Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Boehnlein, D.*; Lautenschlager, G.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2051 - 2054, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The experiment was performed at the anti-proton (pbar) production target station in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. At the pbar target station, an anti-proton production target, consisted of Inconel and copper disks, were irradiated by 120 GeV proton beam. The beam intensity was 2.0  10
10 proton per second. Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were set around the target to investigate the spatial and energy distribution of secondary particles emitted from the target. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The reaction rates of 30 nuclides induced in Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were obtained. The reaction rates of these nuclides increase for samples placed on forward angle position. The angle dependence of these reaction rates becomes larger for increasing threshold energy. These experimental results compared with the calculation. The calculated results generally agree with the experimental results within a factor of 3.
proton per second. Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were set around the target to investigate the spatial and energy distribution of secondary particles emitted from the target. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The reaction rates of 30 nuclides induced in Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were obtained. The reaction rates of these nuclides increase for samples placed on forward angle position. The angle dependence of these reaction rates becomes larger for increasing threshold energy. These experimental results compared with the calculation. The calculated results generally agree with the experimental results within a factor of 3.
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Mokhov, N.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2059 - 2062, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In an antiproton production (Pbar) target station of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL), the secondary particles produced by bombarding a target with 120-GeV protons are shielded by a thick iron shield. In order to obtain experimental data on high-energy proton accelerator facilities, we indirectly measured  100-MeV neutrons at the outside of the iron shield. The measurement was performed by using the Au activation method coupled with a low-background
100-MeV neutrons at the outside of the iron shield. The measurement was performed by using the Au activation method coupled with a low-background  -ray counting system. As an indicator for the neutron flux, we determined the production rates of 8 spallation nuclides (
-ray counting system. As an indicator for the neutron flux, we determined the production rates of 8 spallation nuclides (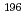 Au,
Au,  Pt,
Pt, 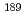 Ir,
Ir,  Os,
Os, 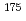 Hf,
Hf, 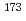 Lu,
Lu, 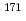 Lu, and
Lu, and 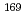 Yb) in the Au activation detector. The measured production rates were compared with the theoretical production rates calculated using PHITS. We proved that the Au activation method can serve as a powerful tool for indirect measurements of
Yb) in the Au activation detector. The measured production rates were compared with the theoretical production rates calculated using PHITS. We proved that the Au activation method can serve as a powerful tool for indirect measurements of  100-MeV neutrons that play a vital role in neutron transport.
100-MeV neutrons that play a vital role in neutron transport.
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
A gold activation detector was studied as a high energy neutron detector at high radiation field in a series of shielding experiment at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. We could measure spallation residual nuclei with wide threshold energy by using a combination method with radiological chemical separation and X-X- coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Hirayama, Hideo*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; et al.
no journal, ,
On the shielding experiment, started on 2007, as collaborative research with Fermilab using high energy proton accelerators, the measurement of reaction rate distributions in the antiproton target station has been carried out. Reaction rates were measured with activation method. Using the reaction rate data, neutron spectra at each measurement position were deduced by means of nonlinear least square method; a shape of the neutron spectrum between 5 and 100 MeV was expressed as a fitting function with 5 fitting parameters, whose values were determined at a minimum of 
 values for the reaction rates. In the presentation, systematics of the variation of neutron spectra in the shield will be discussed.
values for the reaction rates. In the presentation, systematics of the variation of neutron spectra in the shield will be discussed.