Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Narita, Hirokazu*; Nicolson, R. M.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ito, Fumiyuki*; Morisaku, Kazuko*; Goto, Midori*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Heller, W. T.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:75.49(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Makino, Risa; Nakamura, Hironobu
LA-UR-17-23474, 28 Pages, 2017/04
The Inventory Verification Sample system (INVS) has been used for IAEA verification measurement at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility for MOX powder and Pu solution samples (measurement uncertainty: about 3-5%). If the measurement uncertainty can be improved (to  1%), it is expected that the range of usage can be extended and it could reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, we conducted three different types of calibration method that are passive calibration curve method, known-
1%), it is expected that the range of usage can be extended and it could reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, we conducted three different types of calibration method that are passive calibration curve method, known- method and multiplicity method after optimization of detector parameter and sample position. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, a good correlation was found between measured doubles and
method and multiplicity method after optimization of detector parameter and sample position. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, a good correlation was found between measured doubles and  Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the result of the conventional calibration curve method and known-
Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the result of the conventional calibration curve method and known- method met our target uncertainty within 1% (22 hours measurement). Since it is thought that background singles change may affect measurement uncertainty, an additional shielding was installed around the INVS to reduce those effects. This shielding improved measurement uncertainty in known-
method met our target uncertainty within 1% (22 hours measurement). Since it is thought that background singles change may affect measurement uncertainty, an additional shielding was installed around the INVS to reduce those effects. This shielding improved measurement uncertainty in known- method. The results with this shielding suggests passive calibration method and known-
method. The results with this shielding suggests passive calibration method and known- method could achieve the target uncertainty within 1% less than 1 hour measurement time.
method could achieve the target uncertainty within 1% less than 1 hour measurement time.
LaFleur, A. M.*; Nakamura, Hironobu; Menlove, H. O.*; Mukai, Yasunobu; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Kurita, Tsutomu
Proceedings of 37th ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.435 - 441, 2015/08
The IBAS (Improved Holdup Blender Assay System) system for safeguards and nuclear material accountancy (NMA) of holdup measurements is used at PCDF. The purpose of this detector is to measure the doubles rate from each glovebox in order to determine the mass of Pu holdup. In order to establish calibration curves for the IBAS detector and improve the holdup measurement methodology, JAEA conducted the IBAS calibration exercise with LANL support using MOX standards in 2010. In 2011, a cleanout exercise was performed and the results showed that the holdup removed from the glovebox had a significantly higher alpha term (alpha = 15.8 - 31.5) than the MOX standards (alpha = 0.67) used to establish the 2010 calibration curves. To further investigate these findings, JAEA conducted slope validation measurements in 2013 to confirm the validity of IBAS calibration slopes for the case of high alpha holdup. This paper describes the IBAS slope validation tests, analysis of the experimental results, and the evaluation of the need for a correction factor for the high alpha holdup. Quantifying the alpha term of the holdup in each glove box and understanding how this value changes over time is important to improving the overall NMA at PCDF. The results from this work will provide invaluable experimental data that directly supports safeguards and NMA measurements of plutonium holdup in gloveboxes.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Rael, C. D.*; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
The Advanced Fuel Assembly Assay System (AFAS) is an unattended non-destructive assay (NDA) system by neutron measurement to verify the plutonium amount in an LWR plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel assembly. The assembly will be fabricated in the MOX fuel fabrication plant under construction by the Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited. The AFAS has been developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory under the auspices of the Secretariat of Nuclear Regulation Authority in Japan. The AFAS is the first NDA system which will verify the active length of the assembly without inspector attendance. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted the performance test for the AFAS under the contract with Nuclear Material Control Center to demonstrate this active length verification technology by using MOX fuel assemblies owned by JAEA. As the results, it was confirmed that measurement error of the active length for the MOX fuel assembly was less than 0.1% and it was satisfied with requirement by IAEA. This paper provides the performance test results for the active length verification of the AFAS.
 B+
B+ He integrated continuous monitor (BHCM) to holdup monitoring in glove boxes
He integrated continuous monitor (BHCM) to holdup monitoring in glove boxesMukai, Yasunobu; LaFleur, A. M.*; Nakamura, Hironobu; Menlove, H. O.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Kurita, Tsutomu
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2014/07
In order to improve the safeguards and nuclear material accountancy of holdup measurements and establish an alternative technology for  He shortage, we have designed the
He shortage, we have designed the  B +
B +  He Integrated Continuous Monitor (BHCM) and implemented the measurements to continuously monitor the holup in gloveboxes at Plutonium Conversion Developoment Facility. In this paper, we present the outline of BHCM, the comparison between MCNP simulations and the measured results in preliminaly test and a demonstration of process monitoring ability during operation to see the relation between Totals trend and operational status by using
He Integrated Continuous Monitor (BHCM) and implemented the measurements to continuously monitor the holup in gloveboxes at Plutonium Conversion Developoment Facility. In this paper, we present the outline of BHCM, the comparison between MCNP simulations and the measured results in preliminaly test and a demonstration of process monitoring ability during operation to see the relation between Totals trend and operational status by using  B detection tubes.
