Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Inoue, Masao*; Kondo, Takafumi*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Kuwano, Ryo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Inoue, Masao*; Matsumura, Taichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Matsumura, Taichi
no journal, ,
High-penetrating gamma-rays (Co-60) have been mainly used as an external radiation in irradiation experiments on water radiolysis for the 1F decommissioning, while the experiments using electron beams (EB) simulating beta-rays (Sr-90 and others) and X-rays simulating the bremsstrahlung of electrons have been also expected. However these are difficult because of the low-penetrating property of radiations. In this study, the experiments using EB and X-rays were conducted by using reaction vessels sealed with films having a good penetrating property for their radiations to measure H and its geminate product of H
and its geminate product of H O
O as radiolysis products of water.
as radiolysis products of water.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Matsumura, Taichi
no journal, ,
Different from monochromatic photons such as Co-60  -rays, Bremsstrahlung and X-rays with continuous energies provide photons with different radiation quality (RQ) into water, dependent on the width of water layer. Since the photons with different RQ further give different primary yields (G-value) of water radiolysis, the effect of RQ (LET) on G-values would be important in experiments with photons with continuous energies. In this study, the experiments using X-rays simulating Bremsstrahlung from
-rays, Bremsstrahlung and X-rays with continuous energies provide photons with different radiation quality (RQ) into water, dependent on the width of water layer. Since the photons with different RQ further give different primary yields (G-value) of water radiolysis, the effect of RQ (LET) on G-values would be important in experiments with photons with continuous energies. In this study, the experiments using X-rays simulating Bremsstrahlung from  -ray and secondary electrons were conducted with changing the tube voltage and water width to clarify the LET effect on the X-ray radiolysis of water.
-ray and secondary electrons were conducted with changing the tube voltage and water width to clarify the LET effect on the X-ray radiolysis of water.
Matsumura, Taichi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
no journal, ,
The overflow from HIC at ALPS was owing to water radiolysis of beta rays in co-precipitate slurry of carbonate, leading to the volume increase of slurry and supernatant formation. The radiation effects (radiolysis and material degradation) on high-viscous fluids after long-term (high dose) irradiation is quite different from those on low-viscous fluids such as aqueous solutions. The understanding of effects on high-viscous fluids, containing suspension of clay which is planned to be used as a buffer material for final disposal, is important in long-term storage and disposal of radioactive wastes. In this study, the physical and viscosity properties of fluids of co-precipitate and clay systems were measured before and after irradiation of electron beam and gamma ray to discuss the relations among their properties quantitatively.
 retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 1; Estimation of hydrophilicity on the surface of suspended solid
retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 1; Estimation of hydrophilicity on the surface of suspended solidKuwano, Ryo*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Ito, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
The overflow event occurred in carbonate slurry wastes emitted from the 1F ALPS co-precipitation system is due to the highly viscous slurry retaining hydrogen molecules (H ) formed by its radiolysis. Since this high viscosity is caused by the hydrophilicity (water absorption) of surface of suspended solid (SS) particle in the slurry, it is expected that H
) formed by its radiolysis. Since this high viscosity is caused by the hydrophilicity (water absorption) of surface of suspended solid (SS) particle in the slurry, it is expected that H retention would be repressed by coating (modifying) this surface with much lower hydrophilic materials (molecules). In order to discuss the degree of repression quantitatively, it is important to estimate the hydrophilicity of SS particle surface. In this report as the first in a series of presentations, the water vapor adsorption behavior on the SS particle surface was measured under two conditions of drying and moisture adsorption by using a gas adsorption measurement apparatus, and the hydrophilicity of SS particle surface was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
retention would be repressed by coating (modifying) this surface with much lower hydrophilic materials (molecules). In order to discuss the degree of repression quantitatively, it is important to estimate the hydrophilicity of SS particle surface. In this report as the first in a series of presentations, the water vapor adsorption behavior on the SS particle surface was measured under two conditions of drying and moisture adsorption by using a gas adsorption measurement apparatus, and the hydrophilicity of SS particle surface was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
 retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 3; Gamma radiolysis estimation of H
retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 3; Gamma radiolysis estimation of H (gas) retention properties
