Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tani, Keiji*; Honda, Mitsuru; Oikawa, Toshihiro*; Shinohara, Koji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sugie, Tatsuo
Nuclear Fusion, 55(5), p.053010_1 - 053010_15, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.99(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effects of a radial electric field (EF) on the losses of alpha particles and NBI fast ions in typical ITER operation scenarios for both error fields due to test blanket modules (TBMs) and toroidal field (TF) ripple were evaluated using an iterative method to execute an orbit-following Monte-Carlo code and a one-dimensional transport code. The EF effect on the loss of fast ions strongly depends on the operation scenario as well as on the error field. The electric field is very significant in the loss of fast ions in a 9MA ITER operation scenario with a higher safety factor and in the error field associated with TBMs. The EF effect in the error field of TF-ripple is very small in any operation scenario. The radial electric field changes the toroidal precession of fast ions and consequently alter their condition of resonance with the error field, which may account for the EF effect on the loss of fast ions in ITER with TBMs.
Miyamoto, Seiji*; Isayama, Akihiko; Bandyopadhyay, I.*; Jardin, S. C.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; Lukash, V.*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sugihara, Masayoshi*
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083002_1 - 083002_19, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:83.72(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two well-established simulation codes, DINA and TSC, are compared with each other using benchmark scenarios in order to validate the ITER 2D disruption modelling by those codes. Although the simulation models employed in those two codes ought to be equivalent in the resistive time scale, it has long been unanswered whether the one of the two codes is really able to reproduce the other result correctly, since a large number of code-wise differences render the comparison task exceedingly complicated. In this paper, it is demonstrated that after simulations are set up accounting for the model differences, in general, a good agreement is attained on a notable level, corroborating the correctness of the code results. When the halo current generation and its poloidal path in the first wall are included, however, the situation is more complicated. Because of the surface averaged treatment of the magnetic field (current density) diffusion equation, DINA can only approximately handle the poloidal electric currents in the first wall that cross field lines. Validation is carried out for DINA simulations of halo current generation by comparing with TSC simulations, where the treatment of halo current dynamics is more justifiable. The particularity of each code is depicted and the consequence in ITER disruption prediction is discussed.
Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Peterson, B.*; Mase, Atsushi*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(2), P. 164, 2014/02
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013012_1 - 013012_8, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper proposes a new method to calculate a safety factor,  , profile from gridded data of a poloidal flux,
, profile from gridded data of a poloidal flux, 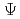 , efficiently and accurately. Difficulties of calculating
, efficiently and accurately. Difficulties of calculating  are derived from a difficulty of specifying a contour line of
are derived from a difficulty of specifying a contour line of 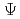 and a singularity at a magnetic axis. In order to solve the first difficulty, the proposed method interpolates knots, which are located on a target
and a singularity at a magnetic axis. In order to solve the first difficulty, the proposed method interpolates knots, which are located on a target 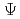 , by utilizing a normalized arc length and constraints expressed by a magnetic field. Regarding the second difficulty, the proposed method identifies
, by utilizing a normalized arc length and constraints expressed by a magnetic field. Regarding the second difficulty, the proposed method identifies 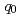 by extrapolating
by extrapolating  profile around a magnetic axis with a constraint of
profile around a magnetic axis with a constraint of 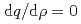 at the magnetic axis. Accuracy assessments of the proposed method are carried out by utilizing Solov'ev type equilibrium. The results show the validity and high performance of the proposed method.
at the magnetic axis. Accuracy assessments of the proposed method are carried out by utilizing Solov'ev type equilibrium. The results show the validity and high performance of the proposed method.
Takeuchi, Masaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ishikawa, Masao; Shimada, Takahiko; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8(Sp.1), p.2402147_1 - 2402147_5, 2013/11
Divertor IR Thermography is one of the diagnostics which Japan is in charge of development in ITER project. The conceptual design has been performed so far, and the progress is reported here. By reducing the size of mirrors, and making the optical path a labyrinthine structure, the design of a new optics that fills requirements of both spatial resolution and neutron shielding has been advanced. To achieve the required measurement accuracy, the detected signal and the noises such as bremsstrahlung light, detector noise and thermal noise of optical components were evaluated. Higher photons than the bremsstrahlung light are obtained, excluding the low temperature range. The simulation calculation of reflection from wall was started. Detailed method of data processing of deriving the profiles of surface temperature in the divertor plates from the observed signals and in-situ calibration strategies of the optical system are important issues and will be discussed.