B detection tubes.
Makino, Risa; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Mukai, Yasunobu; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Nakamura, Hironobu
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2014/07
The Inventory Verification Sample systems (INVS) is a non-destructive assay (NDA) system for small inventory samples to quantify the Pu amount in Pu and U-Pu nitrate solutions and MOX powder with 31.3% counting efficiency (for Cf). It has been used for IAEA safeguards measurement for many years at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility (PCDF) for the samples taken at the time of Random Interim Inspection (RII) and Physical Inventory Verification (PIV), and is currently used as partial defects verification equipment with uncertainty about 3 5% accuracy for solution samples. The INVS is a inline detector therefore it is very convenient to use since it can be used for a sample inside the glove box without bag-out. If the measurement uncertainty can be improved (to
5% accuracy for solution samples. The INVS is a inline detector therefore it is very convenient to use since it can be used for a sample inside the glove box without bag-out. If the measurement uncertainty can be improved (to  1%), it is expected that the usage can be extended to the operator's own measurements in MC&A to reduce effort and the number of destructive analyses (DA). In order to improve the measurement uncertainty, we have performed multiplicity measurements using a variety of solution samples (concentration, acidity and volume) to determine the Pu amount and uncertainty, although the multiplicity analysis is challenging. To control the measurement quality, a few MOX ceramic fuel pellets with known Pu amount are used. The results are evaluated by three kinds of methods (calibration curve, known-
1%), it is expected that the usage can be extended to the operator's own measurements in MC&A to reduce effort and the number of destructive analyses (DA). In order to improve the measurement uncertainty, we have performed multiplicity measurements using a variety of solution samples (concentration, acidity and volume) to determine the Pu amount and uncertainty, although the multiplicity analysis is challenging. To control the measurement quality, a few MOX ceramic fuel pellets with known Pu amount are used. The results are evaluated by three kinds of methods (calibration curve, known- and multiplicity) to determine the best measurement method. In the range of concentration of typical samples, we could confirm good correlations between measured doubles and
and multiplicity) to determine the best measurement method. In the range of concentration of typical samples, we could confirm good correlations between measured doubles and  Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the conventional calibration curve method showed a good performance with short measurement time and small uncertainty when the calibration standards were a good match to the unknown samples. In this paper, we present the INVS system design and measurement results with uncertainty using solution samples and comparison results among the three calibration methods.
Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the conventional calibration curve method showed a good performance with short measurement time and small uncertainty when the calibration standards were a good match to the unknown samples. In this paper, we present the INVS system design and measurement results with uncertainty using solution samples and comparison results among the three calibration methods.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamura, Hironobu; Fujisaku, Sakae; Kurita, Tsutomu; LaFleur, A. M.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
In case of the Pu mass determination in scattered powder in a GB using Continuous Neutron Monitor (CNM) with totals, self-multiplication of neutron (M) and  value are properly required to be set. M can be easily estimated by a simulation code, but it is very difficult to estimate
value are properly required to be set. M can be easily estimated by a simulation code, but it is very difficult to estimate  value by such a simulation because interactions between
value by such a simulation because interactions between  ray generated from Pu and impurities are not consistent. Therefore, we tried to examine an estimation technique of
ray generated from Pu and impurities are not consistent. Therefore, we tried to examine an estimation technique of  value by direct measurement. As a result, by measuring the samples taken from the scattered powder using a multiplicity counter with a dual ring structure of He-3 tubes, we could confirm a good correlation between ring ratio (inner / outer ring count rates) and the
value by direct measurement. As a result, by measuring the samples taken from the scattered powder using a multiplicity counter with a dual ring structure of He-3 tubes, we could confirm a good correlation between ring ratio (inner / outer ring count rates) and the  values. Thus, we can estimate
values. Thus, we can estimate  value in the powder directly by the ring ratio measurement. By applying this technique to CNM and designing a new detector with a double layer structure of neutron detection tubes, we had a prospect that CNM would be able to measure the Pu mass continuously.