(gas) retention propertiesIto, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen molecule (H ) formed as a dissolved species by radiolysis of pore water in the slurry and then turned into a gas is retained by the slurry, and the H
) formed as a dissolved species by radiolysis of pore water in the slurry and then turned into a gas is retained by the slurry, and the H retained amount would be dependent on the viscosity and height of slurry. The hydrophilicity (water absorption)-lowering of carbonate slurry waste emitted from the 1F ALPS co-precipitation system has been considered, and in order to estimate the effectiveness of lowering from the viewpoint of the repression of H
retained amount would be dependent on the viscosity and height of slurry. The hydrophilicity (water absorption)-lowering of carbonate slurry waste emitted from the 1F ALPS co-precipitation system has been considered, and in order to estimate the effectiveness of lowering from the viewpoint of the repression of H retention, it is important to clarify what and how the H
retention, it is important to clarify what and how the H retention property would be changed by this lowering. In this report as the third in a series of presentations, the sample-height dependence of H
retention property would be changed by this lowering. In this report as the third in a series of presentations, the sample-height dependence of H generation yield (G-value) released outside the slurry was measured in the gamma radiolysis experiments, and the H
generation yield (G-value) released outside the slurry was measured in the gamma radiolysis experiments, and the H retention property was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
retention property was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
 retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 2; Pulse radiolysis measurement of local (partial) viscosity of pore water
retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 2; Pulse radiolysis measurement of local (partial) viscosity of pore waterNagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Ito, Tatsuya; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Tamaki, Ryoya*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen molecules (H ) retained by highly viscous suspension such as a carbonate slurry exist in the pore water of suspension in the form of gas (bubble). The H
) retained by highly viscous suspension such as a carbonate slurry exist in the pore water of suspension in the form of gas (bubble). The H behaviors such as the reaction of dissolved species of H
behaviors such as the reaction of dissolved species of H and the process forming H
and the process forming H bubble are mainly determined by the viscosity of pore water, while the H
bubble are mainly determined by the viscosity of pore water, while the H retention by the macroscopic viscosity of suspension. Such local (partial) viscosity is generally unclear. In order to clarify the H
retention by the macroscopic viscosity of suspension. Such local (partial) viscosity is generally unclear. In order to clarify the H retention/release mechanism in the suspension, it is important to estimate this viscosity. In this report as the second in a series of presentations, the reaction (decay) rate of hydrated electrons (e
retention/release mechanism in the suspension, it is important to estimate this viscosity. In this report as the second in a series of presentations, the reaction (decay) rate of hydrated electrons (e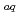
 ) formed as a radiolysis radical of pore water was transiently measured by using ns-pulse radiolysis, and the viscosity of pore water was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
) formed as a radiolysis radical of pore water was transiently measured by using ns-pulse radiolysis, and the viscosity of pore water was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Ito, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
Coagulating sedimentation has been practically used for radioactive multi-nuclide removal in Fukushima Daiichi NPS, emitting radioactive wastes of high-viscous suspension of co-precipitates. The suspension of carbonate slurry has been found out to retain hydrogen molecules (H ) formed in water radiolysis in the previous studies for overflow of water from HIC. However, radiation effects on the H
) formed in water radiolysis in the previous studies for overflow of water from HIC. However, radiation effects on the H retention property have not been elucidated microscopically. In this study, the physical and viscosity properties of simulated slurry were measured before and after the EB and
retention property have not been elucidated microscopically. In this study, the physical and viscosity properties of simulated slurry were measured before and after the EB and  -ray irradiation, and then the radiation effects were discussed. Hydrophilic nature of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)
-ray irradiation, and then the radiation effects were discussed. Hydrophilic nature of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH) ) in suspended solids (SS) is closely related to the viscosity appearance of slurry. It was estimated in a SS particle that water molecules equivalent to Mg or more were bound to Mg(OH)
) in suspended solids (SS) is closely related to the viscosity appearance of slurry. It was estimated in a SS particle that water molecules equivalent to Mg or more were bound to Mg(OH) . In the irradiation experiments, the destruction of SS and the irreversible lowering of viscosity in the slurry were observed to repress the H
. In the irradiation experiments, the destruction of SS and the irreversible lowering of viscosity in the slurry were observed to repress the H retention.
