Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:96.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Materials Science and Technology, 36(15), p.1621 - 1627, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:51.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable phases in aluminum alloys are the primary nano-scale precipitates which have the biggest contribution to the increase in the tangible mechanical properties. The continuous increase in hardness in the 7xxx aluminum alloys is associated with the phase transformation from clusters or GP-zones to the metastable  phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of
phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of  phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
Herranz, L. E.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Nitheanandan, T.*; Sandberg, N.*; Barr , F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
, F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 127, p.103432_1 - 103432_14, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Matsuda, Kenji*; Yasumoto, Toru*; Bendo, A.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Marioara, C. D.*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 60(8), p.1688 - 1696, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:67.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Chen, S.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Rodriguez, T. R.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Calvet, D.*; Ch teau, F.*; Corsi, A.*; Delbart, A.*; et al.
teau, F.*; Corsi, A.*; Delbart, A.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(4), p.041302_1 - 041302_6, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:89.36(Physics, Nuclear) Ni hole-states from (p,d) transfer reactions
Ni hole-states from (p,d) transfer reactionsSanetullaev, A.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Lynch, W. G.*; Lee, J.*; Bazin, D.*; Chan, K. P.*; Coupland, D.*; Hanzl, V.*; Hanzlova, D.*; Kilburn, M.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 736, p.137 - 141, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.34(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Ivanova, T.*; Fernex, F.*; Kolbe, E.*; Vasiliev, A.*; Lee, G. S.*; Woo, S. W.*; Mennerdahl, D.*; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Neuber, J. C.*; Hoefer, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors; Advances in Reactor Physics to Power the Nuclear Renaissance (PHYSOR 2010) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2010/05
The expert group (EG) on Uncertainty Analysis for Criticality Safety Assessment (UACSA) was established within the OECD/NEA Working Party on Nuclear Criticality Safety in December 2007 to promote exchange of information on related topics; compare methods and software tools for uncertainty analysis; test their performance; and assist in selection/development of safe and efficient methodologies for validation of criticality computations. At the current stage, the work of the group is focused on approaches for validation of criticality calculations. With the diversity of the approaches to validate criticality calculations, a thorough description of each approach and assessment of its performance is useful to the criticality safety community. Developers, existing and potential practitioners as well as reviewers of assessments using those approaches should benefit from this effort. Exercise Phase I was conducted in order to illustrate predicting capabilities of criticality validation approaches, which include similarity assessment, definition of  bias and bias uncertainty, and selection of benchmarks. The approaches and results of the exercises will be thoroughly documented in a pending state-of-the-art report from the EG. This paper provides an overview of current and future activities for the EG, a summary of the participant-contributed validation approaches, and a synthesis of the results for the exercises.
bias and bias uncertainty, and selection of benchmarks. The approaches and results of the exercises will be thoroughly documented in a pending state-of-the-art report from the EG. This paper provides an overview of current and future activities for the EG, a summary of the participant-contributed validation approaches, and a synthesis of the results for the exercises.
 Mg; Intruder amplitudes in
Mg; Intruder amplitudes in  Ne and implications for the binding of
Ne and implications for the binding of  F
FFallon, P.*; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.*; Macchiavelli, A. O.*; Gade, A.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Adrich, P.*; Bazin, D.*; Bowen, M.*; Campbell, C. M.*; Clark, R. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 81(4), p.041302_1 - 041302_5, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:88.48(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 lattice antiferromagnet KFe
lattice antiferromagnet KFe (OH)
(OH) (SO
(SO )
)
Matan, K.*; Helton, J. S.*; Grohol, D.*; Nocera, D. G.*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Lee, Y. S.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2529 - 2531, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.37(Physics, Condensed Matter)Uchida, Masahiro; Dershowitz, W.*; Lee, G.*; Shuttle, D.*
Hydrogeology Journal, 17(5), p.1093 - 1110, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:31.47(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)This paper addresses a residual uncertainty after the in-situ tracer experiment and try to demonstrate the usefulness of tracer experiments for safety assessment. There have been long debate on the usefulness of in-situ tracer experiment, because the difference in temporal scale, where in-situ tracer experiments are generally conducted for the period of a few days to several months with high velocity to recover the tracers, whereas safety assessment requires more than ten thousand years with much slower velocity. This paper addresses the issue by comparing breakthrough curves for safety assessment conditions (long-term, slow velocity) with and without calibration to in-situ tracer experiment called STT-1b test at the Aspo Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Authors newly developed a conceptual model of internal structure of fracture, which explicitly addresses fault gouge, coating minerals, altered zone and intact rock, since especially fault gouge has high porosity and likely to affect the tracer migration behavior. The result was that calibrated model showed much tighter distribution of breakthrough curve statistics indicating the constraining power of in-situ tracer experiment.
