Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor
superconductorHu, D.*; Yin, Z.*; Zhang, W.*; Ewings, R. A.*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Roessli, B.*; Wei, Y.*; Zhao, L.*; Chen, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(9), p.094504_1 - 094504_7, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:62.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The temperature and energy dependence of spin excitations in an optimally P-doped BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor (T
superconductor (T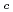 = 30 K) were studied by using inelastic neutron scattering. Experimental results are consistent with calculations from a combined density functional theory and dynamical mean field theory, and suggest that the decreased average pnictogen height in BaFe
= 30 K) were studied by using inelastic neutron scattering. Experimental results are consistent with calculations from a combined density functional theory and dynamical mean field theory, and suggest that the decreased average pnictogen height in BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) reduces the strength of electron correlations and increases the effective bandwidth of magnetic excitation.
reduces the strength of electron correlations and increases the effective bandwidth of magnetic excitation.
Hu, P.*; Yin, Y.-G.; Ishikawa, Satoru*; Suzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Fujimaki, Shu; Igura, Masato*; Yuan, C.*; Huang, J.*; Li, Z.*; et al.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(9), p.6306 - 6316, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:80.00(Environmental Sciences)Shu, Wataru; Luo, G.; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1463 - 1467, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:96.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The mechanisms of retention and blistering in the near-surface region of tungsten exposed to high glux deuterium plasmas of tens of eV were studied with a variety of techniques, such as XRD, TEM, SEM, TDS, NRA and ERDA. The results of small angle XRD at a fixed incident angle of 1.5 indicated that within the experimental error there was a zero change in the lattice parameter after the plasma exposure. This implies that deuterium does not exist in the lattice interstitial sites, but instead forms a deuterium-vacancy complex and then clusters and further bubbles (deuterium molecules in vacancy clusters and voids) in near-surface region. Cross-sectional TEM observations showed that small blisters with a diameter of around 30 nm and nano-cracks formed in the near-surface region before the formation of larger blisters with diameters of up to a few microns (comparable to grain size). The TDS results strongly indicated that deuterium existed in the molecular form in tungsten after the plasma exposure. The NRA and ERDA results suggest that the maximum atomic ratio of deuterium against tungsten reached as high as 1-2% in the near-surface region. These evidences suggest that crystal defects like vacancies should be generated due to lowering of the formation energy of vacancies by the intrusion of a great number of hydrogen isotope atoms into the near-surface region of tungsten.
indicated that within the experimental error there was a zero change in the lattice parameter after the plasma exposure. This implies that deuterium does not exist in the lattice interstitial sites, but instead forms a deuterium-vacancy complex and then clusters and further bubbles (deuterium molecules in vacancy clusters and voids) in near-surface region. Cross-sectional TEM observations showed that small blisters with a diameter of around 30 nm and nano-cracks formed in the near-surface region before the formation of larger blisters with diameters of up to a few microns (comparable to grain size). The TDS results strongly indicated that deuterium existed in the molecular form in tungsten after the plasma exposure. The NRA and ERDA results suggest that the maximum atomic ratio of deuterium against tungsten reached as high as 1-2% in the near-surface region. These evidences suggest that crystal defects like vacancies should be generated due to lowering of the formation energy of vacancies by the intrusion of a great number of hydrogen isotope atoms into the near-surface region of tungsten.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.957 - 962, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:96.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of blistering on deuterium retention in W was investigated using the newly established plasma generator with controllable incident energies ranging from 100 eV down to around 10 eV and incident flux of 1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5
/s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5  C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850
C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850  C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 347(1-2), p.111 - 117, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:98.10(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Polycrystalline tungsten samples have been irradiated at room temperature by high flux (1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7
/s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7  98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering
98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering 
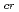 was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies
was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies  20 eV/D,
20 eV/D, 
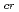 increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of
increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of 
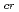 may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2
may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2 m.
m.
