Fujita, Ichiro*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
In order to investigate the effects of the experimental methodology and the notch angle on the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic nuclear graphites IG-110 and IG-430, the three-point-bending test, which has been recently proposed as the methodology to evaluate the fracture toughness of graphite for high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), was performed using two types of the specimens with different notch angles. The results obtained in this study could be summarized as follows: (1) The values of the fracture toughness of IG-110 and IG-430 measured in this study were 0.890 (MPam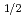 ) and 1.031 (MPam
) and 1.031 (MPam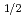 ), respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
), respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*; Nagase, Fumihisa; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 203(2-3), p.185 - 194, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:68.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Yoshioka, Kunihiko*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*; Anada, Hiroyuki*; Nagase, Fumihisa; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 37(8), p.670 - 675, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Akita, Koichi*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tojo, Takuya*; Yamamoto, Takenori*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Aihara, Jun; Tachibana, Yukio
no journal, ,
Fuel compact of high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) with inherent safety employs fuel component which was molded from graphite. Development of oxidation-resistant fuel component has been advancing at present, which is fuel component having oxidation resistance formed by SiC. In this study, mechanical properties were obtained on oxidation-resistant fuel components prepared under various molding parameters. Young's modulus was measured by ultrasonic pulse velocity test, and compressive strength was measured by compression test. High correlation was not observed between Young's modulus and hot pressing conditions of temperature and time. There was no correlation between compressive strength and hot pressing time in range of hot pressing temperature of 1573-1873 K and time of 40-120 min, but high negative correlation was observed within range of hot pressing temperatures. Therefore, it was predicted that compressive strength was increased by decreasing hot pressing temperature.
Iwamoto, Taiki*; Zhang, Yuan*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Hirota, Noriaki; Kobayashi, Yuji*; Kimura, Yuta*
no journal, ,
Nowadays, researches on quantitative evaluation of plastic strain and residual stress of stainless steel with various Electron Backscatter Diffraction (abbreviated to EBSD) parameters have been actively conducted. Generally, it is considered that residual stress accumulated near the grain boundary. It might be caused by dislocations and resulted in the increment of the average value of local misorientations. In this study, we focused on EBSD parameters and investigated the applicability of these parameters as an evaluation metric for the depth direction of residual stress in austenitic stainless steel subjected to laser peening.
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Akita, Koichi; Yamada, Teruaki*; Shimasaki, Tomonori*; Tanigawa, Ryohei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kunimoto, Eiji; Konishi, Takashi; Eto, Motokuni*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Kato, Yutai*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tachibana, Yukio; Ohira, Koichi*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*
no journal, ,
For the purpose of upgrading safety of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR), research on advanced fuel element was conducted with cooperation of Nuclear Fuel Industries and Kumamoto University. The advanced fuel element contains SiC as the matrix material and oxidation resistance is highly improved so that shape and integrity of the fuel element should be maintained even when large unexpected amount of air enters into the core in the air ingress (pipe rupture) accident which is a typical event for the HTGR. This presentation shows outlines of the contracted research from FY2014 to 2016.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Tachibana, Yukio; Kuroda, Masatoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Akita, Koichi; Kobayashi, Yuji*; Tsuji, Toshiya*; Shimasaki, Tomonori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsushima, Yuki*; Yamada, Teruaki*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Sawa, Kazuhiro
no journal, ,
In order to investigate the effect of notch-tip geometry on the fracture toughness of fine-grained isotropic graphite ETU-10, three-point-bending fracture toughness tests have been performed by using two types of single-edge notched beam specimens with different notch angles of approximately 15 and 30
and 30 . The values of the fracture toughness were calculated based on linear elastic fracture mechanics by using the maximum force which could be obtained by the load-displacement curve. As a result, the values of the fracture toughness of the specimens with the notch angles of approximately 15
. The values of the fracture toughness were calculated based on linear elastic fracture mechanics by using the maximum force which could be obtained by the load-displacement curve. As a result, the values of the fracture toughness of the specimens with the notch angles of approximately 15 and 30
and 30 were 0.933 MPa m
were 0.933 MPa m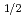 and 0.926 MPa m
and 0.926 MPa m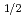 , respectively. This suggested that the values of the fracture toughness were not affected between the notch angles. Further work has been ongoing to discuss the effect of the notch-tip geometry such as angle and root radius of notch in terms of finite element analysis.
, respectively. This suggested that the values of the fracture toughness were not affected between the notch angles. Further work has been ongoing to discuss the effect of the notch-tip geometry such as angle and root radius of notch in terms of finite element analysis.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Tachibana, Yukio; Kuroda, Masatoshi*
no journal, ,
An application of higher heat-resistant ceramic material to the control rod of VHTR is required for the VHTR development, since the core components of the VHTR will be subject to the severer condition than that of the HTGR. The carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite (C/C composite) is one of the major candidate materials as substitute for the metallic materials which has been generally used for the control rod of nuclear reactors. In this study, tension-compression fatigue tests have been carried out by using two types of the 2D-C/C composite (made by Toyo Tanso and Tokai Carbon) to obtain the design data for VHTR. The microstructure of the ruptured specimens was also observed to clarify the fracture mechanism of the 2D-C/C composite. As a result, the fatigue properties were almost the same between the two types of the 2D-composite. On the other hand, the fracture mechanism was different between them depending on their matrix property.