 calibration of ITER in-vessel neutron flux monitor with microfission chamber
calibration of ITER in-vessel neutron flux monitor with microfission chamberIshikawa, Masao; Kondoh, Takashi; Kusama, Yoshinori; Bertalot, L.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.1377 - 1381, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutronic analysis is performed for  calibration of the in-vessel neutron flux monitor in ITER, the Microfission Chamber (MFC). The transfer system of a neutron generator, which consists of two toroidal rings and a neutron generator holder, has been designed and its effect on the detection efficiency of the MFC is estimated through neutronic analysis with MCNP. The result indicates that the designed transfer system is unaffected for the detection efficiency of the MFC.
calibration of the in-vessel neutron flux monitor in ITER, the Microfission Chamber (MFC). The transfer system of a neutron generator, which consists of two toroidal rings and a neutron generator holder, has been designed and its effect on the detection efficiency of the MFC is estimated through neutronic analysis with MCNP. The result indicates that the designed transfer system is unaffected for the detection efficiency of the MFC.  calibrations for the point by point method and the rotation method are simulated and compared through neutronic analysis. It is found that the rotation method is appropriate for full calibration because this method has the advantage that the calibration time can be shortened and all neutron flux monitors can be calibrated simultaneously.
calibrations for the point by point method and the rotation method are simulated and compared through neutronic analysis. It is found that the rotation method is appropriate for full calibration because this method has the advantage that the calibration time can be shortened and all neutron flux monitors can be calibrated simultaneously.
Itami, Kiyoshi; Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Peterson, B.*; Mase, Atsushi*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 89(9), P. 638, 2013/09
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Yonekawa, Izuru*; Ota, Kazuya*; Hosoyama, Hiroki*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Wallander, A.*; Winter, A.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(12), p.2016 - 2019, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)The ITER pulse scheduling system creates, approves and manage parameters that characterize plasma operation of ITER. JAEA analyzed requirements on the ITER plasma operations based on experience operating the JT-60U and designed essential functions. This system was designed to enable the change and reuse of parameters. The functions to support to check consistency between parameters and to assign parameter values are calculated by the system were proposed. These functions are useful to support operators.
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(12), p.123507_1 - 123507_5, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Seiji; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Shinya, Kichiro*; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Toshimitsu, Shinichi*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(11), p.1816 - 1827, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hatae, Takaki; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hayashi, Toshimitsu; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*; Ono, Takehiro; Kusama, Yoshinori
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(10), p.10E344_1 - 10E344_3, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:54.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)A prototype YAG laser system for the edge Thomson scattering system in ITER has been newly developed. Performance of the laser amplifier was improved by using flow tubes made of samarium-doped glass; the small signal gain reached 20 at its maximum. As a result, an output energy of 7.66 J at 100 Hz was successfully achieved, and the performance exceeded the target performance (5 J, 100 Hz).
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Suzuki, Takahiro; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kawano, Yasunori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(7), p.392 - 393, 2012/07
no abstracts in English
Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hatae, Takaki; Fujie, Daijiro*; Kurokawa, Atsuo*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(10), p.10E328_1 - 10E328_3, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)On the edge Thomson scattering (TS) system in ITER, the filter polychromator is used for dispersing the scattered radiation. Since the signal in TS system is very small, it is crucial to reduce the signal loss from the collection optics to the spectrometer. A band of wavelength in the signal is extracted by an interference filter, and the remaining part is reflected at the interference filter. On the conventional polychromator, a number of reflections are necessary for extracting all wavelength bands. We proposed a new type of polychromator. On the new polychromator, both transmitted and reflected signal from an interference filter are dispersed into transmitted and reflected parts again. It enables to reduce the number of reflection at the interference filters. We showed it is possible to apply in the edge TS system in ITER by setting the injection angle of signal light into the interference filters to be approximately less than 10 degrees.
