Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Kawata, Manabu; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2024-001, 206 Pages, 2024/03
In the assessment of seismic safety and the design of building structures in nuclear facilities, lumped mass models have been used as standard methods. Recent advances in computer capabilities allow the use of three-dimensional finite element (3D FE) models to account for the 3D behavior of buildings, material nonlinearity, and the nonlinear soil-structure interaction effect. While 3D analysis method has many advantages, it is necessary to ensure its reliability as a new approach. The International Atomic Energy Agency performed an international benchmark study using the 3D FE analysis model for reactor building of Unit 7 at TEPCO's Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station based on recordings from the Niigataken Chuetsu-oki Earthquake in 2007. Multiple organizations from different countries participated in this study and the variation in their analytical results was significant, indicating an urgent need to improve the reliability of the analytical results by standardization of the analytical methods using 3D FE models. Additionally, it has been pointed out that it is necessary to understand the 3D behavior in the seismic fragility assessment of buildings and equipment, using realistic seismic response analysis method based on 3D FE models. In view of these considerations, a guideline for the seismic response analysis method using a 3D FE model was developed by incorporating the latest knowledge and findings in this area. The purpose of the guideline is to improve the reliability of the seismic response analysis method using 3D FE model of reactor buildings. The guideline consists of a main body, commentaries, and appendixes. The standard procedures, recommendations, key points to note, and technological bases for conducting seismic response analysis on reactor buildings using 3D FE models are provided in the guideline. In addition, the guideline will be revised reflecting the latest knowledge.
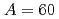
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Kawata, Manabu; Li, Y.; Ota, Akira*; Sonobe, Hideaki*; Ino, Susumu*; Ugata, Takeshi*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.23-00026_1 - 23-00026_11, 2023/08
In the seismic evaluation of nuclear facility buildings, basemat uplift-the phenomenon during which the bottom of the basemat of a building partially rises from the ground owing to overturning moments during earthquakes-is a very important aspect because it affects not only structural strength and integrity, but also the response of equipment installed in the building. However, there are not enough analytical studies on the behavior of buildings with a low ground contact ratio due to basemat uplift during earthquakes. In this study, we conducted a simulation using a three-dimensional finite element model from past experiments on basemat uplift; further, we confirmed the validity of this approach. In order to confirm the difference in the analytical results depending on the analysis code, the simulation was performed under the same analytical conditions using the three analysis codes, which are E-FrontISTR, FINAS/STAR and TDAPIII, and the obtained analysis results were compared. Accordingly, we investigated the influence of the difference in adhesion on the structural response at low ground contact ratio. In addition, we confirmed the effects of significant analysis parameters on the structural response via sensitivity analysis. In this paper, we report the analytical results and insights obtained from these investigations.
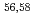 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 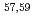 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 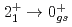 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 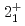 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 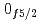 and
and 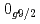 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S
SWang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Zhang, K.*; Zhang, Z. D.*; Li, B.*
Applied Physics Letters, 123(1), p.011903_1 - 011903_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.89(Physics, Applied) X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.7(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Kodeli, I. A.*; Fleming, M.*; Cabellos, O.*; Leal, L.*; Celik, Y.*; Ding, Y.*; Jansky, B.*; Neudecker, D.*; Novak, E.*; Simakov, S.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.15002_1 - 15002_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:92.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Working Party on International Nuclear Data Evaluation Co-operation Subgroup 47 (WPEC SG47) entitled "Use of Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database for Nuclear Data Validation" was started in June 2019 with the objectives to promote more systematic and wider use of shielding benchmark experiments in nuclear data and transport code validation and development, to provide feedback on the Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database (SINBAD). Complementing the database with new features was discussed, for example providing the nuclear data sensitivity profiles more systematically would facilitate and better guide the use of data, and the information on the geometry, (radiation source) and materials is expected to allow an easier and less error prone computational model preparation for different transport codes. Examples of the use and some views on future development of the SINBAD benchmark database will be presented in the paper.
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Nishida, Akemi; Kawata, Manabu; Choi, B.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2023 International Congress on Advanced in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/04
Our research and development are aimed at improving the accuracy of the three-dimensional seismic evaluation analysis method for nuclear buildings, which contributes to the probabilistic risk assessment caused by earthquakes (seismic PRA), using actual seismic observation records in collaboration with the Nuclear Regulation Authority since 2019. In this study, we constructed a large-scale observation system that enabled simultaneous measurements at multiple positions during earthquakes or against artificial waves. The accelerometers of the observation system were installed on/in the soil, floors, and on the walls of the nuclear building. This paper presents an outline of the large-scale observation system and the findings obtained from the analysis of the seismic observation records acquired using the system.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.; Takada, Tsuyoshi
Earthquake Engineering and Resilience (Internet), 1(4), p.427 - 439, 2022/12
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Kunio; Strnadel, B.*; Li, Y.; Lacroix, V.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(6), p.061202_1 - 061202_6, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.34(Engineering, Mechanical)When pipe walls are thin, part-through flaws are easily develop into through-wall flaws, and the likelihood of coolant leakage is high. The ASEM Code Section XI provides final allowable flaw angles of through-wall flaw for thin-wall pipes. The final allowable angles are applied to pipes in order to maintain structural integrity if the part-through flaws become through-wall flaws. To ensure that this stability is compromised, plastic collapse stresses for through-wall flaws are combined with allowable stresses. However, the final allowable angles of through-wall flaws are not identified for thin-walled pipes. This paper compares plastic collapse stresses of through-wall flaws and allowable stresses of part-through flaws for pipes. The comparison of these stresses is used to derive the final allowable angles of through-wall flaws. The angles can be expressed either in the form of exact solutions or as conventional options that are appropriate for various service level conditions.