retention.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Ito, Tatsuya; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Since seawater has been used as emergency cooling water in the 1F accident, knowledge about radiolysis of seawater became important after the accident. In the experimental studies, simulated seawater and aqueous solutions containing halides have been used instead of seawater to elucidate individual events and phenomena and to obtain data. However, it has not been quantitatively clarified whether the radiolysis of seawater is reproduced as a whole. Therefore, in this study, in order to clarify the reproducibility from the initial process of radiolysis to the formation and reaction processes of final products, the transient absorption of radical products was observed using pulse radiolysis, and the molecular products hydrogen and hydrogen peroxide were measured by final product analysis. Based on these experimental results on the radiolysis of seawater, simulated seawater or an aqueous solution containing halides was compared with (natural) seawater.
Ito, Tatsuya; Kuwano, Ryo*; Nagaishi, Ryuji
no journal, ,
Unlike monochromatic photons such as Co-60 gamma rays, continuous energy (spectrum) photons such as bremsstrahlung and X-rays give photons of different radiation quality (energy, spectrum) into water. The radiolysis of water by these photons gives different yields (G-values) and patterns of products. Therefore, since it is important to evaluate their radiation quality (LET) effects in experiments using these photons, using an X-ray irradiation apparatus, we have evaluated dependences of dose, LET and radiolysis G-value on water layer thickness and tube voltage. In this report, we have developed (improved) a method for evaluating molecular formation with high accuracy, such as by fabricating a new glass irradiation vessel, and mainly evaluated the effect of tube voltage (maximum incident energy) on molecular formation. Based on the results, we discussed the LET effect.
Ito, Tatsuya; Kuwano, Ryo*; Nagaishi, Ryuji
no journal, ,
Unlike monochromatic photons such as Co-60 gamma rays, continuous energy (spectrum) photons such as bremsstrahlung and X-rays give photons of different radiation quality (energy, spectrum) into water. The radiolysis of water by these photons gives different yields (G-values) and patterns of products. Therefore, since it is important to evaluate their radiation quality (LET) effects in experiments using these photons, using an X-ray irradiation apparatus, we have evaluated dependences of dose, LET and radiolysis G-value on water layer thickness and tube voltage. In this report, we have developed a method for evaluating molecular formation with high accuracy, such as by fabricating a new glass irradiation vessel, and mainly evaluated the effect of tube voltage on molecular formation. Based on the results, we discussed the LET effect. This presentation is a commemorative lecture given at the general meeting of the Department of Water Chemistry, AESJ, for receiving the Presentation Award.
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Tamaki, Ryoya*
no journal, ,
The use of radiation-resistant resins becomes increasing as vessels for irradiation experiments. Polyimide (Kapton) was used on surfaces in contact with water in our radiolysis experiments, but the obtained results were not same to that when glass vials were used. In this study, to investigate the effect of resin on water radiolysis, the amounts of dichromate reduction and H O
O formation after gamma-irradiation were compared in the presence or absence of resin in the aqueous solutions. The presence of resins increased the reduction but hardly changed the formation. Therefore, the reduction caused by radiolysis in aqueous solution was suggested to be promoted by the presence of resins. The promotion was further studied using pulse radiolysis, etc.
formation after gamma-irradiation were compared in the presence or absence of resin in the aqueous solutions. The presence of resins increased the reduction but hardly changed the formation. Therefore, the reduction caused by radiolysis in aqueous solution was suggested to be promoted by the presence of resins. The promotion was further studied using pulse radiolysis, etc.