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 54(5), p.055005_1 - 055005_7, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:31.61(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Iwamae, Atsushi*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori
JAEA-Research 2011-045, 11 Pages, 2012/02
In order to investigate reflection properties on plasma-facing material in ITER, the bi-directional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) of a tungsten block sample has been measured. On the machining surface of the block, one-directional machining lines are engraved. Two laser diodes  652 nm and
652 nm and  473 nm were used to simulate H
473 nm were used to simulate H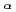 and H
and H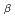 emissions, respectively. The reflected light is affected by the machining surface. The reflected light traces a line when the incident light is injected in the perpendicular direction to the engraved line. On the other hand the reflected light traces an arc shape when the incident light is injected in the parallel direction to the engraved lines. Ray tracing simulation qualitatively explains the experimental results.
emissions, respectively. The reflected light is affected by the machining surface. The reflected light traces a line when the incident light is injected in the perpendicular direction to the engraved line. On the other hand the reflected light traces an arc shape when the incident light is injected in the parallel direction to the engraved lines. Ray tracing simulation qualitatively explains the experimental results.
Tani, Keiji*; Shinohara, Koji; Oikawa, Toshihiro*; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sugie, Tatsuo
Nuclear Fusion, 52(1), p.013012_1 - 013012_21, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:77.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hatae, Takaki; Kusama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Fusion, 51(12), p.123004_1 - 123004_4, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:39.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113022_1 - 113022_8, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:69.20(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have developed the new method for identifying the  -profile from data, whose accuracy is determined in ITER, in order to assess the necessary measurement accuracy of the poloidal polarimeter. We have adopted the finite element method to calculate the ideal MHD equilibrium. Assuming that all measurement data has no error, we have shown the Importance of using the measurement data of the electron temperature,
-profile from data, whose accuracy is determined in ITER, in order to assess the necessary measurement accuracy of the poloidal polarimeter. We have adopted the finite element method to calculate the ideal MHD equilibrium. Assuming that all measurement data has no error, we have shown the Importance of using the measurement data of the electron temperature, 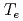 , and the ellipticity angle,
, and the ellipticity angle,  , of the polarization state in the inductive operation scenario II (S2), and the non-inductive operation scenario IV (S4).
, of the polarization state in the inductive operation scenario II (S2), and the non-inductive operation scenario IV (S4). 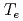 is used to calculate the relativistic effect on the polarization state. When the relativistic effect has not been included in the
is used to calculate the relativistic effect on the polarization state. When the relativistic effect has not been included in the  -profile identification, the error of
-profile identification, the error of  -profile identification has exceeded 7.7
-profile identification has exceeded 7.7 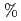 and 15
and 15 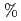 in S2 and S4, respectively.
in S2 and S4, respectively.  is mainly related to the Cotton-Mouton effect, which is an obstacle in measurement of a pure Faraday effect. Taking into account
is mainly related to the Cotton-Mouton effect, which is an obstacle in measurement of a pure Faraday effect. Taking into account  reduced the error of
reduced the error of  -profile identification by 0.5
-profile identification by 0.5 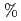 . Finally, we have assessed the necessary accuracy of the orientation angle,
. Finally, we have assessed the necessary accuracy of the orientation angle, 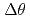 , and the ellipticity angle,
, and the ellipticity angle, 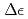 . The polarimetric measurements with accuracy of
. The polarimetric measurements with accuracy of 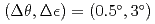 have satisfied the measurement requirement for the
have satisfied the measurement requirement for the  -profile identification (
-profile identification (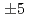
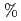 ) in case of that viewing chords are via both equatorial and upper ports.
) in case of that viewing chords are via both equatorial and upper ports.
Sato, Kazuyoshi; Yaguchi, Eiji; Pitcher, C. S.*; Walker, C.*; Encheva, A.*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.1264 - 1267, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Masao; Kawano, Yasunori; Imazawa, Ryota; Sato, Satoshi; Vayakis, G.*; Bertalot, L.*; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hatae, Takaki; Kondoh, Takashi; Kusama, Yoshinori
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.1286 - 1289, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The nuclear heating rates of the optical mirrors of the poloidal polarimeter installed in the equatorial port plug of ITER are calculated. Since the system cannot have a sufficiently labyrinthine structure and the second mirrors are located nearly as close to the plasma as the first mirrors due to limited space, the nuclear heating rate of the second mirrors is as high as that of the first mirrors. However, it is possible to reduce the nuclear heating rates of the mirrors if the blanket shield module provides a sufficient degree of neutron shielding.