Ohira, Shigeru; Luo, G.; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Shu, Wataru; Kitamura, Kazunori*; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.621 - 624, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new conceptual design of a tritium permeation test module assembly was developed for demonstration tests using a strong plasma source constructed in TPL for simulation of practical tritium permeation in the real plasma facing components and validation of the models and codes for evaluation of tritium permeation. The target module, to be irradiated by the high flux plasma beam, consists of a multi-layer structure of a plasma facing material plate and a copper substrate with pressurized coolant cavity. Tests using a preliminary model of the target module has been performed to verify thermal and mechanical behavior of the bonded structure and to assess its structural integrity focused on the bonded interface under the cyclic heat loads. After the heat load testing, no visible defect and crack was observed around the bonded interfaces with magnifying glass, and its structural integrity was verified. Also the first tests using tritium plasma at TSTA/LANL with the preliminary model was performed and process to measured tritium permeated was established.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Ohira, Shigeru; Nishi, Masataka
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(11), p.4374 - 4378, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:85.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)The ion species ratios in low energy high flux deuterium plasma beams formed in a linear plasma generator were measured by a quadrupole mass spectrometer. And the species control in the plasma generator was evaluated by changing the operational parameters like neutral pressure, arc current, and axial magnetic confinement to the plasma column. The measurements reveal that the lower pressures prefer to form more D ions, and the medium magnetic confinement at the higher pressures results in production of more D
ions, and the medium magnetic confinement at the higher pressures results in production of more D
 , while the stronger confinement and /or larger arc current are helpful to D
, while the stronger confinement and /or larger arc current are helpful to D
 conversion into D
conversion into D
 . Therefore, the ion species can be controlled by adjusting the operational parameters of the plasma generator. With suitable adjustment, we can easily achieve plasma beams highly enriched with a single species of D
. Therefore, the ion species can be controlled by adjusting the operational parameters of the plasma generator. With suitable adjustment, we can easily achieve plasma beams highly enriched with a single species of D , D
, D
 , or D
, or D
 , to a ratio over 80%. It has been found that the axial magnetic configuration played a significant role in the formation of D
, to a ratio over 80%. It has been found that the axial magnetic configuration played a significant role in the formation of D
 within the experimental pressure range.
within the experimental pressure range.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Ohira, Shigeru; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2004-031, 27 Pages, 2004/03
A plasma source has been constructed for investigating plasma-surface interactions in a tokamak. It is a compact device with a total length less than 1 m, compared to other existing facilities in the world. However, it can provide with stable plasma beams of low energy ( 100 eV) and high flux (
100 eV) and high flux ( 10
10 /m
/m /s), close to the predicted edge plasma conditions near the ITER divertor. This report presents mainly its configuration and its characteristics, including influence of filament, arc discharge, magnetic field, bias voltage parameters, and so on, on plasma beam being delivered towards the sample. Also shown are the results of preliminary experiments of blister formation on tungsten samples irradiated by a deuterium plasma beam generated with the source.
/s), close to the predicted edge plasma conditions near the ITER divertor. This report presents mainly its configuration and its characteristics, including influence of filament, arc discharge, magnetic field, bias voltage parameters, and so on, on plasma beam being delivered towards the sample. Also shown are the results of preliminary experiments of blister formation on tungsten samples irradiated by a deuterium plasma beam generated with the source.
Shu, Wataru; Kawakubo, Yukio*; Luo, G.; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(12), p.1019 - 1026, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recovery of tritium from co-deposited layers is a crucial issue for fusion machines that use carbon as plasma facing materials. In this study, the removal rate of the JT-60 and TFTR co-deposited layers by KrF laser was measured for varying laser energy density. The removal rate of 5.0  m/pulse was achieved for the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density of 11 J/cm
m/pulse was achieved for the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density of 11 J/cm for KrF excimer laser. Hydrogen (tritium) was released in the form of hydrogen molecules and readily recovered. The formation of cones due to local surface melting was observed at the KrF laser energy density of 0.8 J/cm
for KrF excimer laser. Hydrogen (tritium) was released in the form of hydrogen molecules and readily recovered. The formation of cones due to local surface melting was observed at the KrF laser energy density of 0.8 J/cm , whereas strong melting was determined to be the mechanism of the ablative removal of the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density greater than the ablation threshold.
, whereas strong melting was determined to be the mechanism of the ablative removal of the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density greater than the ablation threshold.
Luo, G.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Physica Scripta, T94, p.21 - 27, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.17(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yamawaki, Michio*; Luo, G.*; Shibuya, Kengo*; Yamaguchi, Kenji*; Hayashi, Kimio
Tokyo Daigaku Kogakubu Sogo Shikenjo Nempo, 59, p.105 - 110, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Yamawaki, Michio*; Suzuki, Atsushi*; Yokota, Toshihiko*; Luo, G.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji*; Hayashi, Kimio
Proceedings of 1st Information Exchange Meeting on Basic Studies on High-Temperature Engineering, p.357 - 364, 1999/09
no abstracts in English