Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Dei, Shuntaro; Shibata, Masahito*; Negishi, Kumi*; Sugiura, Yuki; Amano, Yuki; Bateman, K.*; Wilson, J.*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
Results in Earth Sciences (Internet), 3, p.100097_1 - 100097_16, 2025/12
Interactions between cement and host rock in geological repositories for radioactive waste will result in a chemically disturbed zone, which may potentially affect the long-term safety. This paper investigates the chemical evolution at the interface between cement (Ordinary Portland Cement: OPC and Low Alkaline Cement: LAC) and mudstone after 11 years of in situ reactions at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The study combines various analytical techniques to identify the key reactions at the cement-rock interface, including cement dissolution, precipitation of secondary minerals such as calcite and C-(A-)S-H phases, cation exchange in montmorillonite and reduced porosity in mudstone. The study also highlights the effects of cement-mudstone interactions on radionuclide migration, such as reduction of diffusivity due to reduced porosity and enhancement of sorption due to incorporation into secondary minerals in the altered mudstone.
Aoyama, Takahito; Choudhary, S.*; Pandaleon, A.*; Burns, J. T.*; Kokaly, M.*; Restis, J.*; Ross, J.*; Kelly, R. G.*
Corrosion, 81(6), p.609 - 621, 2025/06
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
Wilson, J.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Tachi, Yukio; Kawama, Daisuke*
Applied Clay Science, 275, p.107862_1 - 107862_15, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0High-Level Radioactive Waste (HLW) repositories include iron or steel-based containers/overpack and bentonite buffers. Over the last 25 years or so, research efforts have attempted to elucidate the nature of iron-bentonite interactions, especially the potential for the deleterious alteration of the swelling clay component (smectite), to iron-rich layer silicates, some of which lack the capacity for intracrystalline swelling. This could result in a reduction or loss in swelling pressure in the bentonite buffer which is designed to protect waste containers from shear forces and also acts to restrict water and solute transport, as part of an engineered barrier system. Most data on iron-bentonite interactions come from experimental and geochemical modelling studies, as natural analogue data are lacking. The data suggests that there is the potential for the development of an iron-rich bentonite alteration zone with smectite (generally present as the aluminous montmorillonite type) undergoing alteration to iron-rich solids, including layer silicates and steel corrosion products such as green rust or magnetite. The evidence available is complex, arguably incomplete, with many potential complex couplings. Many uncertainties remain despite efforts taken over the last 25 years, but plausible scenarios for iron-bentonite interactions have been identified and possible implications for buffer properties have been suggested.
Kato, Masaru*; Zheng, J.*; Deng, Y.*; Saito, Fumie*; Unuma, Yuki*; Oka, Sayuki*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Yagi, Ichizo*
ACS Catalysis, 15(10), p.7710 - 7719, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Hu, F.-F.*; Qin, T.-Y.*; Ao, N.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Shobu, Takahisa; Kang, G.-Z.*; Ren, M.-M.; et al.
Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 25(2), p.75 - 93, 2025/04
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(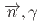 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Lee, J.; Rossi, F.; Kodama, Yu; Hironaka, Kota; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Sano, Tadafumi*; Matsuo, Yasunori*; Hori, Junichi*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.111017_1 - 111017_7, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yoon, J.-Y.*; Takeuchi, Yutaro*; Takechi, Ryota*; Han, J.*; Uchiyama, Tomohiro*; Yamane, Yuta*; Kanai, Shun*; Ieda, Junichi; Ohno, Hideo*; Fukami, Shunsuke*
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.1171_1 - 1171_8, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nozaki, Yukio*; Sukegawa, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Shinichi*; Yunoki, Seiji*; Horaguchi, Taisuke*; Nakayama, Hayato*; Yamanoi, Kazuto*; Wen, Z.*; He, C.*; Song, J.*; et al.
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 26(1), p.2428153_1 - 2428153_39, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metcalfe, R.*; Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Tachi, Yukio
Science of the Total Environment, 958, p.177690_1 - 177690_17, 2025/01
Uplifting fractured granitic rocks occur in substantial areas of countries such as Japan. A repository site would be selected in such an area only if it is possible to make a safety case, accounting for the changing conditions during uplift. The safety case must include robust arguments that chemical processes in the rocks around the repository will contribute sufficiently to minimise radiological doses to biosphere receptors. To provide confidence in the safety arguments, numerical models need to be sufficiently realistic, but also parameterised conservatively (pessimistically). However, model development is challenging because uplift involves many complex couplings between groundwater flow, chemical reactions between water and rock, and changing rock properties. The couplings would affect radionuclide mobilisation and retardation, by influencing diffusive radionuclide fluxes between groundwater flowing in fractures and effectively immobile porewater in the rock matrix and radionuclide partitioning between water and solid phases, via: (i) mineral precipitation/dissolution; (ii) mineral alteration; and (iii) sorption/desorption. It is difficult to represent all this complexity in numerical models while showing that they are parameterised conservatively. Here we present a modelling approach, illustrated by simulation cases for some exemplar radioelements, to identify realistically conservative process conceptualisations and model parameterisations.
Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Fukuda, Shoma; Sueoka, Shigeru; Nakajima, Toru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Wall, C. J.*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Fuisshon, Torakku Nyusureta, (37), p.11 - 13, 2024/12
In recent years, advances in analytical technology have made it possible to measure the U-Th-Pb dating of young geological units (e.g.  1 Ma). However, there are very few young standard samples available for evaluation. In this study, we attempted U-Pb dating using isotope dilution Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ID-TIMS) on young zircon samples (TRG04 and OGPK). As a result, we obtained preliminary U-Pb ages of 2.6654
1 Ma). However, there are very few young standard samples available for evaluation. In this study, we attempted U-Pb dating using isotope dilution Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ID-TIMS) on young zircon samples (TRG04 and OGPK). As a result, we obtained preliminary U-Pb ages of 2.6654  0.0016 Ma and 1.1266
0.0016 Ma and 1.1266  0.0014 Ma, respectively.
0.0014 Ma, respectively.
Xia, C.-J.*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Yasutake, Nobutoshi*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
Physical Review D, 110(11), p.114024_1 - 114024_14, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Watanabe, Tomoaki; Suyama, Kenya; Tada, Kenichi; Ferrer, R. M.*; Hykes, J.*; Wemple, C. A.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 198(11), p.2230 - 2239, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new nuclear data library for the advanced lattice physics code CASMO5 has been prepared based on JENDL-5. In JENDL-5, many essential nuclides for conventional LWR analysis have also been modified based on state-of-the-art evaluations. The new JENDL-5-based CASMO5 library was prepared by replacing as much of the nuclear data of the current CASMO5 ENDF/B-VII.1-based library as possible with JENDL-5. This study verified and validated the new library. Verifications were performed based on the OECD/NEA burnup credit criticality safety benchmark phase III-C, and the calculated k and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
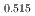 Gd
Gd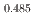 Mn
Mn O
O
Ishii, Yuta*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Lustikova, J.*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Wakabayashi, Yusuke*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*
Physical Review B, 110(18), p.184404_1 - 184404_7, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Wen, J.*; Kamada, Yuto*; Yokoyama, Kosei*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Liu, W.*; Morita, Koji*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 13th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS13) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/11
Wen, J.*; Kamada, Yuto*; Yokoyama, Kosei*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Liu, W.*; Morita, Koji*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/11
Brear, D. J.*; Kondo, Satoru; Sogabe, Joji; Tobita, Yoshiharu*; Kamiyama, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2024-009, 134 Pages, 2024/10
The SIMMER-III/SIMMER-IV computer codes are being used for liquid-metal fast reactor (LMFR) core disruptive accident (CDA) analysis. The sequence of events predicted in a CDA is often influenced by the heat exchanges between LMFR materials, which are controlled by heat transfer coefficients (HTCs) in the respective materials. The mass transfer processes of melting and freezing, and vaporization and condensation are also controlled by HTCs. The complexities in determining HTCs in a multi-component and multi-phase system are the number of HTCs to be defined at binary contact areas of a fluid with other fluids and structure surfaces, and the modes of heat transfer taking into account different flow topologies representing flow regimes with and without structure. As a result, dozens of HTCs are evaluated in each mesh cell for the heat and mass transfer calculations. This report describes the role of HTCs in SIMMER-III/SIMMER-IV, the heat transfer correlations implemented and the calculation of HTCs in all topologies in multi-component, multi-phase flows. A complete description of the physical basis of HTCs and available experimental correlations is contained in Appendices to this report. The major achievement of the code assessment program conducted in parallel with code development is summarized with respect to HTC modeling to demonstrate that the coding is reliable and that the model is applicable to various multi-phase problems with and without reactor materials.
 Zr +
Zr +  at 27 MeV/nucleon
at 27 MeV/nucleonHwang, J.*; Chillery, T.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; 49 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.093D03_1 - 093D03_12, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear transmutation emerges as a promising approach for reprocessing high-level waste, specifically treating long-lived nuclides like  Zr from spent fuel. It is essential to accumulate reaction data for these nuclei to advance this prominent treatment and to build a comprehensive understanding of reaction mechanisms. In this study, the residual production cross-sections resulting from proton-induced reactions on
Zr from spent fuel. It is essential to accumulate reaction data for these nuclei to advance this prominent treatment and to build a comprehensive understanding of reaction mechanisms. In this study, the residual production cross-sections resulting from proton-induced reactions on  Zr were measured at 27 MeV/nucleon in inverse kinematics. At the RIKEN-RIBF facility the OEDO beamline was used to deduce production cross-sections for isotopes,
Zr were measured at 27 MeV/nucleon in inverse kinematics. At the RIKEN-RIBF facility the OEDO beamline was used to deduce production cross-sections for isotopes, 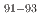 Nb,
Nb, 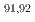 Zr, and
Zr, and 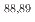 Y. Comparing the results from this study and prior research with calculated excitation functions, a moderate agreement is found with theoretical predictions derived from TALYS and CCONE. Despite the potential limitations of low-energy proton-induced reactions for
Y. Comparing the results from this study and prior research with calculated excitation functions, a moderate agreement is found with theoretical predictions derived from TALYS and CCONE. Despite the potential limitations of low-energy proton-induced reactions for  Zr transmutation, the measured cross-sections offer valuable insights for future considerations in nuclear-waste treatment facilities. This is particularly relevant for facilities exploring innovative methods, such as accelerator-driven systems.
Zr transmutation, the measured cross-sections offer valuable insights for future considerations in nuclear-waste treatment facilities. This is particularly relevant for facilities exploring innovative methods, such as accelerator-driven systems.
Rossi, F.; Lee, J.; Kodama, Yu; Hironaka, Kota; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07