Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; Esaki, Nanse; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Onizawa, Kunio; Kasahara, Naoto*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Li, Y.
Nuclear structural engineering; An Advanced Course in Nuclear Engineering, Vol.6, 595 Pages, 2025/05
no abstracts in English
Niu, X.*; Elakneswaran, Y.*; Li, A.*; Seralathan, S.*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Walkley, B.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 190, p.107814_1 - 107814_17, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized a crystalline graphane nanoribbon (GANR) via pressure-induced polymerization of 2,2'-bipyrazine (BPZ). By performing Rietveld refinement of in situ neutron diffraction data, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectra, and theoretical calculation, we found that BPZ experienced Diels-Alder polymerization between the 

 stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (
stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (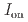 /
/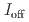 =18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
=18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional van der Waals ferromagnet Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
(FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez Espinoza, V.*; Stakhanova, A.*; Groudev, P.*; Petrova, P.*; Vryashkova, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.110962_1 - 110962_16, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:94.85(Nuclear Science & Technology) neutron imaging and diffraction analysis revealing spatial lithiation phase evolution in an ultra-thick graphite electrode
neutron imaging and diffraction analysis revealing spatial lithiation phase evolution in an ultra-thick graphite electrodeStrobl, M.*; Baur, M. E.*; Samothrakitis, S.*; Molamud, F.*; Zhang, X.*; Tung, P. K. M.*; Schmidt, S.*; Woracek, R.*; Lee, J.*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; et al.
Advanced Energy Materials, p.2405238_1 - 2405238_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:75.15(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatic molecules has emerged as an effective method for synthesizing various carbon-based materials. In this work, PIP of 1,4-difluorobenzene (1,4-DFB) was investigated.  high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H
high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H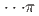 interaction along the [01
interaction along the [01 ] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H
] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H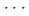 F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01
F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01 ] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Takito, Kiyotaka; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 146(6), p.061301_1 - 061301_12, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Ito, Masaharu; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/11
Most studies conducted till now on local damage of reinforced concrete (RC) slab structures subjected to missile impact are about normal impact, while few research related to oblique impact can be found. The objective of this study is to carry out impact tests under different impact conditions including oblique impacts, to confirm the different impact behaviors of the RC slab structure, to develop an analysis method by investigating the test results and analytical conditions, and to validate the analysis method through comparison with the test results. This study focuses on the effect of the stiffness of the supports for oblique impact on the reaction forces of RC slab. Until now, static loading tests were conducted to confirm the stiffnesses of the supporting parts that supported the RC specimen during oblique impact tests. Based on the obtained load-displacement relationships, and so on, the stiffnesses of the supporting parts are estimated.
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Su, Y. H.; Li, B.*
Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 60(8), p.1001 - 1016, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:36.18(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Takamizawa, Hisashi; Lu, K.*; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 210, p.105219_1 - 105219_7, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In the structural integrity assessment of an embrittled reactor pressure vessel (RPV) based on probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM), it is crucial to consider both of the mean value and the uncertainty of the embrittlement prediction. Typically, the embrittlement prediction uncertainty is given by a normal distribution, and its standard deviation is determined from the residuals of the measured and predicted values of all data used to develop the embrittlement prediction method. Therefore, the same uncertainty is assumed regardless of neutron fluence and the available data. To overcome this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency recently developed the embrittlement prediction method based on machine learning and Bayesian statistics, i.e., the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method, and introduced it to the PFM analysis code. The BNP method can predict the probability distribution according to data scarcity and provide more reasonable uncertainty because it estimates significant uncertainties where the scatter of actual measured data is large and the number of data is small. In this study, PFM analysis for a Japanese model RPV in a pressurized water reactor is conducted using the PFM analysis of structural components in aging light water reactors, where the embrittlement probability distribution calculated using the BNP method is used. Furthermore, the effects of different embrittlement prediction methods and uncertainties on the failure frequency of RPVs are investigated in the PFM analyses, and the results are presented.
Li, C.-Y.; Watanabe, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.935 - 957, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:70.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:94.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Li, S.; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07