 Mg and
Mg and 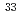 Al
AlTripathi, V.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Mantica, P. F.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Bender, P.*; Cook, J.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Lee, S.*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Pereira, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 101(14), p.142504_1 - 142504_4, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:86.60(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 P
PWiedeking, M.*; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.*; Fallon, P.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Clark, R. M.*; Cline, D.*; Cromaz, M.*; Descovich, M.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Lee, I.-Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 78(3), p.037302_1 - 037302_4, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.05(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.
 Mg
MgTripathi, V.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Bender, P.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Lee, S.*; Pepper, K.*; Perry, M.*; Mantica, P.*; Cook, J. M.*; Pereira, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 77(3), p.034310_1 - 034310_8, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:84.07(Physics, Nuclear)Excited states in  Mg have been observed from a
Mg have been observed from a  -decay experiment of
-decay experiment of  Na which was performed at National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory in Michigan State University. The 2.1 MeV state proposed previously was denied because the corresponding
Na which was performed at National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory in Michigan State University. The 2.1 MeV state proposed previously was denied because the corresponding  ray is found to be located elsewhere. New level scheme is proposed and compared with the Monte Carlo shell model by JAEA. The ground state of
ray is found to be located elsewhere. New level scheme is proposed and compared with the Monte Carlo shell model by JAEA. The ground state of  Na appears to be a negative parity states from the decay pattern and the calculation. We suggested that the configuration of the states which are strongly populated via the
Na appears to be a negative parity states from the decay pattern and the calculation. We suggested that the configuration of the states which are strongly populated via the  decay is 3p-3h, since the ground state of the parent nucleus is most likely 2p-3h character.
decay is 3p-3h, since the ground state of the parent nucleus is most likely 2p-3h character.
Tripathi, V.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Mantica, P. F.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Bender, P.*; Cook, J. M.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Lee, S.*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Pereira, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 76(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_5, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:82.58(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Ru
Ru O
O and the possible formation of Haldane chains in three-dimensional crystals
and the possible formation of Haldane chains in three-dimensional crystalsLee, S.*; Park, J.-G.*; Adroja, D. T.*; Khomskii, D.*; Streltsov, S.*; McEwen, K. A.*; Sakai, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; Anisimov, V. I.*; Mori, Daisuke*; et al.
Nature Materials, 5(6), p.471 - 476, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:94.32(Chemistry, Physical)Here we show that the three-dimensional cubic system of Tl Ru
Ru O
O most probably evolves into a one-dimensional spin-one Haldane system with a spin gap below 120 K, accompanied by anomalies in the structure, resistivity, and susceptibility. We argue that these anomalies are due to an orbital ordering of Ru
most probably evolves into a one-dimensional spin-one Haldane system with a spin gap below 120 K, accompanied by anomalies in the structure, resistivity, and susceptibility. We argue that these anomalies are due to an orbital ordering of Ru 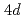 electrons, with a strong coupling among three degrees of freedom: orbital, spin, and lattice. Our work provides a unique example of the spontaneous formation of Haldane system with an insight into the intriguing interplay of different degrees of freedom.
electrons, with a strong coupling among three degrees of freedom: orbital, spin, and lattice. Our work provides a unique example of the spontaneous formation of Haldane system with an insight into the intriguing interplay of different degrees of freedom.
Moribayashi, Kengo; Lee, K.*; Kagawa, Takashi*; Kim, D. E.*
Laser Physics, 16(2), p.322 - 324, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.08(Optics)no abstracts in English
Cullen, D. E.*; Blomquist, R. N.*; Dean, C.*; Heinrichs, D.*; Kalugin, M. A.*; Lee, M.*; Lee, Y. K.*; MacFarlane, R.*; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Trkov, A.*
UCRL-TR-203892, p.1 - 40, 2004/04
no abstracts in English
Nishijima, Toshiji*; Hearne, S. M.*; Jamieson, D. N.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Lee, K. K.; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.196 - 200, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)The radiation damage in silicon carbide (SiC) schottky diode was studied using ion beam induced current (IBIC). Schottky diodes with electrodes of 30  m on n- or p-type 6H-SiC were fabricated using the evaporation of Al, Ni, and Au. To study the radiation damage of diodes, the 2MeV-He ion micro beam with a diameter of 1
m on n- or p-type 6H-SiC were fabricated using the evaporation of Al, Ni, and Au. To study the radiation damage of diodes, the 2MeV-He ion micro beam with a diameter of 1  m was irradiated from 10
m was irradiated from 10 to 10
to 10 /cm
/cm into a 10
into a 10  m
m  10
10  m area. As the result, the value of IBIC decreased with increasing the dose of 2 MeV-He. This indicates that the charge collection decreases by the recombination centers introduced by irradiation.
m area. As the result, the value of IBIC decreased with increasing the dose of 2 MeV-He. This indicates that the charge collection decreases by the recombination centers introduced by irradiation.