Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H. S.*; Soha, A.*; Ramberg, E.*; Coleman, R.*; Jensen, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 337, p.68 - 77, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.43(Instruments & Instrumentation)The energy spectra of neutrons were measured by a time-of-flight method for 120 GeV protons on thick graphite, aluminum, copper, and tungsten targets with an NE213 scintillator at the Fermilab Test Beam Facility. Neutron energy spectra were obtained between 25 and 3000 MeV at emission angles of 30, 45, 120, and 150 . The spectra were parameterized as neutron emissions from three moving sources and then compared with theoretical spectra calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes. The yields of the theoretical spectra were substantially underestimated compared with the yields of measured spectra. The integrated neutron yields from 25 to 3000 MeV calculated with PHITS code were 16-36% of the experimental yields and those calculated with FLUKA code were 26-57% of the experimental yields for all targets and emission angles.
. The spectra were parameterized as neutron emissions from three moving sources and then compared with theoretical spectra calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes. The yields of the theoretical spectra were substantially underestimated compared with the yields of measured spectra. The integrated neutron yields from 25 to 3000 MeV calculated with PHITS code were 16-36% of the experimental yields and those calculated with FLUKA code were 26-57% of the experimental yields for all targets and emission angles.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Sekimoto, Shun*; Oishi, Koji*; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.337 - 340, 2014/04
The Neutrinos at the Main Injector (NuMI) at Fermilab produces intense neutrino beam to investigate the phenomena of the neutrino mixing and oscillation. The Hadron Absorber, consists of thick blocks of aluminum, iron and concrete, is placed at the end of decay volume as a dump for primary proton and secondary particles generated in NuMI. In order to estimate the shielding effect, the reaction rate measurements with activation detector were carried out on the back surface of the absorber. The induced activities in the detectors were measured by analyzing their  -ray spectra using HPGe detectors. Two kind of peak was showed on two-dimensional distributions of obtained reaction rates at right angle to the beam direction. One was strong peaks at the both horizontal side. And, another smaller was at the top. It was concluded that these peaks were the results of particles streaming through the gaps in the Hadron Absorber shielding.
-ray spectra using HPGe detectors. Two kind of peak was showed on two-dimensional distributions of obtained reaction rates at right angle to the beam direction. One was strong peaks at the both horizontal side. And, another smaller was at the top. It was concluded that these peaks were the results of particles streaming through the gaps in the Hadron Absorber shielding.
 and 90
and 90 bombarded with 120-GeV protons
bombarded with 120-GeV protonsIwamoto, Yosuke; Sanami, Toshiya*; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H. S.*; Soha, A.*; Ramberg, E.*; Coleman, R.*; Jensen, D.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 3, p.65 - 68, 2012/10
Neutron energy spectra at 15 and 90
and 90 produced from carbon, aluminum, copper and tungsten targets bombarded with 120-GeV protons were measured at Fermilab Test Beam Facility (FTBF) for the validation of simulation codes. The target thicknesses were 60 cm for graphite, 50 cm for aluminum, 20, 40, and 60 cm for copper and 10 cm for tungsten, respectively. The neutron time-of-flight measurements were performed using an NE213 organic liquid scintillator at 5.2 m for 90
produced from carbon, aluminum, copper and tungsten targets bombarded with 120-GeV protons were measured at Fermilab Test Beam Facility (FTBF) for the validation of simulation codes. The target thicknesses were 60 cm for graphite, 50 cm for aluminum, 20, 40, and 60 cm for copper and 10 cm for tungsten, respectively. The neutron time-of-flight measurements were performed using an NE213 organic liquid scintillator at 5.2 m for 90 and 8.0 m for 15
and 8.0 m for 15 measuring from the center of the target to the surface of the detector. The raw signals (waveforms) obtained from photomultiplier tubes were recorded using the 10 bit digitizer (Agilent-acqiris DC282) with 0.5 ns sampling and 500 ns duration. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations with the PHITS, MARS and FLUKA codes were performed. It was found that these calculated results underestimate the experimental results in the whole energy range.
measuring from the center of the target to the surface of the detector. The raw signals (waveforms) obtained from photomultiplier tubes were recorded using the 10 bit digitizer (Agilent-acqiris DC282) with 0.5 ns sampling and 500 ns duration. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations with the PHITS, MARS and FLUKA codes were performed. It was found that these calculated results underestimate the experimental results in the whole energy range.
Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; et al.
