Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Shaimerdenov, A.*; Gizatulin, Sh.*; Sairanbayev, D.*; Bugybay, Zh.*; Silnyagin, P.*; Akhanov, A.*; Fuyushima, Takumi; Hirota, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 548, p.165235_1 - 165235_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)Compared to conditions in other types of installations, cable insulation in nuclear reactors is exposed to mixed conditions (high temperatures, radiation, pressure, humidity, aggressive environments) and at the same time they must maintain their performance characteristics for a long time (about 40-50 years). As a result of irradiation to such conditions, the electrical properties of the cable insulation are degraded, which leads to an increase in current loss. This is because the charge is induced by radiation into the insulator. At the WWR-K reactor, studies were started on the radiation resistance of signal cables with two types of mineral insulation (MgO and Al O
O ). As part of these studies, new experimental data will be obtained on the behavior of signal cables with mineral insulation of two types in mixed operating conditions (radiation field and high temperature). It is planned to accumulate fluence of fast neutrons
). As part of these studies, new experimental data will be obtained on the behavior of signal cables with mineral insulation of two types in mixed operating conditions (radiation field and high temperature). It is planned to accumulate fluence of fast neutrons  10
10 cm
cm in cables. The irradiation temperature will be (500
in cables. The irradiation temperature will be (500  50)
50) C). The study of the degradation of the electrical properties of the insulation of signal cables will be carried out in real time (in-situ). For this, a special design of the experimental device and a technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics were developed. This paper presents a sketch of the capsule design, the results of complex calculations for the development of the capsule design, the expected neutron fluences, the dpa in steel, the technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics, and a work plan for the future indicating the expected results. The cable irradiation time until the target neutron fluence is reached will be about 100 effective days. This research is funded by the International Scientific-Technical Center.
C). The study of the degradation of the electrical properties of the insulation of signal cables will be carried out in real time (in-situ). For this, a special design of the experimental device and a technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics were developed. This paper presents a sketch of the capsule design, the results of complex calculations for the development of the capsule design, the expected neutron fluences, the dpa in steel, the technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics, and a work plan for the future indicating the expected results. The cable irradiation time until the target neutron fluence is reached will be about 100 effective days. This research is funded by the International Scientific-Technical Center.
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Okita, Hidefumi; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Saha, P. K.; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072005_1 - 072005_7, 2024/01
Longitudinal phase space tomography is an effective measurement tool for acquiring the longitudinal phase space distribution. For the J-PARC synchrotrons, tomography, which can take into account the beam dynamics such as longitudinal space charge effect and nonlinearity, is desired, as the beam power increases. In this study, for the J-PARC synchrotron, the CERN's tomography, which employs the hybrid algorithm that can consider the beam dynamics for reconstruction, is introduced and benchmarked. The benchmark results show that the CERN's tomography has the ability to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution accurately, in the high-power beam operation at the J-PARC synchrotrons.
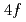 states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
Fujimori, Shinichi; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Sasabe, Norimasa*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Nakamura, Ai*; Maruya, A.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Electronic Structure (Internet), 5(4), p.045009_1 - 045009_7, 2023/11
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be  m.
m.
 Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from
Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from  -MoO
-MoO to water
to waterQuach, N. M.*; Ngo, M. C.*; Yang, Y.*; Nguyen, T. B.*; Nguyen, V. T.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Do, T. M. D.*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(10), p.4057 - 4064, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 (
Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 ( Mo). Production of
Mo). Production of  Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived
Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived  Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of
Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of  Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous
Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting
wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting  Mo. Porous
Mo. Porous  -MoO
-MoO wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of
wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of  Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous
Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of
wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of  Mo extraction in the porous
Mo extraction in the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was comparable to that of commercial
wire was comparable to that of commercial  -MoO
-MoO powder.
powder.
 -MoO
-MoO whiskers in
whiskers in  Mo/
Mo/ Tc radioisotope production and
Tc radioisotope production and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc extraction using hot atoms
Tc extraction using hot atomsNgo, M. C.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Do, T. M. D.*; Seki, Misaki; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Niihara, Koichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(32), p.13140 - 13147, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.
Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.  Tc is a daughter product of the
Tc is a daughter product of the  Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce
Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n,
Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n, ) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n,
) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n, ) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,
) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,  -MoO
-MoO whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and
whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and  -MoO
-MoO particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce
particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the
Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc. As a result,
Tc. As a result,  -MoO
-MoO whisker yielded higher
whisker yielded higher  Mo extraction rate than that from
Mo extraction rate than that from  -MoO
-MoO . In addition, by comparing the dissolved
. In addition, by comparing the dissolved  Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of
Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of  -MoO
-MoO whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of
whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of  -MoO
-MoO being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,
being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,  -MoO
-MoO is considered a promising irradiation target for producing
is considered a promising irradiation target for producing  Mo/
Mo/ Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:83.53(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki*; Shimada, Asako; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
Li, S.; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.; Deng, D.*
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/07

Kinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Matsumura, Hiroki*; Hori, Fumiya*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 9(30), p.2736_1 - 2736_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Nakamine, Genki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(5), p.053702_1 - 053702_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:76.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -axis knight shift on UTe
-axis knight shift on UTe with
with  = 2.1 K
= 2.1 KMatsumura, Hiroki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(6), p.063701_1 - 063701_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:93.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary) rays from a neutron-induced
rays from a neutron-induced  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Xe
XeOkudaira, Takuya*; Tani, Yuika*; Endo, Shunsuke; Doskow, J.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kameda, Kento*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Luxnat, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 107(5), p.054602_1 - 054602_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:83.53(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Physics, Applied)Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Ma, J.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:87.72(Physics, Applied) induced by magnetic field
induced by magnetic fieldKinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(6), p.L060502_1 - L060502_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:94.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)