Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Chettah, A.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
Injecting high-energy heavy ions in the electronic stopping regime into solids can create cylindrical damage zones called latent ion tracks. Although these tracks form in many materials, none have ever been observed in diamond, even when irradiated with high-energy GeV uranium ions. Here we report the first observation of ion track formation in diamond irradiated with 2-9 MeV C fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which
fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which  -bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
-bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
 No
NoBronis, A.*; He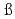 berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Andel, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Andel, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(1), p.014602_1 - 014602_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear) s isomeric state in
s isomeric state in 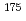 Ir
IrGillespie, S. A.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Al Monthery, M.*; Barton, C. J.*; Antalic, S.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Cox, D.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; O'Donnell, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(6), p.064310_1 - 064310_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.64(Physics, Nuclear)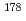 Hg
HgM ller-Gatermann, C.*; Dewald, A.*; Fransen, C.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Beckers, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Braunroth, T.*; Cullen, D. M.*; Fruet, G.*; et al.
ller-Gatermann, C.*; Dewald, A.*; Fransen, C.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Beckers, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Braunroth, T.*; Cullen, D. M.*; Fruet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054325_1 - 054325_7, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:64.15(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 is not a prerequisite for the core/shell ion tracks or ion shaping
is not a prerequisite for the core/shell ion tracks or ion shapingAmekura, Hiroshi*; Kluth, P.*; Mota-Santiago, P.*; Sahlberg, I.*; Jantunen, V.*; Leino, A. A.*; Vazquez, H.*; Nordlund, K.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Okubo, Nariaki; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 2(9), p.096001_1 - 096001_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:37.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)When a swift heavy ion (SHI) penetrates amorphous SiO , a core/shell (C/S) ion track is formed due to vaporization, where the ion track consists of a lower-density core and a higher-density shell. Here we reexamine this hypothesis. The MD simulations indicate that the vaporization is not induced under 50-MeV Si irradiation (
, a core/shell (C/S) ion track is formed due to vaporization, where the ion track consists of a lower-density core and a higher-density shell. Here we reexamine this hypothesis. The MD simulations indicate that the vaporization is not induced under 50-MeV Si irradiation (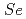 = 3 keV/nm), but the C/S tracks and the ion shaping of nanoparticles are nevertheless induced. Thus, the vaporization is not a prerequisite for the C/S tracks and the ion shaping.
= 3 keV/nm), but the C/S tracks and the ion shaping of nanoparticles are nevertheless induced. Thus, the vaporization is not a prerequisite for the C/S tracks and the ion shaping.
 Es and
Es and  Bk
BkKonki, J.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Uusitalo, J.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Block, M.*; Briselet, R.*; Cox, D. M.*; Dasgupta, M.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 764, p.265 - 270, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:79.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics) -ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element; The
-ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element; The  Rf
RfRubert, J.*; Dorvaux, O.*; Gall, B. J. P.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Asfari, Z.*; Piot, J.*; Andersson, L. L.*; Asai, Masato; Cox, D. M.*; Dechery, F.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 420, p.012010_1 - 012010_10, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Physics, Nuclear)The first prompt in-beam  -ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element,
-ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element,  Rf, has been performed successfully. A development of an intense isotopically enriched
Rf, has been performed successfully. A development of an intense isotopically enriched  Ti beam using the MIVOC method enabled us to perform this experiment. A rotational band up to a spin of 20
Ti beam using the MIVOC method enabled us to perform this experiment. A rotational band up to a spin of 20  has been discovered in
has been discovered in  Rf, and its moment of inertia has been extracted. These data suggest that there is no evidence of a significant deformed shell gap at
Rf, and its moment of inertia has been extracted. These data suggest that there is no evidence of a significant deformed shell gap at  = 104.
= 104.
 -delayed fission of
-delayed fission of 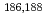 Bi isotopes
Bi isotopesLane, J. F. W.*; Andreyev, A. N.*; Antalic, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Gerl, J.*; He berger, F. P.*; Hofmann, S.*; Huyse, M.*; Kettunen, H.*; Kleinb
berger, F. P.*; Hofmann, S.*; Huyse, M.*; Kettunen, H.*; Kleinb hl, A.*; et al.