Reactor Dosimetry; 14th International Symposium (ASTM STP 1550), p.675 - 689, 2012/08
Under the collaborative study project of JASMIN, shielding experiments has been carried out using the anti-proton target station (Pbar) of Fermilab. In the experiment, the multi-foil activation technique was utilized, and the neutron spectra in high-energy region between 1 and 100 MeV were deduced by using the "fitting method", which is newly developed. In this method, we made an assumption that neutron energy spectra could be expressed with a simple function. The validity of the fitting method was confirmed by comparison with the results of the unfolding method and the theoretical calculations. Finally, it was found that there are simple correlations between reaction rates and the adjusting parameters in the fitting function. The correlations are useful for estimating the adjusting parameters easily, and a neutron spectrum in the high-energy region can be deduced from a set of reaction-rate data without the complicated calculations of unfolding.
Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Boehnlein, D.*; Lautenschlager, G.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2051 - 2054, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The experiment was performed at the anti-proton (pbar) production target station in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. At the pbar target station, an anti-proton production target, consisted of Inconel and copper disks, were irradiated by 120 GeV proton beam. The beam intensity was 2.0  10
10 proton per second. Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were set around the target to investigate the spatial and energy distribution of secondary particles emitted from the target. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The reaction rates of 30 nuclides induced in Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were obtained. The reaction rates of these nuclides increase for samples placed on forward angle position. The angle dependence of these reaction rates becomes larger for increasing threshold energy. These experimental results compared with the calculation. The calculated results generally agree with the experimental results within a factor of 3.
proton per second. Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were set around the target to investigate the spatial and energy distribution of secondary particles emitted from the target. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The reaction rates of 30 nuclides induced in Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were obtained. The reaction rates of these nuclides increase for samples placed on forward angle position. The angle dependence of these reaction rates becomes larger for increasing threshold energy. These experimental results compared with the calculation. The calculated results generally agree with the experimental results within a factor of 3.
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Mokhov, N.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2059 - 2062, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In an antiproton production (Pbar) target station of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL), the secondary particles produced by bombarding a target with 120-GeV protons are shielded by a thick iron shield. In order to obtain experimental data on high-energy proton accelerator facilities, we indirectly measured  100-MeV neutrons at the outside of the iron shield. The measurement was performed by using the Au activation method coupled with a low-background
100-MeV neutrons at the outside of the iron shield. The measurement was performed by using the Au activation method coupled with a low-background  -ray counting system. As an indicator for the neutron flux, we determined the production rates of 8 spallation nuclides (
-ray counting system. As an indicator for the neutron flux, we determined the production rates of 8 spallation nuclides (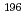 Au,
Au,  Pt,
Pt, 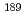 Ir,
Ir,  Os,
Os, 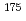 Hf,
Hf, 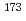 Lu,
Lu, 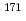 Lu, and
Lu, and 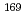 Yb) in the Au activation detector. The measured production rates were compared with the theoretical production rates calculated using PHITS. We proved that the Au activation method can serve as a powerful tool for indirect measurements of
Yb) in the Au activation detector. The measured production rates were compared with the theoretical production rates calculated using PHITS. We proved that the Au activation method can serve as a powerful tool for indirect measurements of  100-MeV neutrons that play a vital role in neutron transport.
100-MeV neutrons that play a vital role in neutron transport.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Mokhov, N.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2055 - 2058, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It is important to obtain neutron spectra and its intensity on shielding experiment. Deduction of high-energy neutron spectra were done using fitting and unfolding methods based on the shielding data obtained at the anti-proton (pbar) target station in Fermilab. The neutron spectra for fitting method is useful to be easily obtained and the values gave reasonable results compared with nuclear data. Therefore, that for unfolding methods included inconsistency. Furthermore, the deduced neutron spectra were verified through the calculation analyses by PHITS code.
Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H.-S.*; Leveling, A.*; Vaziri, K.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Mokhov, N.*; Sakamoto, Yukio; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.44 - 47, 2011/02
Muons become important particle for radiation safety design of high energy and intense accelerator since muons penetrate a thick shielding wall. In this study, the dose rate distributions around high intensity muon beam were measured at the muon alcoves and the bypass tunnel of Neutrinos at the Main Injector (NuMI) facility in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab). The dosimeters of Luxel budges (OSL, CR39) and TLD budges (UD813PQ) were placed in the second, third and forth alcoves to measure muons, photons, and, thermal and fast neutrons. Neutrons and photons were measured in the bypass tunnel using a Bonner sphere and an ionization chamber. The spatial distribution of muons is calculated using MARS code. The results of dosimeters show same spatial distribution including attenuation along the beam line in comparison with the calculation results.
