Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
 -Ti alloy
-Ti alloyZhang, B.*; Xin, S.*; Huang, M.*; Mao, W.; Jia, W.*; Li, Q.*; Li, S.*; Zhang, S.*; Mao, C.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 890, p.145898_1 - 145898_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A significant increase in the recovery strain of a high-Zr  -Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the
-Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the  -grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
-grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:85.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.33(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.63(Engineering, Civil) isomers in
isomers in  Cf
CfOrlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Ito, Yuta; Suzaki, Fumi; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064301_1 - 064301_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear) isomer in
isomer in 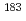 Hg and
Hg and  (
(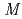 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Pb
PbZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; Li, Z. H.*; Li, J. G.*; Guo, C. Y.*; 34 of others*
Physics Letters B, 829, p.137129_1 - 137129_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:65.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Zhang, W. Q.*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Fang, C. H.*; Yoshida, Koji*; Zhou, Y. Q.*; Zhu, F. Y.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Li, W.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 348, p.118080_1 - 118080_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.49(Chemistry, Physical)The ion hydration and association and hydrogen-bonded water structure in an aqueous 3 mol/kg RbCl solution were investigated at 298 K/0.1 MPa, 298 K/1 GPa, 523 K/1 GPa, and 523 K/4 GPa by neutron diffraction combined with EPSR methods. The second hydration layer of Rb and Cl
and Cl becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb
becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb (Cl
(Cl ) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb
) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl
and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb
does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb -Cl
-Cl decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
Kong, L.*; Gong, J.*; Hu, Q.*; Capitani, F.*; Celeste, A.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Li, N.*; Yang, W.*; Liu, G.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 31(9), p.2009131_1 - 2009131_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:82.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The soft nature of organic-inorganic halide perovskites renders their lattice particularly tunable to external stimuli such as pressure, undoubtedly offering an effective way to modify their structure for extraordinary optoelectronic properties. However, these soft materials meanwhile feature a general characteristic that even a very mild pressure will lead to detrimental lattice distortion and weaken the critical light-matter interaction, thereby triggering the performance degradation. Here, using the methylammonium lead iodide as a representative exploratory platform, we observed the pressure-driven lattice disorder can be significantly suppressed via hydrogen isotope effect, which is crucial for better optical and mechanical properties previously unattainable.
Wang, Y.*; Jia, G.*; Cui, X.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Q.*; Gu, L.*; Zheng, L.*; Li, L. H.*; Wu, Q.*; Singh, D. J.*; et al.
Chem, 7(2), p.436 - 449, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:297 Percentile:99.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,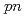 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 decay of
decay of 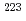 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.82(Astronomy & Astrophysics)