hl, A.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(1), p.014318_1 - 014318_7, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.29(Physics, Nuclear) =104 nucleus
=104 nucleus  Rf
RfGreenlees, P. T.*; Rubert, J.*; Piot, J.*; Gall, B. J. P.*; Andersson, L. L.*; Asai, Masato; Asfari, Z.*; Cox, D. M.*; Dechery, F.*; Dorvaux, O.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 109(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_5, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:88.75(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Rotational band structure of the  =104 nucleus
=104 nucleus  Rf has been observed for the first time using an in-beam
Rf has been observed for the first time using an in-beam  -ray spectroscopic technique. This nucleus is the heaviest among the nuclei whose rotational band structure has ever been observed. Thus, the present result provides valuable information on the single-particle shell structure and pairing interaction in the heaviest extreme of nuclei. The deduced moment of inertia indicates that there is no deformed shell gap at
-ray spectroscopic technique. This nucleus is the heaviest among the nuclei whose rotational band structure has ever been observed. Thus, the present result provides valuable information on the single-particle shell structure and pairing interaction in the heaviest extreme of nuclei. The deduced moment of inertia indicates that there is no deformed shell gap at  =104, which is predicted in a number of current self-consistent mean-field models.
=104, which is predicted in a number of current self-consistent mean-field models.
 Ca +
Ca +  Cm
Cm 
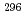 116
116 studied at the GSI-SHIP
studied at the GSI-SHIPHofmann, S.*; Heinz, S.*; Mann, R.*; Maurer, J.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Barth, B.*; Block, M.*; Burkhard, H. G.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 48(5), p.62_1 - 62_23, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:167 Percentile:98.87(Physics, Nuclear) No
NoHe berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Sulignano, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Kindler, B.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kojouharov, I.*; Kuusiniemi, P.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Sulignano, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Kindler, B.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kojouharov, I.*; Kuusiniemi, P.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 43(1), p.55 - 66, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:95.13(Physics, Nuclear) Ca+
Ca+ U
U 
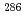 112
112 studied at the GSI-SHIP
studied at the GSI-SHIPHofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Burkhard, H. G.*; Comas, V. F.*; Dressler, R.*; Gan, Z.*; Heinz, S.*; Heredia, J. A.*; He berger, F. P.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 32(3), p.251 - 260, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:260 Percentile:99.7(Physics, Nuclear) decay studies of
decay studies of  Rf,
Rf, 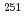 No and
No and 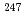 Fm
FmHe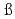 berger, F. P.*; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; Kuusiniemi, P.*; Leino, M.*; Lommel, B.*; Mann, R.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; Kuusiniemi, P.*; Leino, M.*; Lommel, B.*; Mann, R.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 30(3), p.561 - 569, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:91.67(Physics, Nuclear)Decay properties of  Rf,
Rf, 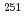 No and
No and 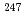 Fm were investigated by measuring the
Fm were investigated by measuring the  and
and  decays. The experiment was carried out by using the linear accelerator UNILAC and velocity filter SHIP at GSI. The evaporation residues were separated by the SHIP and implanted into a silicon detector located at the focal plane. The
decays. The experiment was carried out by using the linear accelerator UNILAC and velocity filter SHIP at GSI. The evaporation residues were separated by the SHIP and implanted into a silicon detector located at the focal plane. The  decays were detected by the silicon detector itself and the
decays were detected by the silicon detector itself and the  rays were detected by Ge detectors. These isotopes were produced by the reaction
rays were detected by Ge detectors. These isotopes were produced by the reaction  Pb(
Pb( Ti, 2n)
Ti, 2n) Rf and the
Rf and the  decay daughters from
decay daughters from  Rf, or by the reaction
Rf, or by the reaction  Pb(
Pb( Ca, 3n)
Ca, 3n)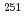 No and the
No and the  decay daughter of
decay daughter of 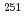 No. It was found that (1) the 1.0 s isomeric state in
No. It was found that (1) the 1.0 s isomeric state in 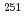 No is located in the level of 106 keV. (2) The new isomeric state with 2
No is located in the level of 106 keV. (2) The new isomeric state with 2  s was found in
s was found in 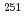 No, which was directly populated in the reaction
No, which was directly populated in the reaction  Pb(
Pb( Ca,3n)
Ca,3n)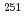 No. The state is located at the level larger than 1700 keV and decays by accompanying two
No. The state is located at the level larger than 1700 keV and decays by accompanying two  rays. These two
rays. These two  -ray energies agreed with the lines which was followed by the
-ray energies agreed with the lines which was followed by the  decay of
decay of  Rf.
Rf.
 decay studies of
decay studies of  No
NoHe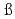 berger, F. P.*; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; Kuusiniemi, P.*; Leino, M.*; Lommel, B.*; Mann, R.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; Kuusiniemi, P.*; Leino, M.*; Lommel, B.*; Mann, R.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 29(2), p.165 - 173, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:88.45(Physics, Nuclear)