Yashima, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.48 - 51, 2011/02
The shielding experiment was performed at the anti-proton production target station in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. Aluminum, Bismath, Niobium, Copper and Indium samples were placed behind the shields. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The spatial distribution of reaction rate of samples which were placed behind the iron and concrete shields were obtained. The measured data shows that the reaction rates on the outer surfaces of the iron and concrete shields increases toward the downstream of the target. The obtained reaction rates were also fitted to Moyer's formula, and the attenuation lengths for iron and concrete shields were obtained.
Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; Nakamura, Takashi*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.52 - 56, 2011/02
In pbar target station, the pulsed proton beam with the power of around 75 kW and the time structure of 1.6  s pulse width and 2.2 s cycle time bombards the pbar production target and produces high instantaneous intensity neutron (burst neutron) fields. The duration of the burst neutrons, which is less than
s pulse width and 2.2 s cycle time bombards the pbar production target and produces high instantaneous intensity neutron (burst neutron) fields. The duration of the burst neutrons, which is less than  s, is very severe condition to measure neutron spectra with a conventional Bonner sphere technique with pulse readout electronics because of signal pile-up problem. In this study, we have developed a current readout Bonner sphere technique to measure neutron spectra in a burst neutron field. We have measured the neutron spectra on the pbar target and graphite dump. The neutron spectra obtained with the present technique show generally good agreements with the calculation results using MARS code except difference of the thermal neutron flux due to the geometrical problem.
s, is very severe condition to measure neutron spectra with a conventional Bonner sphere technique with pulse readout electronics because of signal pile-up problem. In this study, we have developed a current readout Bonner sphere technique to measure neutron spectra in a burst neutron field. We have measured the neutron spectra on the pbar target and graphite dump. The neutron spectra obtained with the present technique show generally good agreements with the calculation results using MARS code except difference of the thermal neutron flux due to the geometrical problem.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.57 - 60, 2011/02
The anti-proton (pbar) production target in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory can be produced a wide variety of secondary particles including of anti-protons, by bombarding with protons accelerated to 120 GeV. The shielding experimental data, which was obtained around the pbar target, make possible to validate the accuracies of the general-purpose Monte Carlo simulation codes. In this paper, spatial distribution of reaction rates were calculated with two-dimensional (r-z) geometry simplified the real pbar target station using the PHITS, MARS and MCNPX code. These experimental data in iron shield were compared with the calculated data. The comparison for attenuation length of iron were good agreement between the experiments and calculations.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 168(2), p.482 - 486, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental studies of shielding and radiation effects have been started using 120-GeV proton synchrotron at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) under collaboration between FNAL and Japan. The first campaign of the experiment was carried out at the Pbar target station and Numi experimental station at FNAL, using antiproton and neutrino production targets irradiated by 120-GeV protons. The generated secondary particles passing through steel, concrete and rock were measured by activation methods as well as by other detectors such as scintillator with a veto counter, phoswich detector and a Bonner ball counter on trial. Preliminary experimental results are presented.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Sekimoto, Shun*; Oishi, Koji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Mokhov, N.*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; Sanami, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Several multi-purpose high-energy radiation transport codes are used in many research fields such as high-energy physics as well as accelerator facility shielding designs. The codes are benchmarked against experimental data on a regular basis. To promote this to a higher level and to a hardly explored field of neutron radiation induced by energetic muons, a JASMIN collaboration (Japanese-American Study of Muon Interaction and Neutron detection), has been created with several Laboratories and Universities of Japan and U.S.A. The collaboration has performed a series of experiments at the Pbar target station and NuMI facility at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, using irradiation of targets with 120 GeV protons for antiproton and neutrino production. This paper reviews recent activities and results.
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
A gold activation detector was studied as a high energy neutron detector at high radiation field in a series of shielding experiment at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. We could measure spallation residual nuclei with wide threshold energy by using a combination method with radiological chemical separation and X-X- coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Hirayama, Hideo*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; et al.
no journal, ,
On the shielding experiment, started on 2007, as collaborative research with Fermilab using high energy proton accelerators, the measurement of reaction rate distributions in the antiproton target station has been carried out. Reaction rates were measured with activation method. Using the reaction rate data, neutron spectra at each measurement position were deduced by means of nonlinear least square method; a shape of the neutron spectrum between 5 and 100 MeV was expressed as a fitting function with 5 fitting parameters, whose values were determined at a minimum of 
 values for the reaction rates. In the presentation, systematics of the variation of neutron spectra in the shield will be discussed.
values for the reaction rates. In the presentation, systematics of the variation of neutron spectra in the shield will be discussed.