Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lin, Z. M.*; Liu, B. X.*; Ming, K. S.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F. X.*; Zheng, S. J.*
Scripta Materialia, 263, p.116692_1 - 116692_7, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Cho, S. H.*; Cho, S. W.*; Lv, Z.*; Sekine, Yurina; Liu, S.*; Zhou, M.*; Nuxoll, R. F.*; Kanatzidis, E. E.*; Ghaffari, R.*; Kim, D.*; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 9 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biochemical Research Methods)Amino acids are essential for protein synthesis and metabolic processes in support of homeostatic balance and healthy body functions. This study quantitatively investigates eccrine sweat as a significant channel for loss of amino acids during exercise, to improve an understanding of amino acid turnover and to provide feedback to users on the need for supplement intake. The measurement platform consists of a soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic system for real-time analysis of amino acid content in eccrine sweat. This system relies on integrated fluorometric assays and smartphone-based imaging techniques for quantitative analysis.
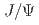 system
systemPan, Y.-W.*; Liu, Z.-W.*; Geng, L.-S.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Liu, X.*
Physical Review D, 110(9), p.094004_1 - 094004_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:88.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:97.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:97.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.81(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:83.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; Fukatsu, Yuta
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:66.70(Energy & Fuels) Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(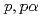 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:93.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The cluster structure of the neutron-rich isotope  Be has been probed via the (
Be has been probed via the (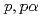 ) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the
pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the  Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
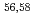 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:85.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 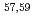 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 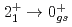 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 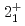 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 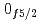 and
and 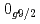 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 ; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activity
; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activityFang, Y.*; Kong, L.*; Wang, R.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Bu, K.*; Liu, X.*; Yan, S.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Materials Today Physics (Internet), 34, p.101083_1 - 101083_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:74.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered van der Waals halides are particularly sensitive to external pressure, suggesting a feasible route to pinpoint their structure with extraordinary behavior. However, a very sensitive pressure response usually lead to a detrimental phase transition and/or lattice distortion, making the approach of materials manipulation in a continuous manner remain challenging. Here, the extremely weak interlayer coupling and high tunability of layered RhI crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Chenaud, M.-S.*; Tsige-Tamirat, H.*; Sumner, T.*; Lee, J.*; Liu, S.*; Peregudova, O.*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The Generation IV (GEN-IV) international forum is a framework for international co-operation in research and development for the next generation of nuclear energy systems. Within the GEN-IV sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) system arrangement, the SFR Safety and Operation (SO) project addresses the areas of safety technology and reactor operation technology developments. The aims of the SO project include (1) analyses and experiments that support establishment of the safety approaches and validate the performance of specific safety features, (2) development and verification of computational tools and validation of models employed in safety assessment and facility licensing, and (3) acquisition of reactor operation technology, as determined largely from experience and testing in operating SFR plants. The tasks in the SO topics are categorized into the following three work packages (WP): WP-SO-1 "Methods, Models and Codes" is devoted to the development of tools for the evaluation of safety. WP-SO-2 "Experimental Programs and Operational Experience" includes the operation, maintenance and testing experiences in experimental facilities and SFRs, and WP-SO-3 "Studies of Innovative Design and Safety Systems" relates to safety technologies for GEN-IV reactors such as active and passive safety systems and other specific design features. This paper reports recent activities within the SO project.
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.90(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:88.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:83.88(Mechanics)Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; Yu, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:64.95(Physics, Applied)Liu, S.*; Yang, D. S.*; Wang, S.*; Luan, H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Model, J. B.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Ghaffari, R.*; Rogers, J. A.*
EcoMat (Internet), 5(1), p.e12270_1 - e12270_18, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:92.75(Chemistry, Physical)Advanced capabilities in noninvasive, in situ monitoring of sweat serve as the basis for obtaining real-time insights into human physiological state, health, and performance. Although recently reported microfluidic systems support powerful functions, most are designed as single-use disposables. Here, we introduce materials and molding techniques that bypass these concerns through biodegradable microfluidic systems with a full range of features. The key components fully degrade through the enzymatic action of microorganisms in natural soil environments. Detailed characterization of the device reveal a set of essential performance parameters that are comparable to, or even better than, those of non-degradable counterparts. Human subject studies illustrate the ability of these devices to acquire accurate measurements of sweat loss, sweat rate, pH, and chloride concentration.