Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
 synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation test
synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation testIm, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Lim, S.*; et al.
Construction and Building Materials, 365, p.130034_1 - 130034_18, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.68(Construction & Building Technology)Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:81.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
Kristo, M. J.*; Williams, R.*; Gaffney, A. M.*; Kayzar-Boggs, T. M.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Lagerkvist, P.*; Vesterlund, A.*; Rameb ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.425 - 434, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:79.90(Chemistry, Analytical)In a recent international exercise, 10 international nuclear forensics laboratories successfully performed radiochronometry on three low enriched uranium oxide samples, providing 12 analytical results using three different parent-daughter pairs serving as independent chronometers. The vast majority of the results were consistent with one another and consistent with the known processing history of the materials. In general, for these particular samples, mass spectrometry gave more accurate and more precise analytical results than decay counting measurements. In addition, the concordance of the  U-
U-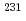 Pa and
Pa and  U-
U- Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Ho, D. M. L.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Okubo, Ayako; Rameb ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.353 - 363, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.04(Chemistry, Analytical)The Fourth Collaborative Material Exercise (CMX-4) of the Nuclear Forensics International Technical Working Group (ITWG) registered the largest participation for this exercise in nuclear forensics, with seven of the 17 laboratories participating for the first time. In this paper, participants from five of the first-time laboratories shared their individual experience in this exercise, from preparation to analysis of samples. The exercise proved to be highly useful for testing procedures, repurposing established methods, exercising skills, and improving the understanding of nuclear forensic signatures and their interpretation trough the post-exercise review meeting.
Haneklaus, N.*; Reyes, R.*; Lim, W. G.*; Tabora, E. U.*; Palattao, B. L.*; Petrache, C.*; Vargas, E. P.*; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sakaba, Nariaki; et al.
Philippine Journal of Science, 144(1), p.69 - 79, 2015/06
The Philippines may profit from extracting uranium (U) from phosphoric acid during fertilizer production in a way that the recovered U can be beneficiated and taken as raw material for nuclear reactor fuel. Used in a high temperature reactor (HTR) that provides electricity and/or process heat for fertilizer processing and U extraction, energy-neutral fertilizer production, an idea first proposed by Haneklaus et al., is possible. This paper presents a first case study of the concept regarding a representative phosphate fertilizer plant in the Philippines and exemplary HTR designs (HTR50S and GTHTR300C) developed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Three different arrangements (version I-III), ranging from basic electricity supply to overall power supply including on site hydrogen production for ammonia conversion, are introduced and discussed.
Hatanaka, Koichiro; Lim, D.-H.*; Ishii, Eiichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1265, 6 Pages, 2010/00
A three-dimensional DFN geo-descriptive model is developed for WCFs in the sedimentary formations of Horonobe URL in Japan. Fracturing and faulting system in/around the URL area, which is the main investigation area of the Horonobe URL project, is characterized by taking into account borehole geophysical logging data, regional geologic/structural data, and fracture/fault data (orientation, intensity, size) obtained from the surface-based investigations. Volumetric fracture intensity potential is estimated by the correlation and the multi-linear regression analysis of observed data, and is used as one of controls for 3-D DFN model. A regional scale 3-D geo-descriptive DFN model is constructed based on the analyzed fracturing system identified for the WCFs. The current 3-D geo-descriptive model could be utilized explicitly to derive PA parameters for the hypothetical repository of the high-level radioactive wastes in Japan, and to assist optimization of the safe repository design.
Ostermeyer, M.*; Kong, H.-J.*; Kovalev, V. I.*; Harrison, R. G.*; Fotiadi, A. A.*; M gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 26(3), p.297 - 362, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:55.03(Physics, Applied)Lim, D.-H.*; Uchida, Masahiro; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Sawada, Atsushi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1107, p.567 - 575, 2007/00
Lim, D. H.
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-010, 19 Pages, 2006/03
A two-dimensional numerical code, MCFT2D (Multiple-Canister Flow and Transport code in 2-Dimensional space), has been developed for groundwater flow and radionuclide transport analyses in a water-saturated high-level radioactive waste (HLW) repository with multiple canisters. A multiple-canister configuration and a heterogeneous flow field of the host rock are incorporated in the MCFT2D code. Effects of heterogeneous flow field of the host rock on migration of nuclides can be investigated using MCFT2D. The MCFT2D enables to take into account the various degrees of the dependency of canisters configuration for nuclide migration in a water-saturated HLW repository [1,2], while the dependency was assumed to be either independent [3-5] or perfectly dependent [6,7] in previous studies. This report presents features of the MCFT2D code, numerical simulation using MCFT2D code, and graphical representation of the numerical results.
Lim, D. H.
Water Resources Research, 42(2), p.W02601_1 - W02601_3, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:87.20(Environmental Sciences)An extended random-walk reflection scheme taking into account the local mass conservation error around the interface between different materials is developed for the molecular diffusion in composite porous media with different porosity as well as with different diffusivity. The local mass conservation error is a physically infeasible gathering of mass around the interface, and is caused by random-walk simulations without proper treatments for discontinuity in hydraulic and transport properties such as porosity and diffusivity. In the random-walk reflection scheme, in order to conserve the mass at the interface, once particles reach the interface for a unit time step, the further displacements of particles for remaining time step are determined based on transition-probabilities whether these particles can be reflected at the interface or entered into another region. In the current study, the transition-probabilities are derived from the analytical solutions for the diffusion in the composite media. An extended random-walk reflection scheme incorporating the transition-probabilities is developed and compared with the analytical solutions. A selected previous study, i.e. generalized SDE (Stochastic Differential Equations) scheme, is also compared with the analytical solutions especially for the media with different porosity. The current study shows that i) the newly developed extended random-walk reflection scheme has a good agreement with the analytical solutions for the composite media with different porosity as well as with different diffusivity, while the generalized SDE scheme has a good agreement for the composite media with the same porosity or with the porosity ratio less than 1, ii) a random-walk scheme without completely solving the local mass conservation error causes numerical error such as an overestimation of the maximum release rate of mass.
Lim, D. H.
Supplement Abst. H24A-01, 0 Pages, 2004/00
Discontinuities in hydraulic and transport properties, such as diffusivity and porosity, exist in transport models consisting of different materials. Random-walk simulations without proper treatments for such discontinuities cause local mass conservation errors, i.e. a physically infeasible gathering of mass around the interface between different materials. To resolve the local mass conservation problem, random-walk schemes (e.g. interpolation [1], reflection [2], generalized Stochastic Differential Equation (SDE) [3]) have been developed. However, application of these schemes into composite porous media especially with different medium porosity is in question because (1) the accuracy of the interpolation scheme suffers unless one refines the space discretization step and the time step simultaneously, (2) the medium porosity was not taken into account in the reflection scheme, and (3) the generalized SDE scheme was not fully justified with respect to the medium porosity. In the current study, the validity of the generalized SDE scheme [3] is investigated, especially in terms of the porosity. A random-walk reflection scheme is (1) developed by deriving transition-probabilities at the interface between two different homogeneous porous media, and (2) verified with an analytical solution. Transition-probabilities at the interface between two different homogeneous media with respect to region 1 and region 2 are obtained in the current study, respectively, where region 1 represents the region containing the source. Preliminary numerical results demonstrate that the reflection scheme by using above P1 and P2 shows good agreement with the analytical solution, while the agreement between numerical results generated by the generalized SDE scheme [3] and the analytical solution becomes worse as the porosity ratio between two media increases.
Oba, Hironori; Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Saeki, Morihisa; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Lim, D.-H.*; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Ishii, Eiichi*
no journal, ,
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,