 isomers in
isomers in  Cf
CfOrlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Ito, Yuta; Suzaki, Fumi; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064301_1 - 064301_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:33.4(Physics, Nuclear)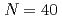 island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in
island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in  V and
V and  V
VElekes, Z.*; Juh sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064321_1 - 064321_10, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying level structure of  V and
V and  V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for
V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for  V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for
V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for  V. Four and five new transitions were determined for
V. Four and five new transitions were determined for  V and
V and  V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed
V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed  rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2
rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2 and 9/2
and 9/2 levels. The (
levels. The ( ,
,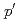 ) excitation cross sections for
) excitation cross sections for  V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,
V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,  V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
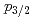 neutron orbital and the
neutron orbital and the 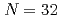 shell closure in
shell closure in  Ca
CaEnciu, M.*; Liu, H. N.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Poves, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 129(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:46.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The one-neutron knockout from  Ca was performed at
Ca was performed at  230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt
230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt  spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of
spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of 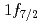 and
and 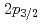 neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number
neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number 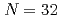 , found as strong as at
, found as strong as at 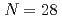 and
and 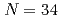 in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron
in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron 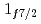 and
and 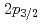 orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the
orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the 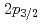 orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
Hasegawa, Kunio; Li, Y.; Strnadel, B.*; Udyawar, A.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(5), p.051305_1 - 051305_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.34(Engineering, Mechanical)Fully plastic collapse stresses for circumferentially part-through cracked pipes subjected to bending stresses are estimated by Limit Load Criteria provided by the ASME Code Section XI. Allowable crack depths were determined by using the Limit Load Criteria and that are tabulated in the ASME Code Section XI for different plant service level conditions. On the other hand, crack penetration bending stresses for part-through cracked pipes were estimated by using the Local Approach of Limit Load Criteria. By using these Criteria, the study presented in this paper obtained allowable crack depths at penetration for circumferentially part-through cracked pipes. Comparing the allowable crack depths obtained by both methods for each service level, it is evident that the allowable crack depths at penetration calculated by the Local Approach of Limit Load Criteria are almost always smaller than those at fully plastic collapse stresses calculated by the Limit Load Criteria. It was found that the allowable crack depths provided by the ASME Code Section XI are less conservative for crack penetrations.
 isomer in
isomer in 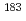 Hg and
Hg and  (
(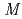 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Kawata, Manabu; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2022/08
In the seismic evaluation of nuclear facility buildings, basemat uplift-the phenomenon during which the bottom of the basemat of a building partially rises from the ground owing to overturning moments during earthquakes-is a very important aspect because it affects not only structural strength and integrity, but also the response of equipment installed in the building. However, there are not enough analytical studies on the behavior of buildings with a low ground contact ratio due to basemat uplift during earthquakes. In this study, we conducted a simulation using a three-dimensional finite element model from past experiments on basemat uplift; further, we confirmed the validity of this approach. In order to confirm the difference in the analytical results depending on the analysis code, the simulation was performed under the same analytical conditions using the three analysis codes, which are E-FrontISTR, FINAS/STAR and TDAPIII, and the obtained analysis results were compared. Accordingly, we investigated the influence of the difference in adhesion on the structural response at low ground contact ratio. In addition, we confirmed the effects of significant analysis parameters on the structural response via sensitivity analysis. In this paper, we report the analytical results and insights obtained from these investigations.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Kawata, Manabu; Li, Y.
Transactions of 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/07
In order to improve the seismic probabilistic risk assessment method, the authors are developing methods related to realistic response, realistic resistance and fragility assessment for buildings and equipment that are important for seismic safety. In this study, in order to identify of building damage mode subjected to large seismic motions, pushover analyses using multiple analysis codes were performed using a 3D FE model of a reactor building. We obtained the analysis results for the identification of local damage mode that contributes to the fragility assessment. In this paper, we report the progress of local damage mode and ultimate strength of the building by the pushover analysis. We also compared this result with the seismic response analysis results.