value in the powder directly by the ring ratio measurement. By applying this technique to CNM and designing a new detector with a double layer structure of neutron detection tubes, we had a prospect that CNM would be able to measure the Pu mass continuously.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Asano, Takashi; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; Kumakura, Shinichi*; Watanabe, Takehito*; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
The Advanced Verification for Inventory Sample System (AVIS) is a nondestructive assay (NDA) system in order to verify the plutonium mass in the small MOX samples at Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL) MOX fuel fabrication plant (J-MOX) under construction. The AVIS is required the high measurement performance because the AVIS will be used as a verification tool to substitute destructive analysis for a part of the samples which needs the bias defect verification. Therefore, the AVIS will fulfill an important role in the safeguards approach for J-MOX. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducted the performance test of the AVIS under the contract with NMCC. As the results of these tests, we confirmed that the AVIS could almost satisfy the required performance by IAEA.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Asano, Takashi; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Rael, C. D.*; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; Kumakura, Shinichi*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/07
The advanced verification inventory system (AVIS) is a nondestructive assay (NDA) system developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) to measure small samples of bulk plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) powder and pellets at the Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL) mixed oxide fuel fabrication plant (J-MOX). In order to mitigate the workload on the Rokkasho On-Site Laboratory (OSL), it is intended that the AVIS measurement will be substituted for a part of the Destructive Assay (DA) for J-MOX. Based on the commission from Office for Nuclear Non-Proliferation and Safeguards (JSGO) of Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and Nuclear Material Control Center (NMCC), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted the performance test of the AVIS in order to confirm the system performance before installation at the J-MOX site. The performance test consists of two phases. In the phase 1 test, detector parameters such as detector efficiency and die-away time were evaluated by using a californium-252 neutron source. These results agreed well with design value and were reported at the 53rd INMM annual meeting. JAEA conducted the phase 2 test by using MOX materials in order to evaluate the total measurement uncertainty (TMU). In the test, influence of sample density, plutonium concentration and organic additives in samples were also evaluated. Consequently, it is expected that AVIS can achieve the target TMU of 0.5% required in user requirement of IAEA by optimizing measurement condition and by using well-characterized standards. This paper provides a summary of the results of comprehensive performance test of AVIS.
Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A. M.*; Mukai, Yasunobu; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Kurita, Tsutomu
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
To improve safeguards and material accountancy of holdup measurements, a continuous neutron monitor (CNM) that continuously monitors the singles rate from holdup in glove boxes was designed and implemented at PCDF. In totals neutron counting, it is impossible to get Pu mass directly from the singles count rate without predetermination of alpha value and multiplication (M). In case of holdup deposits, since M can be seen as 1, the determination of the alpha value by direct measurement of the holdup is very important. In this research, we have developed a new approach called Direct Alpha Estimation technique. To establish the relation, the ring ratio of the FCAS which has dual ring He-3 tubes was applied. By using different alpha of samples, relation between alpha and ring ratio was studied. As a result, a good correlation between them was obtained. Thus, since the ring ratio can estimate alpha value, we would propose that this technique with dual ringed CNM be extended to not only Pu mass determination, but also to monitor the impurity contents or Pu isotopic composition change in holdup.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Nakajima, Shinji; Asano, Takashi; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Rael, C. D.*; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; Kumakura, Shinichi*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 53rd Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2012/07
The advanced verification for inventory sample system (AVIS) is a nondestructive assay (NDA) system designed to measure small samples of bulk plutonium uranium mixed oxide (MOX) powder and pellets at the proposed Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL) mixed oxide fuel fabrication plant (J-MOX). The system consists of a  He-based passive neutron well counter with an integrated high-purity germanium
He-based passive neutron well counter with an integrated high-purity germanium  system. The AVIS is intended to meet a performance specification of a total measurement uncertainty of less than 0.5% in the neutron (
system. The AVIS is intended to meet a performance specification of a total measurement uncertainty of less than 0.5% in the neutron ( Pu effective) measurement. It is intended that the AVIS measurement will be substituted for a fraction of the DA samples from J-MOX. JAEA has conducted performance testing on the AVIS in order to confirm the system performance before installation and to minimize the period of calibration at J-MOX site. In this paper, we provide a summary of the result of performance test phase 1 and the test plan of performance test phase 2 of the AVIS.
Pu effective) measurement. It is intended that the AVIS measurement will be substituted for a fraction of the DA samples from J-MOX. JAEA has conducted performance testing on the AVIS in order to confirm the system performance before installation and to minimize the period of calibration at J-MOX site. In this paper, we provide a summary of the result of performance test phase 1 and the test plan of performance test phase 2 of the AVIS.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 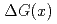 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.